
(a)
Interpretation:
The preparation of the 1-bromo-3-nitrobenzene from benzene or toluene or phenol has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Activating and deactivating groups:
The effect of substituents on the reaction rate of
Activating groups – ortho/para directing groups. The
Deactivating groups – metadirecting groups. The rate of reaction is decreased by a deactivating groups (electron withdrawing groups) relative to hydrogen.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Given target compound,
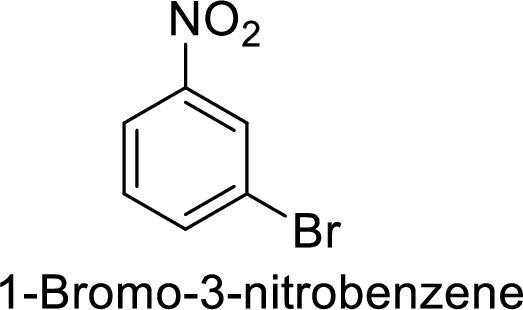
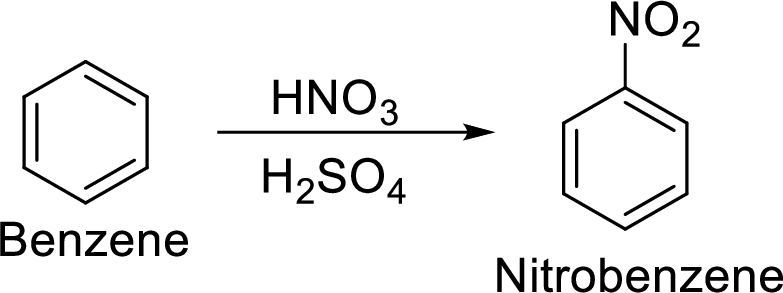
Step 1: Nitration of benzene ring by the reaction of benzene with nitrating mixture.
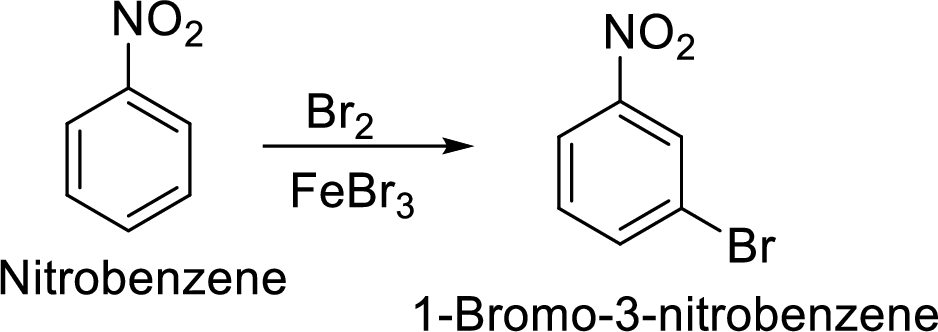
Step 2: Halogenation of nitrobenzene by the reaction of nitrobenzene with bromine in the presence of Lewis acid.
(b)
Interpretation:
The preparation of the 1-bromo-4-nitrobenzene from benzene or toluene or phenol has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Activating and deactivating groups:
The effect of substituents on the reaction rate of aromatic electrophilic substitution is given by activating or deactivating groups.
Activating groups – ortho/para directing groups. The rate of reaction is increased by an activating groups (electron donating groups) relative to hydrogen.
Deactivating groups – metadirecting groups. The rate of reaction is decreased by a deactivating groups (electron withdrawing groups) relative to hydrogen.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Given target compound,
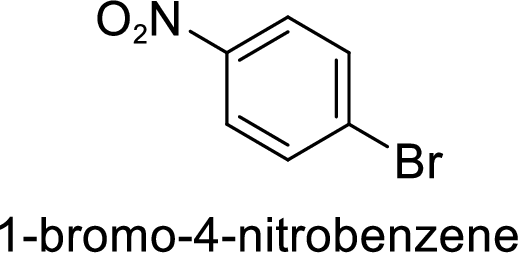
Step 1: Halogenation of benzene by the reaction of benzene with bromine in the presence of Lewis acid.
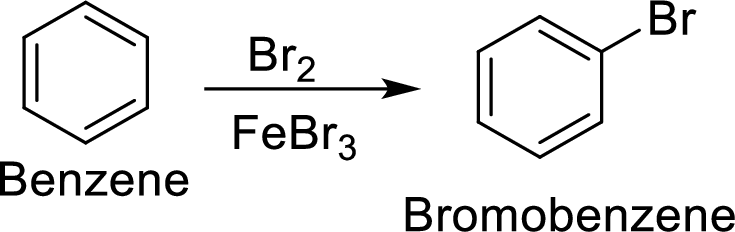
Step 2: Nitration of bromobenzene by the reaction of bromobenzene with nitrating mixture.
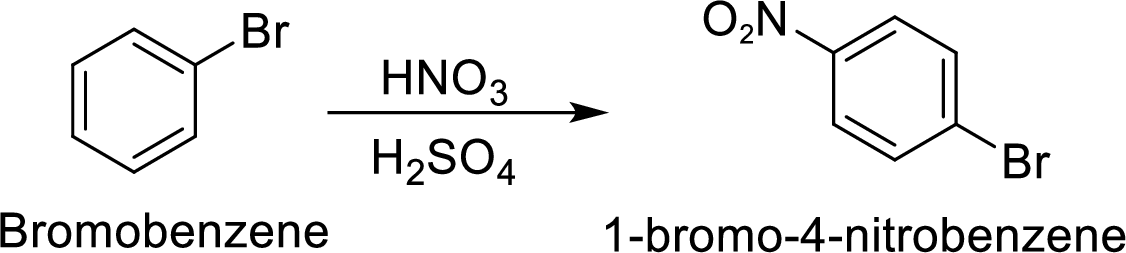
(c)
Interpretation:
The preparation of the 2,4-6-trinitrotoluene from benzene or toluene or phenol has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Activating and deactivating groups:
The effect of substituents on the reaction rate of aromatic electrophilic substitution is given by activating or deactivating groups.
Activating groups – ortho/para directing groups. The rate of reaction is increased by an activating groups (electron donating groups) relative to hydrogen.
Deactivating groups – metadirecting groups. The rate of reaction is decreased by a deactivating groups (electron withdrawing groups) relative to hydrogen.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Given target compound,
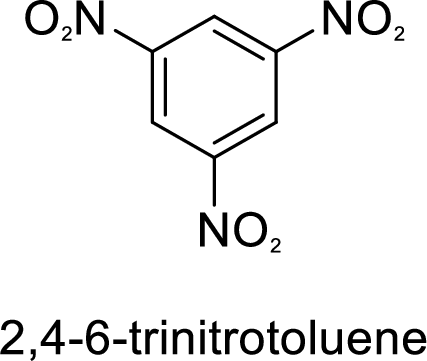
Methyl group in toluene is an activating and ortho-para directing group, so three times nitration of toluene gives the target compound.
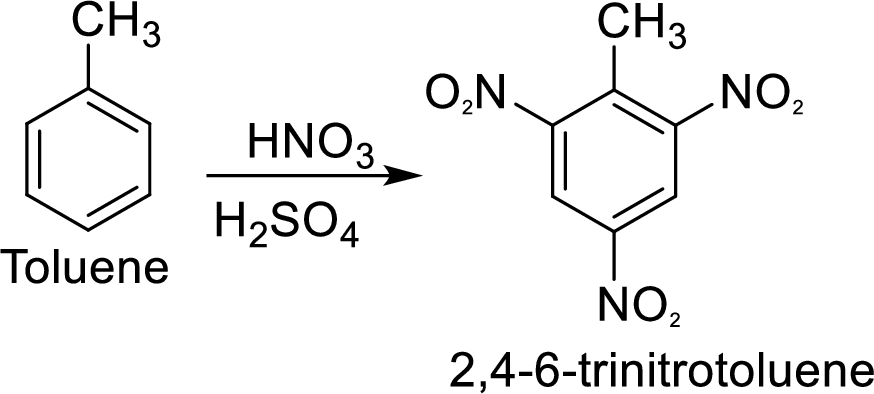
(d)
Interpretation:
The preparation of the m-chlorobenzoic acid from benzene or toluene or phenol has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Activating and deactivating groups:
The effect of substituents on the reaction rate of aromatic electrophilic substitution is given by activating or deactivating groups.
Activating groups – ortho/para directing groups. The rate of reaction is increased by an activating groups (electron donating groups) relative to hydrogen.
Deactivating groups – metadirecting groups. The rate of reaction is decreased by a deactivating groups (electron withdrawing groups) relative to hydrogen.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Given target compound,
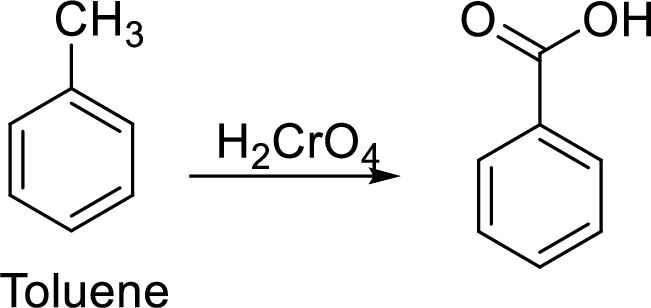
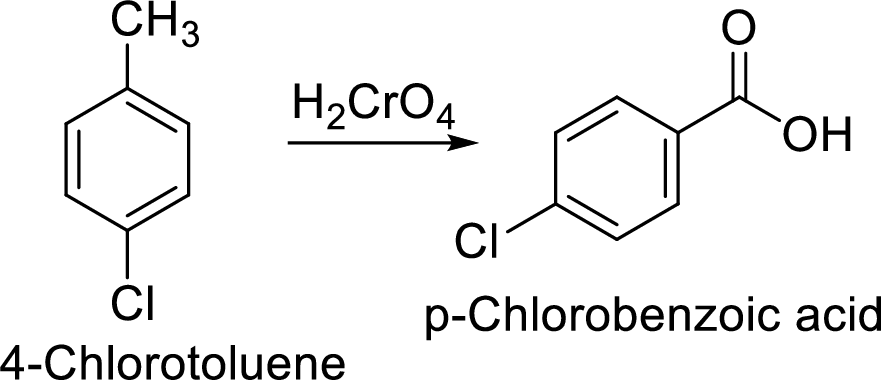
Step 1: Oxidation of toluene with chromic acid gives the benzoic acid.
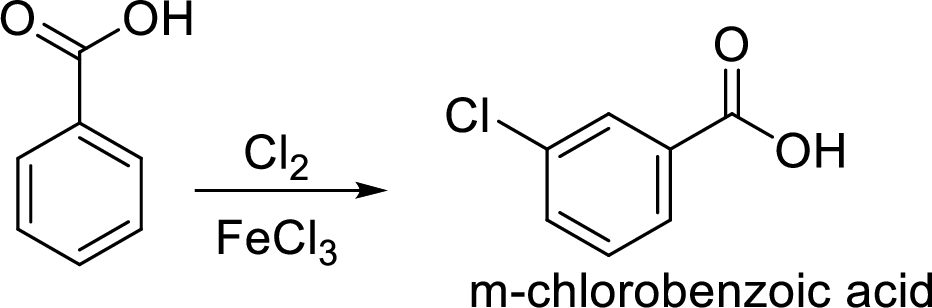
Step 2: Carboxyl group is a deactivating and meta directing group so the chlorination takes place at the meta position.
(e)
Interpretation:
The preparation of the p-chlorobenzoic acid from benzene or toluene or phenol has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Activating and deactivating groups:
The effect of substituents on the reaction rate of aromatic electrophilic substitution is given by activating or deactivating groups.
Activating groups – ortho/para directing groups. The rate of reaction is increased by an activating groups (electron donating groups) relative to hydrogen.
Deactivating groups – metadirecting groups. The rate of reaction is decreased by a deactivating groups (electron withdrawing groups) relative to hydrogen.
(e)
Explanation of Solution
Given target compound,
Step 1: Halogenation of toluene by the reaction of toluene with chlorine in the presence of Lewis acid.
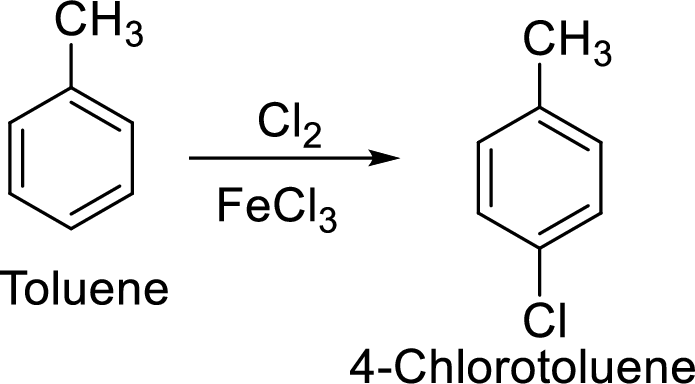
Step 2: Oxidation of 4-chlorotoluene by chromic acid gives the target compound.
(f)
Interpretation:
The preparation of the p-dichlorobenzene from benzene or toluene or phenol has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Activating and deactivating groups:
The effect of substituents on the reaction rate of aromatic electrophilic substitution is given by activating or deactivating groups.
Activating groups – ortho/para directing groups. The rate of reaction is increased by an activating groups (electron donating groups) relative to hydrogen.
Deactivating groups – metadirecting groups. The rate of reaction is decreased by a deactivating groups (electron withdrawing groups) relative to hydrogen.
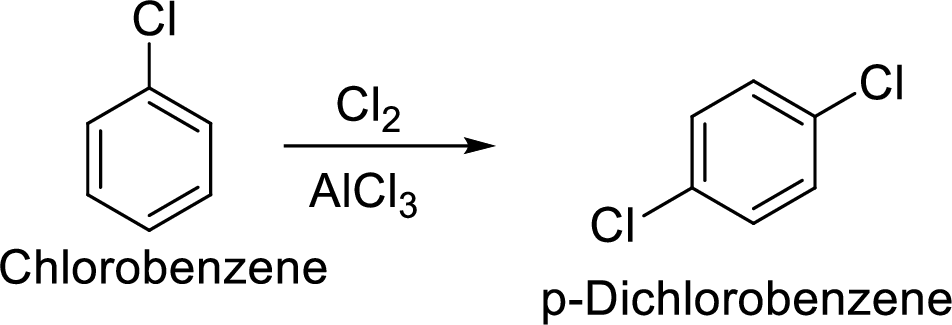
(f)
Explanation of Solution
Given target compound,
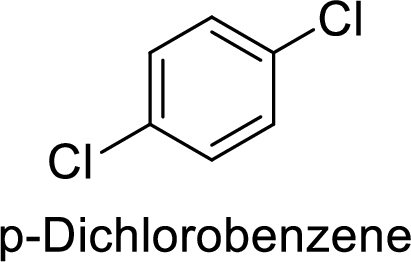
Step 1: Halogenation of benzene by the reaction of benzene with chlorine in the presence of Lewis acid.
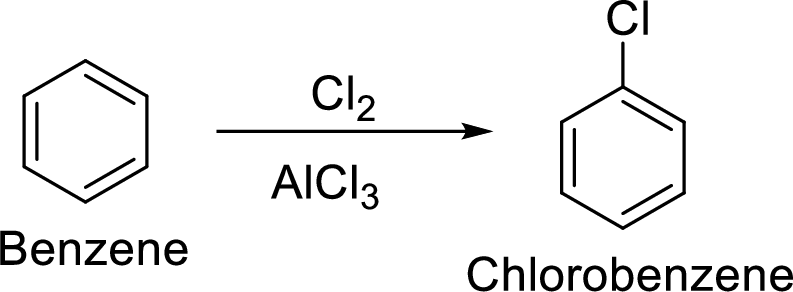
Step 2: Second halogenation of chlorobenzene by the reaction of chlorobenzene with chlorine in the presence of Lewis acid.
(g)
Interpretation:
The preparation of the 1-bromo-4-nitrobenzene from benzene or toluene or phenol has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Activating and deactivating groups:
The effect of substituents on the reaction rate of aromatic electrophilic substitution is given by activating or deactivating groups.
Activating groups – ortho/para directing groups. The rate of reaction is increased by an activating groups (electron donating groups) relative to hydrogen.
Deactivating groups – metadirecting groups. The rate of reaction is decreased by a deactivating groups (electron withdrawing groups) relative to hydrogen.
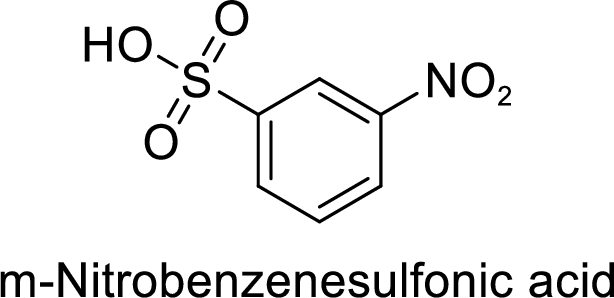
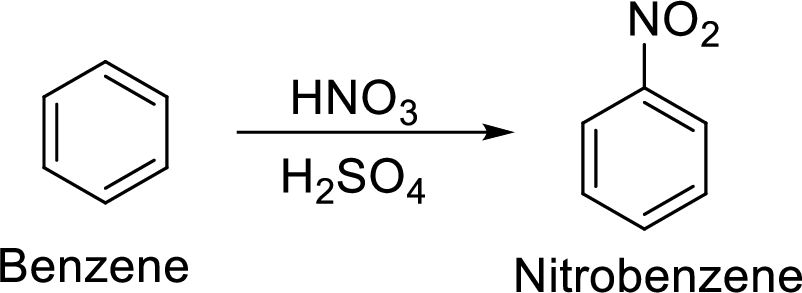
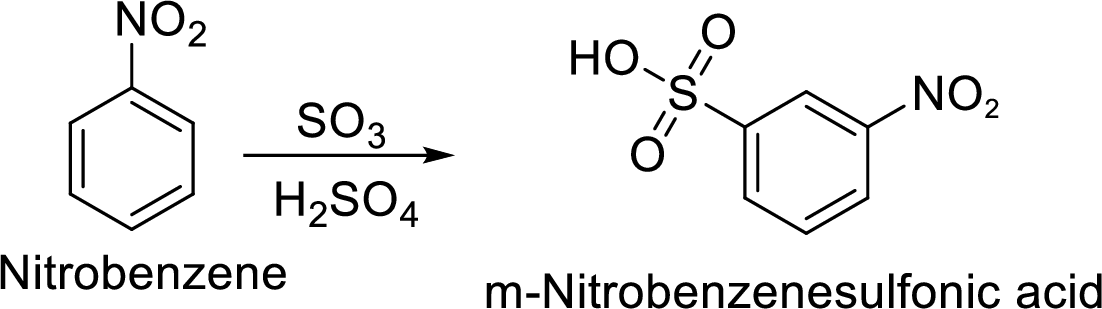
(g)
Explanation of Solution
Given target compound,
Step 1: Nitration of benzene by the reaction of benzene with nitrating mixture.
Step 2: Sulfonation of nitrobenzene by the reaction with
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Propose a synthesis of 1-butanamine from the following: (a) a chloroalkane of three carbons (b) a chloroalkane of four carbonsarrow_forwardSelect the stronger base from each pair of compounds. (a) H₂CNH₂ or EtzN (b) CI or NH2 NH2 (c) .Q or EtzN (d) or (e) N or (f) H or Harrow_forward4. Provide a clear arrow-pushing mechanism for each of the following reactions. Do not skip proton transfers, do not combine steps, and make sure your arrows are clear enough to be interpreted without ambiguity. a. 2. 1. LDA 3. H3O+ HOarrow_forward
- b. H3C CH3 H3O+ ✓ H OHarrow_forward2. Provide reagents/conditions to accomplish the following syntheses. More than one step is required in some cases. a. CH3arrow_forwardIdentify and provide an explanation that distinguishes a qualitative and quantitative chemical analysis. Provide examples.arrow_forward
- Identify and provide an explanation of the operational principles behind a Atomic Absorption Spectrometer (AAS). List the steps involved.arrow_forwardInstructions: Complete the questions in the space provided. Show all your work 1. You are trying to determine the rate law expression for a reaction that you are completing at 25°C. You measure the initial reaction rate and the starting concentrations of the reactions for 4 trials. BrO³¯ (aq) + 5Br¯ (aq) + 6H* (aq) → 3Br₂ (l) + 3H2O (l) Initial rate Trial [BrO3] [H*] [Br] (mol/L) (mol/L) | (mol/L) (mol/L.s) 1 0.10 0.10 0.10 8.0 2 0.20 0.10 0.10 16 3 0.10 0.20 0.10 16 4 0.10 0.10 0.20 32 a. Based on the above data what is the rate law expression? b. Solve for the value of k (make sure to include proper units) 2. The proposed reaction mechanism is as follows: i. ii. BrО¸¯ (aq) + H+ (aq) → HBrO3 (aq) HBrO³ (aq) + H* (aq) → H₂BrO3* (aq) iii. H₂BrO³* (aq) + Br¯ (aq) → Br₂O₂ (aq) + H2O (l) [Fast] [Medium] [Slow] iv. Br₂O₂ (aq) + 4H*(aq) + 4Br(aq) → 3Br₂ (l) + H2O (l) [Fast] Evaluate the validity of this proposed reaction. Justify your answer.arrow_forwardе. Д CH3 D*, D20arrow_forward
 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning

