
Concept explainers
(a)
The current for the given circuit
Answer to Problem 50PE
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The voltage of alkaline cell is
An internal resistance is
Voltmeter is used with
The given figure is
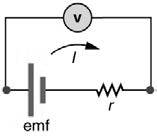
Introduction:
Kirchhoff's second rule states that in a closed loop the sum of all the voltages is equal to zero.
Kirchhoff's junction rule states that the sum of all the currents entering a junction is equal to the sum of all the currents leaving the junction.
Ohms law states that at constant temperature potential difference
Where
Equivalent resistance of several resistors connected in series is
It is known that
Ohms law states that at constant temperature potential difference
Where
Equivalent resistance of several resistors connected in series is
It is given that
Resistors are connected in series so
Substitute all the values in
Conclusion:
The current for the given circuit is
(b)
The terminal voltage of the given circuit
Answer to Problem 50PE
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The voltage of alkaline cell is
An internal resistance is
Voltmeter is used with
The given figure is
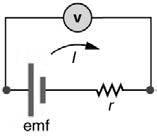
Introduction:
Kirchhoff's second rule states that in a closed loop the sum of all the voltages is equal to zero.
Kirchhoff's junction rule states that the sum of all the currents entering a junction is equal to the sum of all the currents leaving the junction.
Ohms law states that at constant temperature potential difference
Where
Equivalent resistance of several resistors connected in series is
It is known that
Ohms law states that at constant temperature potential difference
Where
It is given that
Substitute all the values in
Conclusion:
The terminal voltage of the given circuit is
(c)
The ratio of the measured terminal voltage to the emf for the given circuit
Answer to Problem 50PE
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The voltage of alkaline cell is
An internal resistance is
Voltmeter is used with
The given figure is
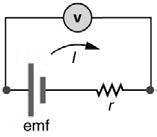
Introduction:
Kirchhoff's second rule states that in a closed loop the sum of all the voltages is equal to zero.
Kirchhoff's junction rule states that the sum of all the currents entering a junction is equal to the sum of all the currents leaving the junction.
Ohms law states that at constant temperature potential difference
Where
Equivalent resistance of several resistors connected in series is
The terminal voltage of the given circuit is
The given emf is
The ratio of the measured terminal voltage to the emf for the given circuit is
Conclusion:
The ratio of the measured terminal voltage to the emf for the given circuit is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
College Physics
- Four capacitors are connected as shown in the figure below. (Let C = 12.0 µF.) A circuit consists of four capacitors. It begins at point a before the wire splits in two directions. On the upper split, there is a capacitor C followed by a 3.00 µF capacitor. On the lower split, there is a 6.00 µF capacitor. The two splits reconnect and are followed by a 20.0 µF capacitor, which is then followed by point b. (a) Find the equivalent capacitance between points a and b. µF(b) Calculate the charge on each capacitor, taking ΔVab = 16.0 V. 20.0 µF capacitor µC 6.00 µF capacitor µC 3.00 µF capacitor µC capacitor C µCarrow_forwardTwo conductors having net charges of +14.0 µC and -14.0 µC have a potential difference of 14.0 V between them. (a) Determine the capacitance of the system. F (b) What is the potential difference between the two conductors if the charges on each are increased to +196.0 µC and -196.0 µC? Varrow_forwardPlease see the attached image and answer the set of questions with proof.arrow_forward
- How, Please type the whole transcript correctly using comma and periods as needed. I have uploaded the picture of a video on YouTube. Thanks,arrow_forwardA spectra is a graph that has amplitude on the Y-axis and frequency on the X-axis. A harmonic spectra simply draws a vertical line at each frequency that a harmonic would be produced. The height of the line indicates the amplitude at which that harmonic would be produced. If the Fo of a sound is 125 Hz, please sketch a spectra (amplitude on the Y axis, frequency on the X axis) of the harmonic series up to the 4th harmonic. Include actual values on Y and X axis.arrow_forwardSketch a sign wave depicting 3 seconds of wave activity for a 5 Hz tone.arrow_forward
- Sketch a sine wave depicting 3 seconds of wave activity for a 5 Hz tone.arrow_forwardThe drawing shows two long, straight wires that are suspended from the ceiling. The mass per unit length of each wire is 0.050 kg/m. Each of the four strings suspending the wires has a length of 1.2 m. When the wires carry identical currents in opposite directions, the angle between the strings holding the two wires is 20°. (a) Draw the free-body diagram showing the forces that act on the right wire with respect to the x axis. Account for each of the strings separately. (b) What is the current in each wire? 1.2 m 20° I -20° 1.2 marrow_forwardplease solve thisarrow_forward
- please solve everything in detailarrow_forward6). What is the magnitude of the potential difference across the 20-02 resistor? 10 Ω 11 V - -Imm 20 Ω 10 Ω 5.00 10 Ω a. 3.2 V b. 7.8 V C. 11 V d. 5.0 V e. 8.6 Varrow_forward2). How much energy is stored in the 50-μF capacitor when Va - V₁ = 22V? 25 µF b 25 µF 50 µFarrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





