
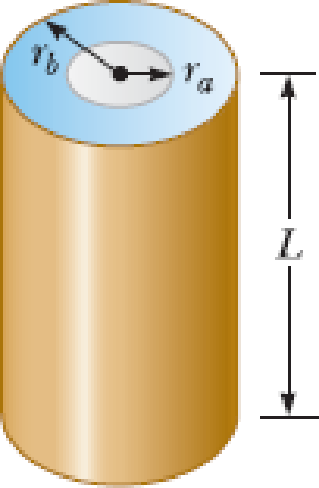
An oceanographer is studying how the ion concentration in seawater depends on depth. She makes a measurement by lowering into the water a pair of concentric metallic cylinders (Fig. P21.66) at the end of a cable and taking data to determine the resistance between these electrodes as a function of depth. The water between the two cylinders forms a cylindrical shell of inner radius ra, outer radius rb, and length L much larger than rb. The scientist applies a potential difference ΔV between the inner and outer surfaces, producing an outward radial current I. Let ρ represent the resistivity of the water. (a) Find the resistance of the water between the cylinders in terms of L, ρ, ra, an rb. (b) Express the resistivity of the water in terms of the measured quantities L, ra, rb, ΔV, and I.
Figure P21.66
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 21 Solutions
Bundle: Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text, 5th + WebAssign Printed Access Card for Serway/Jewett's Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text, 5th Edition, Multi-Term
- Uniform Circular motion. 1. Mini Lecture 2. Let the position of a particle be given by: (t) = Rcos (wt)i + Rsin (wt)j 3. Calculate the expression for the velocity vector and show that the velocity vector is tangential to the circumference of the circle. 4. Calculate the expression for the acceleration vector and show that the acceleration vector points radially inward. 5. Calculate the magnitude of the velocity and magnitude of the acceleration, and therefore show that v2 a = Rarrow_forward4. A ball is thrown vertically up, its speed. slowing under the influence of gravity. Suppose (A) we film this motion and play the tape backward (so the tape begins with the ball at its highest point and ends with it reaching the point from which it was released), and (B) we observe the motion of the ball from a frame of reference moving up at the initial speed of the ball. The ball has a downward acceleration g in: a. A and B b. Only A c. Only B d. Neither A nor Barrow_forward2. Consider a 2.4 m long propeller that operated at a constant 350 rpm. Find the acceleration of a particle at the tip of the propeller.arrow_forward
- 2. A football is kicked at an angle 37.0° above the horizontal with a velocity of 20.0 m/s, as Calculate (a) the maximum height, (b) the time of travel before the football hits the ground, and (c) how far away it hits the ground. Assume the ball leaves the foot at ground level, and ignore air resistance, wind, and rotation of the ball.arrow_forwardPlease don't use Chatgpt will upvote and give handwritten solutionarrow_forwardCam mechanisms are used in many machines. For example, cams open and close the valves in your car engine to admit gasoline vapor to each cylinder and to allow the escape of exhaust. The principle is illustrated in the figure below, showing a follower rod (also called a pushrod) of mass m resting on a wedge of mass M. The sliding wedge duplicates the function of a rotating eccentric disk on a camshaft in your car. Assume that there is no friction between the wedge and the base, between the pushrod and the wedge, or between the rod and the guide through which it slides. When the wedge is pushed to the left by the force F, the rod moves upward and does something such as opening a valve. By varying the shape of the wedge, the motion of the follower rod could be made quite complex, but assume that the wedge makes a constant angle of 0 = 15.0°. Suppose you want the wedge and the rod to start from rest and move with constant acceleration, with the rod moving upward 1.00 mm in 8.00 ms. Take m…arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





