
(a)
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction between acetic anhydride and the given reagent is to be predicted. The complete mechanism is to be drawn if the reaction occurs.
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 21.37P
The product of the given reaction is
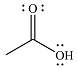
The complete mechanism for the reaction is
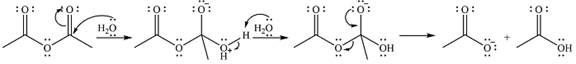
Explanation of Solution
The reagent is a weak nucleophile
The next step is the nucleophile elimination step. One lone pair of the negatively charged oxygen will move back toward carbon to reform the carbonyl group and eliminate the acetate anion to form the final product, acetic acid.
Thus, the product of the reaction is

And the complete mechanism of the reaction can be drawn as

The product and mechanism of the given reaction were determined on the basis of nucleophilic addition-elimination mechanism.
(b)
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction between acetic anhydride and the given reagent is to be predicted. The complete mechanism is to be drawn if the reaction occurs.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid derivatives undergo acyl group substitution reactions when treated with appropriate nucleophiles. The reaction occurs via nucleophilic addition-elimination involving a tetrahedral intermediate. It may also involve proton transfer step(s), paticularly when the nucleophile being added in the first step is not a strong nucleophile. The reaction occurs if the possible product is more stable than the reactant. If the two are of comparable stability, the reaction will occur reversibly. The order of increasing stability of acid derivatives is
Answer to Problem 21.37P
The product of the given reaction is
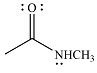
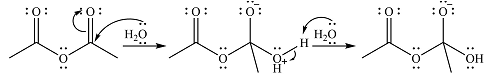
The complete mechanism for the reaction is
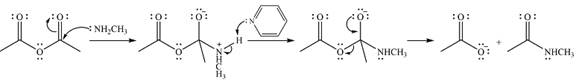
Explanation of Solution
The reagent in this case is
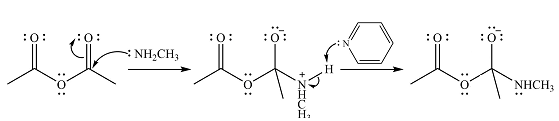
In the next step, one lone pair of negatively charged oxygen moves back to reform the carbonyl group, eliminating the acetate leaving group to form the product.
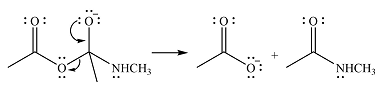
Thus, the product of the reaction is

And the complete mechanism for the reaction is

The product and mechanism of the given reaction were determined on the basis of nucleophilic addition-elimination mechanism.
(c)
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction between acetic anhydride and the given reagent is to be predicted. The complete mechanism is to be drawn if the reaction occurs.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid derivatives undergo acyl group substitution reactions when treated with appropriate nucleophiles. The reaction occurs via nucleophilic addition-elimination involving a tetrahedral intermediate. It may also involve proton transfer step(s), paticularly when the nucleophile being added in the first step is not a strong nucleophile. The reaction occurs if the possible product is more stable than the reactant. If the two are of comparable stability, the reaction will occur reversibly. The order of increasing stability of acid derivatives is
Answer to Problem 21.37P
The product of the given reaction is
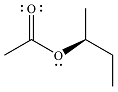
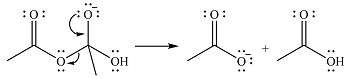
The complete mechanism for the reaction is
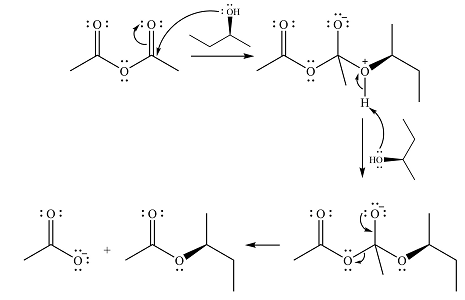
Explanation of Solution
The reagent in this case is a weak nucleophile
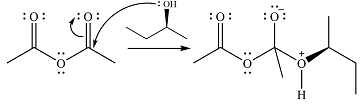
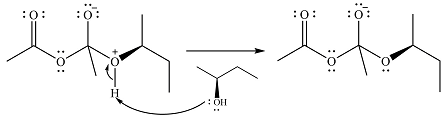
In the next step, the lone pair on negatively charged oxygen will move back to reform the carbonyl group. This will also eliminate the acetate leaving group and form the product.
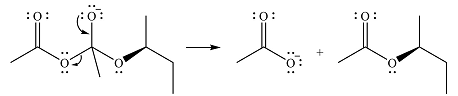
Thus, the product of the reaction is

And the complete mechanism can be drawn as

The product and mechanism of the given reaction were determined on the basis of nucleophilic addition-elimination mechanism.
(d)
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction between acetic anhydride and the given reagent is to be predicted. The complete mechanism is to be drawn if the reaction occurs.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid derivatives undergo acyl group substitution reactions when treated with appropriate nucleophiles. The reaction occurs via nucleophilic addition-elimination involving a tetrahedral intermediate. It may also involve proton transfer step(s), paticularly when the nucleophile being added in the first step is not a strong nucleophile. The reaction occurs if the possible product is more stable than the reactant. If the two are of comparable stability, the reaction will occur reversibly. The order of increasing stability of acid derivatives is
Answer to Problem 21.37P
There is no reaction.
Explanation of Solution
The reagent in this case is an ether. The nucleophilic addition step will produce an unstable intermediate with positively charged oxygen. Since the nucleophile added is an ether, it has no hydrogen attached to oxygen, deprotoantion of this unstable intermediate is not possible.
Therefore, there will be no reaction.
The reaction will not occur as it involves an unstable intermediate with positively charged oxygen.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
EBK GET READY FOR ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- Draw a Newman projection for the molecule below from the perspective indicated. Which of the groups (letters A-H) are methyl groups? CH3 H H H A H B ☑ >> H. ABCDEFG I H -H CH3 G D CH F E Numeric 4 points How many gauche interactions exist in the conformation shown in the previous problem? 1arrow_forwardHELP NOW PLEASE ! ASAP! URGENT!arrow_forwardHELP NOW PLEASE ! ASAP! URGENT!arrow_forward
- Would the following organic synthesis occur in one step? Add any missing products, required catalysts, inorganic reagents, and other important conditions. Please include a detailed explanation and drawings showing how the reaction may occur in one step.arrow_forwardPls help.arrow_forward13) When solid barium phosphate is in equilibrium with its ions, the ratio of barium ions to phosphate ions would be: a. 1:1 b. 2:3 c. 3:2 d. 2:1 14) The pH of a 0.05 M solution of HCl(aq) at 25°C is 15) The pH of a 0.20 M solution of KOH at 25°C isarrow_forward
- Pls help.arrow_forwardPls help.arrow_forward16) A 2.0 L flask containing 2.0 x 10-3 mol H2(g), 3.0 x 10-3 mol Cl2(g), and 4.0 x 10-3 mol HCl(g) at equilibrium. This system is represented by the following chemical equation: H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) → 2HCl(g) Calculate the equilibrium constant for this reaction.arrow_forward
- 7) The pH of a 0.05M solution of HCl(aq) at 25°C is a. 1.3 b. 2.3 c. 3.3 d. 12.7arrow_forward11) The Ksp expression for copper (II) sulfate is: a. [Cu2+][SO4²¯] b. [Cu²+]² [SO4²]² c. [Cu²+]²[SO4²] d. [CuSO4] 12) Which of the following is true about a chemical system in equilibrium? a. All chemical reactions have stopped b. The concentration of reactants is equal to the concertation of products c. The forward and reverse reaction rates become equal d. The system will remain at equilibrium regardless of any external factorsarrow_forward21) Explain the difference between the rate of a reaction and the extent of a reaction. Why are both of these concepts important, if you are a chemical engineer that is trying to develop a process to produce a large volume of a specific type of chemical compound?arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





