
Concept explainers
Consider the following mRNA sequence:
- What amino acid sequence is coded for by this mRNA?
- What is the amino acid sequence if a mutation converts CAG to AAC?
- What is the amino acid sequence if a mutation converts CUU to CUC?
- What occurs when a mutation converts CAG to UAG?
- What occurs if CU is deleted from the beginning of the chain?
(a)
Interpretation:
Peptide synthesized by the 5' CUU CAG CAC 3' mRNA should be identified.
Concept Introduction:
DNA and RNA transform genetic information of the living cells through triplet code, which is a sequence of three nucleotides on DNA or RNA molecules codes for a specific amino acid in protein synthesis.
Answer to Problem 22.75P
Peptide − Leu-Gln-His
Explanation of Solution
Codons are written from 5 prime end (5) to 3 prime end (3) of mRNA. There is a unique triplet representation for a particular amino acid. Below mentioned table represent the relationship between nucleotides and amino acids.
The Genetic Code- Triplets in Messenger RNA
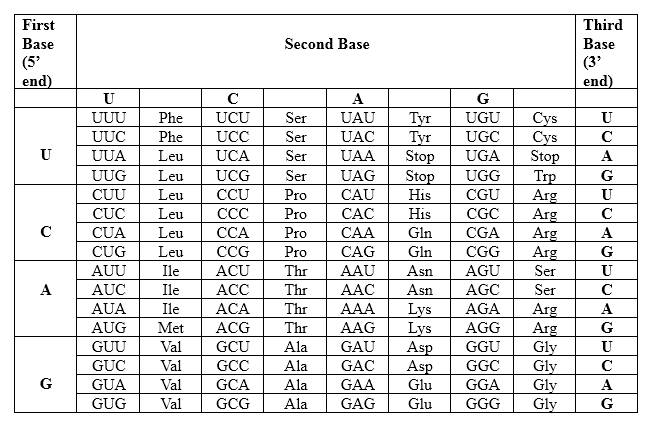
According to the above table; one amino acid has several triplets, but triplet code is unique for amino acid. CUU triplet is unique for Leucine. CAG triplet is unique for Glutamine. CAC is unique for Histidine.
Therefore, Leu-Gln-His is the amino acid sequence for 5' CUU CAG CAC 3'.
(b)
Interpretation:
Peptide formed from mutated mRNA5' CUU CAG AAC3' should be identified.
Concept Introduction:
DNA and RNA transform genetic information of the living cells through triplet code, which is a sequence of three nucleotides on DNA or RNA molecules codes for a specific amino acid in protein synthesis.
Mutation is an alteration of a sequence of nucleotides in DNA. Mutations can be classified based on the change that results in a DNA molecule.
Answer to Problem 22.75P
Peptide − Leu-Gln-Asn
Explanation of Solution
Mutation is an alteration of a sequence of nucleotides in DNA. When mutation happens at a particular position of a DNA molecule, that mutation goes through mRNA and translate a wrong peptide.
Mutations can be classified based on the change that results in a DNA molecule. There are three types of mutations which can be classified as follows;
- Point mutations − A substitution of one nucleotide for another nucleotide.
- Deletion mutations − One or more nucleotides is lost from a particular DNA molecule.
- Insertion mutations − One or more nucleotides is added to a DNA molecule.
Codons are written from 5 prime end (5') to 3 prime end (3') of mRNA. There is a specific sequence of nucleotides for each amino acid. Below mentioned table represent the relationship between nucleotides and amino acids.
The Genetic Code- Triplets in Messenger RNA
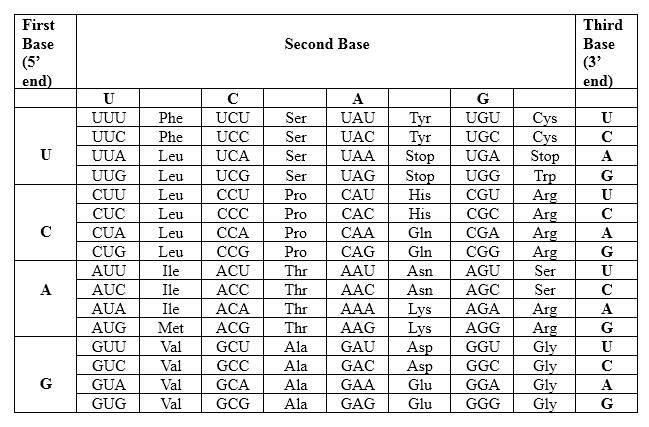
According to the above table; one amino acid has several triplets, but triplet code is unique for amino acid. CUU triplet is unique for Leucine. CAG triplet is unique for Glutamine. AAC is unique for Asparagine. There is a point mutation in the mRNA strand, which CAC in the normal strand converts to AAC in the mutated strand. The resulting protein is different from the un-mutated one.
Therefore, Leu-Gln-Asn is the amino acid sequence for 5' CUU CAG AAC 3'.
(c)
Interpretation:
Peptide formed from mutated mRNA 5' CUC CAG CAC 3' should be identified.
Concept Introduction:
DNA and RNA transform genetic information of the living cells through triplet code, which is a sequence of three nucleotides on DNA or RNA molecules codes for a specific amino acid in protein synthesis.
Mutation is an alteration of a sequence of nucleotides in DNA. Mutations can be classified based on the change that results in a DNA molecule.
Answer to Problem 22.75P
Peptide − Leu-Gln-His.
Explanation of Solution
Mutation is an alteration of a sequence of nucleotides in DNA. When mutation happens at a particular position of a DNA molecule, that mutation goes through mRNA and translate a wrong peptide.
Mutations can be classified based on the change that results in a DNA molecule. There are three types of mutations which can be classified as follows;
- Point mutations − A substitution of one nucleotide for another nucleotide.
- Deletion mutations − One or more nucleotides is lost from a particular DNA molecule.
- Insertion mutations − One or more nucleotides is added to a DNA molecule.
Codons are written from 5 prime end (5') to 3 prime end (3') of mRNA. There is a specific sequence of nucleotides for each amino acid. Below mentioned table represent the relationship between nucleotides and amino acids.
The Genetic Code- Triplets in Messenger RNA
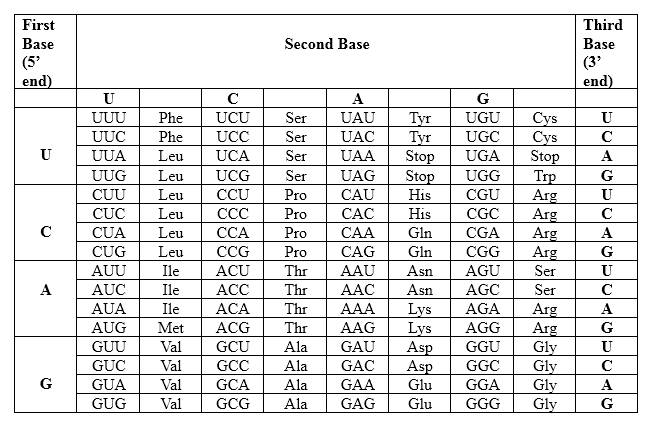
According to the above table; one amino acid has several triplets, but triplet code is unique for amino acid. CUC triplet is unique for Leucine. CAG triplet is unique for Glutamine. CAC triplet is unique for Histidine. There is a point mutation in the mRNA strand, which CUU in the normal strand converts to CUC in the mutated strand. Though there is a point mutation in the strand, the resulting protein is not different from the un-mutated one.
Therefore, Leu-Gln-His is the amino acid sequence for 5' CUC CAG CAC 3'.
(d)
Interpretation:
Peptide formed from mutated mRNA 5' CUU UAG CAC 3' should be identified.
Concept Introduction:
DNA and RNA transform genetic information of the living cells through triplet code, which is a sequence of three nucleotides on DNA or RNA molecules codes for a specific amino acid in protein synthesis.
Mutation is an alteration of a sequence of nucleotides in DNA. Mutations can be classified based on the change that results in a DNA molecule.
Answer to Problem 22.75P
Amino acid is Leucine and after that amino acid sequence generation is terminated.
Explanation of Solution
Mutation is an alteration of a sequence of nucleotides in DNA. When mutation happens at a particular position of a DNA molecule, that mutation goes through mRNA and translate a wrong peptide.
Mutations can be classified based on the change that results in a DNA molecule. There are three types of mutations which can be classified as follows;
- Point mutations − A substitution of one nucleotide for another nucleotide.
- Deletion mutations − One or more nucleotides is lost from a particular DNA molecule.
- Insertion mutations − One or more nucleotides is added to a DNA molecule.
Codons are written from 5 prime end (5') to 3 prime end (3') of mRNA. There is a specific sequence of nucleotides for each amino acid. Below mentioned table represent the relationship between nucleotides and amino acids.
The Genetic Code- Triplets in Messenger RNA
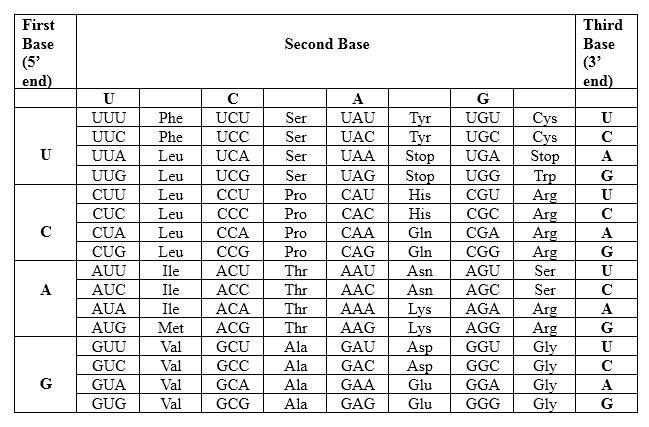
According to the above table; one amino acid has several triplets, but triplet code is unique for amino acid. CUC triplet is unique for Leucine. UAG triplet is a unique for a stop codon. Hence, after this codon peptide synthesis is terminated. In this case required protein is not synthesized. Hence, the effect of this mutation may be catastrophic to the organism.
Therefore, Leu is the amino acid sequence for 5' CUU UAG CAC 3'
(e)
Interpretation:
Peptide formed from mutated mRNA 5' UCAGCAC 3' should be identified.
Concept Introduction:
DNA and RNA transform genetic information of the living cells through triplet code, which is a sequence of three nucleotides on DNA or RNA molecules codes for a specific amino acid in protein synthesis.
Mutation is an alteration of a sequence of nucleotides in DNA. Mutations can be classified based on the change that results in a DNA molecule.
Answer to Problem 22.75P
Peptide − Ser-Ala
Explanation of Solution
Mutation is an alteration of a sequence of nucleotides in DNA. When mutation happens at a particular position of a DNA molecule, that mutation goes through mRNA and translate a wrong peptide.
Mutations can be classified based on the change that results in a DNA molecule. There are three types of mutations which can be classified as follows;
- Point mutations − A substitution of one nucleotide for another nucleotide.
- Deletion mutations − One or more nucleotides is lost from a particular DNA molecule.
- Insertion mutations − One or more nucleotides is added to a DNA molecule.
Codons are written from 5 prime end (5') to 3 prime end (3') of mRNA. There is a specific sequence of nucleotides for each amino acid. Below mentioned table represent the relationship between nucleotides and amino acids.
The Genetic Code- Triplets in Messenger RNA
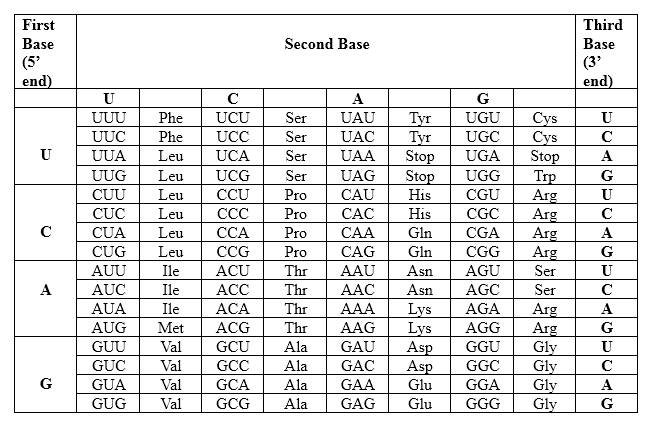
According to the above table; one amino acid has several triplets, but triplet code is unique for amino acid. Codons are written from 5 prime end (5') to 3 prime end (3') of mRNA and read as triplets, because of the deletion mutation which occurred here because of deletion of CU in the beginning of the mRNA, triplets are read as follows. UCA triplet is unique for Serine and GCA triplet is unique for Alanine. There is an additional A nucleotide, which is not involved into this peptide. Furthermore, this mutation generates totally different peptide and generated peptide is as follows; Ser-Ala is the amino acid sequence for 5' UCAGCAC 3'.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
EBK GENERAL, ORGANIC, & BIOLOGICAL CHEM
- Using Luther's rule, determine the reference potentials of the electrodes corresponding to the low stability systems Co³+/Co and Cr²+/Cr from the data in the table. Electrodo ΕΝ Co²+/Co Co3+/Co²+ -0,28 +1,808 Cr³+ / Cr -0,508 Cr3+ / Cr²+ -0,41arrow_forwardThe molecule PYRIDINE, 6tt electrons and is there pore aromuntre and is Assigned the Following structure contenus Since aromatk moleculey undergo electrophilic allomatic substitution, Pyridine should undergo The Following reaction + HNO3 12504 a. write all of the possible Mononitration Products that could Result From this roaction Based upon the reaction the reaction mechanism determine which of these producty would be the major Product of the hegetionarrow_forwardUsing Benzene as starting materia Show how each of the Following molecules could Ve synthesked 9. CHI d. 10450 b 0 -50311 ८ City -5034 1-0-650 e NO2arrow_forward
- BA HBr of the fol 1)=MgCI 2) H₂O major NaOEt Ts Cl Py (pyridine) 1) 03 2) Me2S 1arrow_forward4. Provide a clear arrow-pushing mechanism for the following reactions. Do not skip proton transfers, do not combine steps, and make sure your arrows are clear enough to be interpreted without ambiguity. a) NHBoc ⚫OBn HO. H3C CO2CH3 -OBn H3C H3C. H3C. NHBOC CI CO2CH3arrow_forwardDraw structures of the following compounds and identify their role: mCPBA (MCPBA) DMS Py 9-BBN LAH Sia₂BH TsCI PCC t-BuOK LDA MeLi n-BuLi DMSO DMF Sodium Borohydride Lithium DiisopropylAmide 2arrow_forward
- Using Luther's rule, calculate the reference potential of the Hg2+/Hg redox electrode. DATA: Electrode potentials E° = 0,854 V y E 0,788 V Hg2+/Hg 2+ Hg2/Hgarrow_forward1) NaNH2 (excess) 1) NaNH2 CI CI 2) H₂O 2) Mel 1) 03 2) (CH3)2S Na NH3 (liquid) 1arrow_forwardCI 1) n-BuLi 2) 1) 03 HH T&Cl 2) H₂O 2arrow_forward
- Help with a!arrow_forwardFor the following compound: HO -H Draw a mechanism for the tautomerization process under BASIC conditions: Mechanism A: H-O: H-OH H-O HH H-OO Mechanism B: H-Q Mechanism C: Θ OH H-O: Mechanism D: H-O H- H-OO C H-OO H- H- H-OO HH OH -H - HON H :OH H-Harrow_forwardidentify the product (or multiple products) for each of the following reactions: CI 1) NaNH2 (excess) ठ Cl 2) H₂O Hz H₂SO₂, H₂O HgSO Lindlar's catalyst 1) n-BuLi 2) 1)9-BBN 2) H₂O, NaOH ? Br H A B C afó gó H OA B O c OD E OF D E F H H Na, NHarrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





