
Bundle: Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text, 5th + WebAssign Printed Access Card for Serway/Jewett's Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text, 5th Edition, Multi-Term
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781133422013
Author: Raymond A. Serway; John W. Jewett
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 21.9, Problem 21.8QQ
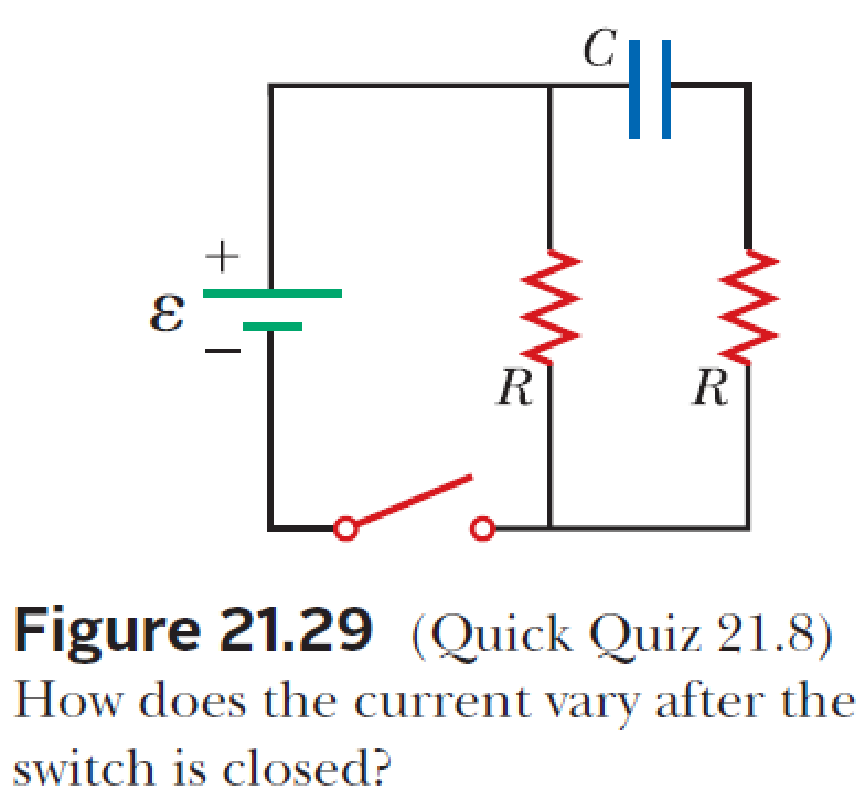
Consider the circuit in Figure 21.29 and assume the batter has no internal resistance. (i) Just after the switch is closed, what is the current in the battery? (a) 0 (b)
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
The shear leg derrick is used to haul the 200-kg net of fish onto the dock as shown in. Assume the force in each leg acts along
its axis.
5.6 m.
4 m-
B
Part A
Determine the compressive force along leg AB.
Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.
FAB =
Value
Submit
Request Answer
Part B
Units
?
Determine the compressive force along leg CB.
Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.
FCB=
Value
Submit
Request Answer
Part C
?
Units
Determine the tension in the winch cable DB.
Express your answer with the appropriate units.
2m
Part A
(Figure 1) shows a bucket suspended from a cable by means of a small
pulley at C.
If the bucket and its contents have a mass of 10 kg, determine the location of the pulley for equilibrium. The cable is 6 m long.
Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.
Figure
4 m
B
НА
x =
Value
Submit
Request Answer
Provide Feedback
<
1 of 1
T
1 m
Units
?
The particle in is in equilibrium and F4 = 165 lb.
Part A
Determine the magnitude of F1.
Express your answer in pounds to three significant figures.
ΑΣΦ
tvec
F₁ =
Submit
Request Answer
Part B
Determine the magnitude of F2.
Express your answer in pounds to three significant figures.
ΑΣΦ
It vec
F2 =
Submit
Request Answer
Part C
Determine the magnitude of F3.
Express your answer in pounds to three significant figures.
?
?
lb
lb
F₂
225 lb
135°
45°
30°
-60°-
Chapter 21 Solutions
Bundle: Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text, 5th + WebAssign Printed Access Card for Serway/Jewett's Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text, 5th Edition, Multi-Term
Ch. 21.1 - Consider positive and negative charges moving...Ch. 21.2 - Prob. 21.2QQCh. 21.2 - When does an incandescent lightbulb carry more...Ch. 21.5 - For the two incandescent lightbulbs shown in...Ch. 21.7 - Prob. 21.5QQCh. 21.7 - With the switch in the circuit of Figure 21.18a...Ch. 21.7 - Prob. 21.7QQCh. 21.9 - Consider the circuit in Figure 21.29 and assume...Ch. 21 - If the terminals of a battery with zero internal...Ch. 21 - Wire B has twice the length and twice the radius...
Ch. 21 - The current-versus-voltage behavior of a certain...Ch. 21 - Prob. 4OQCh. 21 - A potential difference of 1.00 V is maintained...Ch. 21 - Prob. 6OQCh. 21 - A metal wire of resistance R is cut into three...Ch. 21 - The terminals of a battery are connected across...Ch. 21 - Prob. 9OQCh. 21 - Two conducting wires A and B of the same length...Ch. 21 - When resistors with different resistances are...Ch. 21 - When operating on a 120-V circuit, an electric...Ch. 21 - Prob. 13OQCh. 21 - Prob. 14OQCh. 21 - In the circuit shown in Figure OQ21.15, each...Ch. 21 - Prob. 1CQCh. 21 - Prob. 2CQCh. 21 - Prob. 3CQCh. 21 - Referring to Figure CQ21.4, describe what happens...Ch. 21 - When the potential difference across a certain...Ch. 21 - Use the atomic theory of matter to explain why the...Ch. 21 - Prob. 7CQCh. 21 - (a) What advantage does 120-V operation offer over...Ch. 21 - Prob. 9CQCh. 21 - Prob. 10CQCh. 21 - If you were to design an electric heater using...Ch. 21 - Prob. 12CQCh. 21 - Prob. 13CQCh. 21 - Prob. 14CQCh. 21 - Why is it possible for a bird to sit on a...Ch. 21 - Prob. 1PCh. 21 - Prob. 2PCh. 21 - The quantity of charge q (in coulombs) that has...Ch. 21 - Prob. 4PCh. 21 - Prob. 5PCh. 21 - Figure P21.6 represents a section of a conductor...Ch. 21 - Prob. 7PCh. 21 - A 0.900-V potential difference is maintained...Ch. 21 - Prob. 9PCh. 21 - A lightbulb has a resistance of 240 when...Ch. 21 - Prob. 11PCh. 21 - Prob. 12PCh. 21 - While taking photographs in Death Valley on a day...Ch. 21 - Prob. 14PCh. 21 - If the current carried by a conductor is doubled,...Ch. 21 - Prob. 16PCh. 21 - Prob. 17PCh. 21 - Prob. 18PCh. 21 - Prob. 19PCh. 21 - Prob. 20PCh. 21 - Prob. 21PCh. 21 - Prob. 22PCh. 21 - Prob. 23PCh. 21 - Prob. 24PCh. 21 - A 100-W lightbulb connected to a 120-V source...Ch. 21 - Prob. 26PCh. 21 - Prob. 27PCh. 21 - Prob. 28PCh. 21 - A toaster is rated at 600 W when connected to a...Ch. 21 - Prob. 30PCh. 21 - Prob. 31PCh. 21 - Review. A well-insulated electric water heater...Ch. 21 - A battery has an emf of 15.0 V. The terminal...Ch. 21 - Two 1.50-V batterieswith their positive terminals...Ch. 21 - An automobile battery has an emf of 12.6 V and an...Ch. 21 - Prob. 36PCh. 21 - Prob. 37PCh. 21 - Prob. 38PCh. 21 - Consider the circuit shown in Figure P21.39. Find...Ch. 21 - Four resistors are connected to a battery as shown...Ch. 21 - Three 100- resistors are connected as shown in...Ch. 21 - Prob. 42PCh. 21 - Calculate the power delivered to each resistor in...Ch. 21 - Prob. 44PCh. 21 - The ammeter shown in Figure P21.45 reads 2.00 A....Ch. 21 - Prob. 46PCh. 21 - The circuit shown in Figure P21.47 is connected...Ch. 21 - In Figure P21.47, show how to add just enough...Ch. 21 - Taking R = 1.00 k and = 250 V in Figure P21.49,...Ch. 21 - For the circuit shown in Figure P21.50, we wish to...Ch. 21 - In the circuit of Figure P21.51, determine (a) the...Ch. 21 - Jumper cables are connected from a fresh battery...Ch. 21 - Prob. 53PCh. 21 - Prob. 54PCh. 21 - Prob. 55PCh. 21 - Prob. 56PCh. 21 - In the circuit of Figure P21.57, the switch S has...Ch. 21 - Prob. 58PCh. 21 - The circuit in Figure P21.59 has been connected...Ch. 21 - Assume that global lightning on the Earth...Ch. 21 - Prob. 61PCh. 21 - Prob. 62PCh. 21 - Prob. 63PCh. 21 - Prob. 64PCh. 21 - Prob. 65PCh. 21 - An oceanographer is studying how the ion...Ch. 21 - The values of the components in a simple series RC...Ch. 21 - Prob. 68PCh. 21 - Prob. 69PCh. 21 - Prob. 70PCh. 21 - The student engineer of a campus radio station...Ch. 21 - Prob. 72PCh. 21 - A battery has an emf and internal resistance r. A...Ch. 21 - Prob. 74PCh. 21 - Prob. 75PCh. 21 - Prob. 76PCh. 21 - Prob. 77P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The 10-lb weight is supported by the cord AC and roller and by the spring that has a stiffness of k = 10 lb/in. and an unstretched length of 12 in. as shown in. Part A Determine the distance d to maintain equilibrium. Express your answer in inches to three significant figures. 節 ΕΠΙ ΑΣΦ d = *k J vec 5 t 0 ? d C A in. 12 in. Barrow_forwardThe members of a truss are connected to the gusset plate as shown in . The forces are concurrent at point O. Take = 90° and T₁ = 7.5 kN. Part A Determine the magnitude of F for equilibrium. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. F = Value Submit Request Answer Part B 0 ? Units Determine the magnitude of T2 for equilibrium. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. ? T₂ = Value Units T₁ Carrow_forwardpls help on botharrow_forward
- pls helparrow_forwardpls helparrow_forward6. 6. There are 1000 turns on the primary side of a transformer and 200 turns on thesecondary side. If 440 V are supplied to the primary winding, what is the voltageinduced in the secondary winding? Is this a step-up or step-down transformer? 7. 80 V are supplied to the primary winding of a transformer that has 50 turns. If thesecondary side has 50,000 turns, what is the voltage induced on the secondary side?Is this a step-up or step-down transformer? 8. There are 50 turns on the primary side of a transformer and 500 turns on thesecondary side. The current through the primary winding is 6 A. What is the turnsratio of this transformer? What is the current, in milliamps, through the secondarywinding?9. The current through the primary winding on a transformer is 5 A. There are 1000turns on the primary winding and 20 turns on the secondary winding. What is theturns ratio of this transformer? What is the current, in amps, through the secondarywinding?arrow_forward
- No chatgpt plsarrow_forwardWhat is the current, in amps, across a conductor that has a resistance of10 Ω and a voltage of 20 V? 2. A conductor draws a current of 100 A and a resistance of 5 Ω. What is thevoltageacross the conductor? 3. What is the resistance, in ohm’s, of a conductor that has a voltage of 80 kVand acurrent of 200 mA? 4. An x-ray imaging system that draws a current of 90 A is supplied with 220V. What is the power consumed? 5. An x-ray is produced using 800 mA and 100 kV. What is the powerconsumed in kilowatts?arrow_forwardՍՈՈՒ XVirginia Western Community Coll x P Course Home X + astering.pearson.com/?courseld=13289599#/ Figure y (mm) x=0x = 0.0900 m All ✓ Correct For either the time for one full cycle is 0.040 s; this is the period. Part C - ON You are told that the two points x = 0 and x = 0.0900 m are within one wavelength of each other. If the wave is moving in the +x-direction, determine the wavelength. Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. 0 t(s) λ = Value m 0.01 0.03 0.05 0.07 Copyright © 2025 Pearson Education Inc. All rights reserved. 日 F3 F4 F5 1775 % F6 F7 B F8 Submit Previous Answers Request Answer ? × Incorrect; Try Again; 3 attempts remaining | Terms of Use | Privacy Policy | Permissions | Contact Us | Cookie Settings 28°F Clear 4 9:23 PM 1/20/2025 F9 prt sc F10 home F11 end F12 insert delete 6 7 29 & * ( 8 9 0 t = back Οarrow_forward
- Part C Find the height yi from which the rock was launched. Express your answer in meters to three significant figures. Learning Goal: To practice Problem-Solving Strategy 4.1 for projectile motion problems. A rock thrown with speed 12.0 m/s and launch angle 30.0 ∘ (above the horizontal) travels a horizontal distance of d = 19.0 m before hitting the ground. From what height was the rock thrown? Use the value g = 9.800 m/s2 for the free-fall acceleration. PROBLEM-SOLVING STRATEGY 4.1 Projectile motion problems MODEL: Is it reasonable to ignore air resistance? If so, use the projectile motion model. VISUALIZE: Establish a coordinate system with the x-axis horizontal and the y-axis vertical. Define symbols and identify what the problem is trying to find. For a launch at angle θ, the initial velocity components are vix=v0cosθ and viy=v0sinθ. SOLVE: The acceleration is known: ax=0 and ay=−g. Thus, the problem becomes one of…arrow_forwardPhys 25arrow_forwardPhys 22arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning
What is Electromagnetic Induction? | Faraday's Laws and Lenz Law | iKen | iKen Edu | iKen App; Author: Iken Edu;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3HyORmBip-w;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY