
Concept explainers
a. How many amide bonds join the amino acids in the peptide chain?
b.Give the name of the N-terminal amino acid.
c.Give the name of the C-terminal amino acid. 
(a)
Interpretation:
The number of amide bonds that join the amino acids in the: IRCFITPDIT-51 amino acid-CNPFPTRKRP peptide chain.
Concept Introduction:
Amino acids are organic compounds containing two functional groups namely amino and carboxylic group. The amino group is attached to the alpha carbon, carbon adjacent to the carbonyl group making them alpha-amino acids.
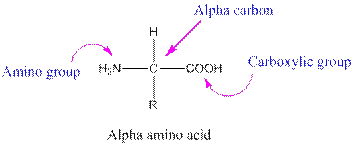
Answer to Problem 38P
There are
Explanation of Solution
When amino acids joined to one another by amide bonds to form large molecules are called peptides. The amide bonds present in peptides are called peptides bonds.
To make a dipeptide, the amino group
To calculate the number of amide bonds present in any sequence will be one less the number of amino acids present in the sequence.
For example, there are two amino acids present in a dipeptide. Then, the number of amide bonds will be one.
The given sequence is as follows:
IRCFITPDIT-51 amino acid-CNPFPTRKRP
There are total
(b)
Interpretation:
The name of the N-terminal amino acid of the given amino acid sequence present in the bee venom should be determined.
IRCFITPDIT-51 amino acid-CNPFPTRKRP
Concept Introduction:
Amino acids are organic compounds containing two functional groups namely amino and carboxylic group. The amino group is attached to the alpha carbon, carbon adjacent to the carbonyl group making them alpha-amino acids.
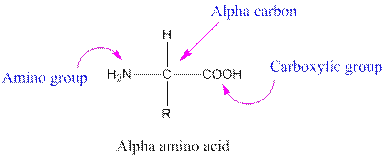
Answer to Problem 38P
Isoleucine (I) will be the N-terminal amino acid present in the given sequence IRCFITPDIT-51amino acid-CNPFPTRKRP.
Explanation of Solution
Amino acid having a free
The name, one-letter and three-letter abbreviation of the amino acids are mentioned in the table given below:
| Name of Amino Acid | Three-letter abbreviation | One-letter abbreviation |
| Alanine | Ala | A |
| Asparagine | Asn | N |
| Cysteine | Cys | C |
| Glutamine | Gln | Q |
| Glycine | Gly | G |
| Isoleucine | Ile | I |
| Leucine | Leu | L |
| Methionine | Met | M |
| Phenylalanine | Phe | F |
| Proline | Pro | P |
| Serine | Ser | S |
| Threonine | Thr | T |
| Tryptophan | Trp | W |
| Tyrosine | Tyr | Y |
| Valine | Val | V |
| Aspartic acid | Asp | D |
| Glutamic acid | Glu | E |
| Arginine | Arg | R |
| Histidine | His | H |
| Lysine | Lys | K |
The given sequence is as follows:
IRCFITPDIT-51 amino acid-CNPFPTRKRP
From the table, 'I' will be the amino acid present at the N-terminal. And 'I' is the 'Isoleucine' amino acid.
(c)
Interpretation:
The name of the C-terminal amino acid of the given amino acid sequence present in the bee venom should be determined.
IRCFITPDIT-51 amino acid-CNPFPTRKRP
Concept Introduction:
Amino acids are organic compounds containing two functional groups namely amino and carboxylic group. The amino group is attached to the alpha carbon, carbon adjacent to the carbonyl group making them alpha-amino acids.
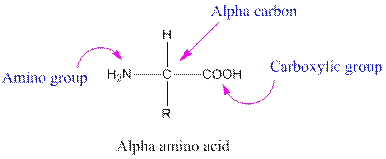
Answer to Problem 38P
Proline (P) will be the C-terminal amino acid present in the given sequence IRCFITPDIT-51amino acid-CNPFPTRKRP.
Explanation of Solution
Amino acid having a free
The name, one-letter and three-letter abbreviation of the amino acids are mentioned in the table given below:
| Name of Amino Acid | Three-letter abbreviation | One-letter abbreviation |
| Alanine | Ala | A |
| Asparagine | Asn | N |
| Cysteine | Cys | C |
| Glutamine | Gln | Q |
| Glycine | Gly | G |
| Isoleucine | Ile | I |
| Leucine | Leu | L |
| Methionine | Met | M |
| Phenylalanine | Phe | F |
| Proline | Pro | P |
| Serine | Ser | S |
| Threonine | Thr | T |
| Tryptophan | Trp | W |
| Tyrosine | Tyr | Y |
| Valine | Val | V |
| Aspartic acid | Asp | D |
| Glutamic acid | Glu | E |
| Arginine | Arg | R |
| Histidine | His | H |
| Lysine | Lys | K |
The given sequence is as follows:
IRCFITPDIT-51amino acid-CNPFPTRKRP
From the table, 'P' will be the amino acid present at the C-terminal. And 'P' is the 'Proline' amino acid.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Connect One Semester Access Card for General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry
- In an induced absorption process:a) the population of the fundamental state is diminishingb) the population of the excited state decreasesc) the non-radiating component is the predominant oned) the emission radiation is consistentarrow_forwardhow a - Cyanostilbenes are made? provide 3 different methods for their synthesisarrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forward
- Don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardDraw a Lewis dot structure for C2H4Oarrow_forward3.3 Consider the variation of molar Gibbs energy with pressure. 3.3.1 Write the mathematical expression for the slope of graph of molar Gibbs energy against 3.3.2 pressure at constant temperature. Draw in same diagram graphs showing variation with pressure of molar Gibbs energies of a substance in gaseous, liquid and solid forms at constant temperature. 3.3.3 Indicate in your graphs melting and boiling points. 3.3.4 Indicate for the respective phases the regions of relative stability.arrow_forward
- In 2-chloropropane, the signal for the H on the C next to Cl should be split into how many peaks?arrow_forward4.4 Consider as perfect gas 3.0 mol of argon gas to which 229 J of energy is supplied as heat at constant pressure and temperature increases by 2.55 K. Calculate 4.4.1 constant pressure molar heat capacity. 4.4.2 constant volume molar heat capacity.arrow_forward3.2 32 Consider calibrating a calorimeter and measuring heat transferred. A sample of compound was burned in a calorimeter and a temperature change of 3.33°C recorded. When a 1.23 A current from a 12.0 V source was passed through a heater in the same calorimeter for 156 s, the temperature changed of 4.47°C was recorded. 3.2.1 Calculate the heat supplied by the heater. 3.2.2 Calculate the calorimeter constant. 3.2.3 Calculate the heat released by the combustion reaction.arrow_forward
- -.1 Consider the standard enthalpy of formation of gaseous water at 25°C as -241.82 kJ/mol and calculate the standard enthalpy of formation of gaseous water at 100°C.arrow_forward3.5 Complete the following sentences to make correct scientific meaning. 3.5.1 The entropy of a perfect gas. 3.5.2 when it expands isothermally. The change in entropy of a substance accompanying a change of state at its transition 3.5.3 temperature is calculated from its of transition. The increase in entropy when a substance is heated is calculated from itsarrow_forward3.4 Consider the internal energy of a substance 3.4.1 Draw a graph showing the variation of internal energy with temperature at constant volume 3.4.2 Write the mathematical expression for the slope in your graph in 3.4.1arrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning





