
Concept explainers
Insect-Assisted Fertilization in Moss Moss sperm can swim, but plant ecologist Nils Cronberg suspected that they sometimes hitch a ride on crawling insects or mites (tiny animals related to spiders). To test this hypothesis he carried out an experiment. He placed patches of male and female moss gametophytes in dishes, either next to one another or with water-absorbing plaster between them. The plaster prevented sperm from Swimming between plants. He then looked at how the presence or absence of insects affected the number of sporophytes formed. FIGURE 22.8 shows his results.
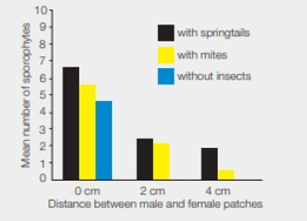
FIGURE 22.8 Sporophyte production in female moss patches with and without either crawling insects (springtails) or mites. No Sporophytes formed in the animal-free dishes when moss patches were 2 or 4 centimeters apart
Why is sporophyte formation a good way to determine if fertilization occurred?
To determine: The chemical that was produced in the greatest amount and its stimulus.
Concept introduction: Secondary metabolites are produced as metabolic intermediate or product but they are not essential for growth. They play a role in reinforcement of tissues for example cellulose, suberin, lignin; protection, and serve as attractants for pollinators. They contribute in plant’s ability to compete and survive. Volatile compounds are such secondary metabolites produced by plants. They attract insects for pollination as well as provide defensive signaling systems against pests and diseases.
Answer to Problem 1DAA
Correct answer: The chemical β-Caryophyllene was produced in greatest amount in response to the treatment with budworms and thrips.
Explanation of Solution
As given in the problem statement, the researchers studied the production of different volatile chemicals by tobacco plants in response to predation by insects- western flower thrips and tobacco budworms.
Refer Fig. 30.19, “Volatile (airborne) compounds produced by tobacco plants in response to predation by different insects” in the textbook. It shows the results of volatile compounds produced (ng/ day) in untreated plants (C), plants that are mechanically wounded (W), attacked by thrips (T), mechanically wounded and attacked by thrips (WT), attacked by budworms (HV), or attacked by budworms and thrips (HVT). When tobacco plants were treated with budworms and thrips (HVT), the chemical β-Caryophyllene was produced that was measured as 6,166 ng/ day. This was the highest amount of chemical produced among all the treatments.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biological Science (6th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
SEELEY'S ANATOMY+PHYSIOLOGY
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Physics of Everyday Phenomena
- This entire structure using lifecycle terminology is called what? megastrobilus microstrobilus megasporophyll microsporophyll microsporangium megasporangium none of thesearrow_forwardHow much protein should Sarah add to her diet if she gets pregnant? Sarah's protein requirements during pregnancy would be higher. See Hint B2. During calculations, use numbers rounded to the first decimal place. In your answer, round the number of grams to the nearest whole number. _______ g ?arrow_forwardC MasteringHealth MasteringNu X session.healthandnutrition-mastering.pearson.com/myct/itemView?assignment ProblemID=17396422&attemptNo=1&offset=prevarrow_forwardMost people, even those who exercise regularly at low to average intensity (1 hour at the gym or a 2- to 3-mile walk several times per week), do not need an increased protein intake. What would be the protein needs of a man named Josh who exercises moderately and is the same age and size as Wayne? Josh is 5 ft, 8 in tall and weighs 183 lb. Round the number of grams to the nearest whole number. During calculations, use numbers rounded to the first decimal place. Because protein requirement is a range, please enter two numbers: lower and upper range values, respectively. Separate the lower and upper range values, in that order, by a comma. ___, ___ g ?arrow_forwardC MasteringHealth MasteringNu X session.healthandnutrition-mastering.pearson.com/myct/itemView?assignment ProblemID=17396422&attemptNo=1&offset=prevarrow_forwardIf left untreated, most HIV-infected individuals will develop AIDS. Current treatments are focused on highlyactive antiretroviral therapy (HAART). HAART usually consists of an orally delivered drug cocktail containingtwo different reverse transcriptase inhibitors and one other drug, such as a protease inhibitor. Question: Develop a pharmacokinetic model of HAART treatment. Consider all 3 drugs. Make sure to include adiagram that illustrates your thinking, state all assumptions, and define your variables. Whatparameters would you need to know to find the concentration of drug in the plasma? In the T cells?(You do not need to write out or solve any equations.)arrow_forwardnot use ai pleseaarrow_forward(A) 25 20 20 15 NPP (Mg C/ha/yr) 10 10 5 0 0 2,000 4,000 6,000 ECOLOGY 4e, Figure 20.11 (Part 1) 2017 Sinauer Associates, Inc. Average annual precipitation (mm) 8,000arrow_forwardexplain the cascade of events (starting with relaxing trade winds) that occurs during El Niño in the eastern Pacific (off the coasts of California/North America and Peru/South America) and which lead to food-chain collapse - start with changes in the physical/oceanographic conditions, andthen systematically describe the cascading effects at each level of the food chain -arrow_forward3) Which statement(s) about the Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO) is/are TRUE? CIRCLE ALL THAT APPLY. A. It is a major driver of salmon populations in the Pacific B. It affects sea surface temperatures in the eastern Pacific C. Its cycles typically do not last as long as those of ENSO D. Evidence that it has occurred over many centuries has been gathered from tree ring dataarrow_forward4.arrow_forward2arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_iosRecommended textbooks for you

 Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning

 Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning