
Spreadsheet from
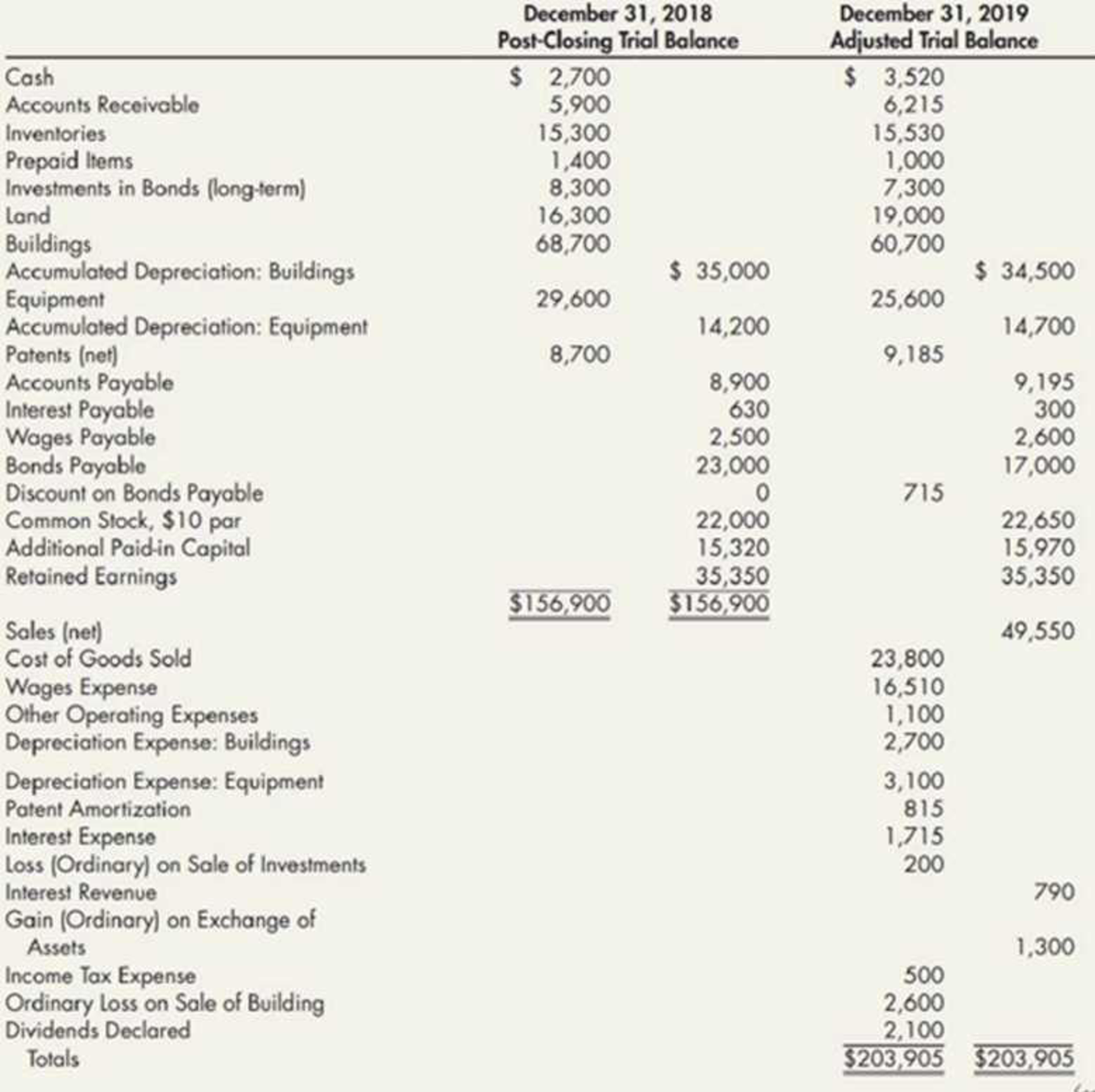
A review of the accounting records reveals the following additional information:
- a. Bomb payable with a face value, book value, and market value of $14,000 were retired on June 30, 2019.
- b. Bonds payable with a face value of $8,000 were issued at 90.25 on August 1, 2019. They mature on August 1, 2024. The company uses the straight-line method to amortize the bond discount.
- c. The company sold a building that had an original cost of $8,000 and a book value of $4,800. The company received $2,200 in cash for the building and recorded a loss of $2,600.
- d. Equipment with a cost of $4,000 and a book value of $1,400 was exchanged for an acre of land valued at $2,700. No cash was exchanged.
- e. Long-term investments in bonds being held to maturity with a cost of $ 1,000 were sold for $800.
- f. Sixty-five shares of common stock were exchanged for a patent. The common stock was selling for $20 per share at the time of the exchange.
Required:
Prepare a spreadsheet to support a statement of
Prepare a spreadsheet to support a cash flow statement of H Company for the year 2019.
Explanation of Solution
Statement of cash flows: Cash flow statement reports all the cash transactions which are responsible for inflow and outflow of cash, and result of these transactions is reported as ending balance of cash at the end of reported period. Statement of cash flows includes the changes in cash balance due to operating, investing, and financing activities.
Worksheet: A worksheet is a spreadsheet used while preparing a financial statement. It is a type of form having multiple columns and it is used in the adjustment process. The use of a worksheet is optional for any organization. A worksheet can neither be considered as a journal nor a part of the general ledger.
Prepare a spreadsheet to support the statement of cash flows.
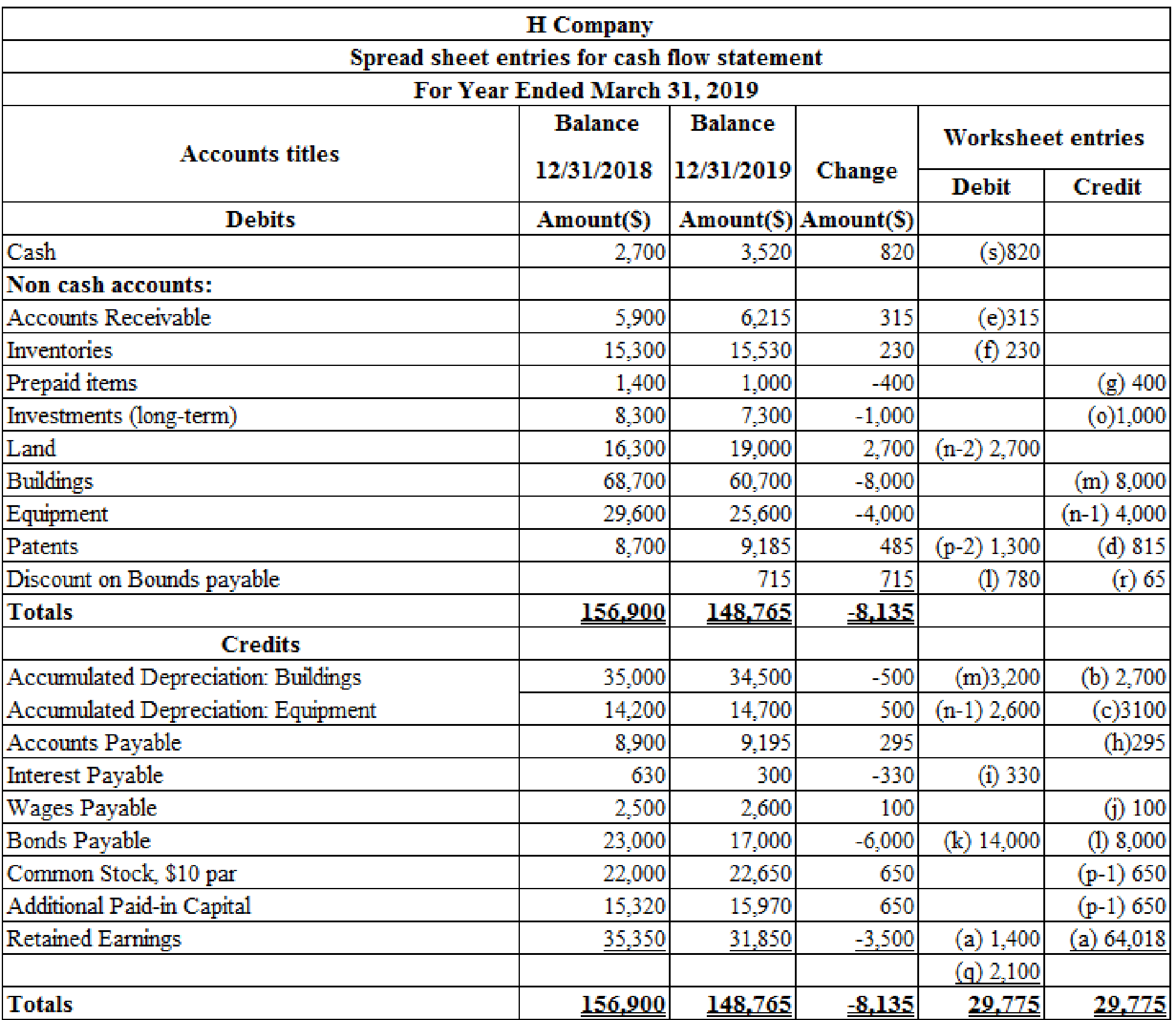
Table (1)
A statement of cash flows of H Company for the year 2019:
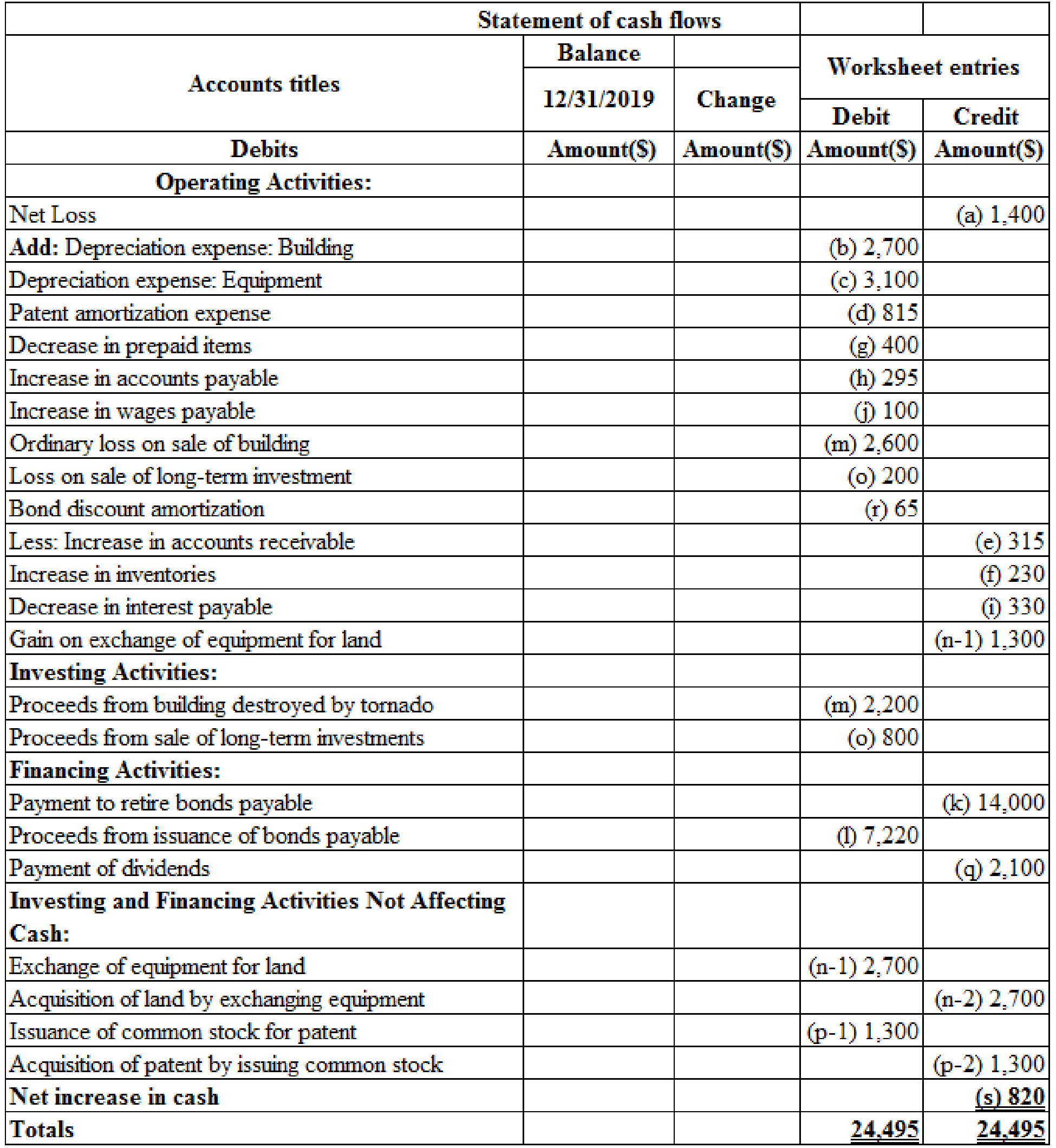
Table (2)
Working notes:
(a) Calculate the net loss.
| Particulars | Amount($) | Amount($) |
| Revenues : | ||
| Sales | 49,550 | |
| Interest revenue | 790 | |
| Gain on exchange of assets | 1,300 | |
| Total revenue | 51,640 | |
| Expenses: | ||
| Cost of goods sold | 23,800 | |
| Wages expense | 16,510 | |
| Other operating expenses | 1,100 | |
| Depreciation expense: buildings | 2,700 | |
| Depreciation expense: equipment | 3,100 | |
| Patent amortization | 815 | |
| Interest expense | 1,715 | |
| Loss on sale of investments | 200 | |
| Loss on sale of building | (2,600) | |
| Income tax expense | 500 | |
| Total expenses | (53,040) | |
| Net Loss | (1,400) |
Table (2)
Note: The $31,850 ending retained earnings balance is derived by subtracting the $1,400 net loss and the $2,100 dividends from the $35,350 beginning retained earnings balance.
(e) Calculate the increase in accounts receivable.
(f) Calculate the increase in inventories.
(g) Calculate the decrease in prepaid items.
(h) Calculate the increase in accounts payable.
(i) Calculate the decrease in interest payable.
(j) Calculate the increase in wages payable.
(l) Proceeds from issuance of bonds payable.
(m) Students may have difficulty with the extraordinary loss transaction. This may be shown in journal entry form as follows:
| Date | Accounts and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Proceeds from sale of building | 2,200 | ||
| Accumulated Depreciation | 3,200 | ||
| Ordinary Loss(net) | 2,600 | ||
| Buildings | 8000 | ||
| (To record the sale of building) |
Table (3)
(n-1) Calculate the exchange of equipment for land.
(o)Calculate the proceeds from sale of long-term investment.
(p-1) Calculate the issuance of common stock for patent.
(p-2) Acquisition of patent by issuing common stock is $1,300,
(r) Calculate the bond discount amortization.
(s) Calculate net increase in cash.
Therefore, the net increase in cash is $820.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College


