
(a)
Interpretation:
The mechanism and the major organic product for the given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Migratory Aptitude in a Baeyer–Villiger Oxidation:
Answer to Problem 21.60P
The mechanism and the major organic product for the given reaction are:
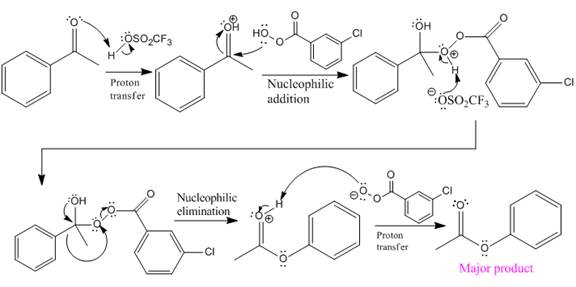
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is:
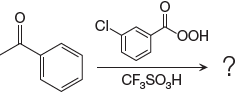
The ketone, substrate in the reaction, is asymmetrical ketone. carbonyl C is bonded to a primary alkyl group and an aryl group. According to migratory aptitude, the aryl group has greater migratory aptitude, so its bond will prefentially break.
In this reaction, an O atom from the acid is inserted between carbonyl C and phenyl group, initially bonded to the carbonyl C. C=O is activated by
The complete mechanism and the ester formed as a product for the reaction are:
The mechanism and the product for the reaction are drawn on the basis of the given reaction conditions.
(b)
Interpretation:
The mechanism and the major organic product for the given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Migratory Aptitude in a Baeyer–Villiger Oxidation:
Answer to Problem 21.60P
The mechanism and the major organic product for the given reaction are:
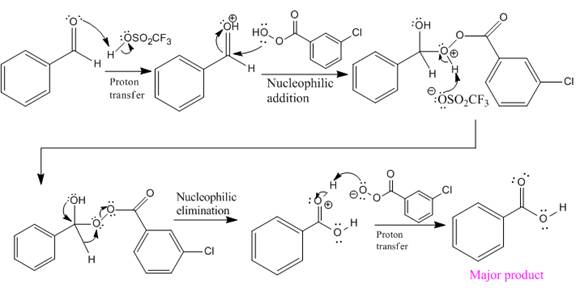
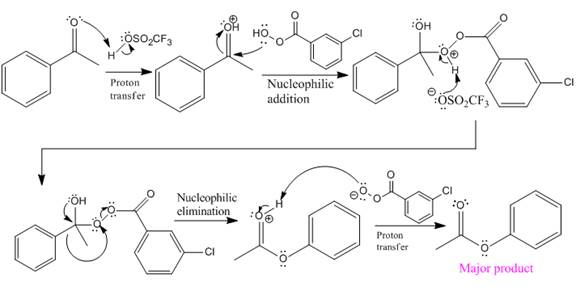
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is:
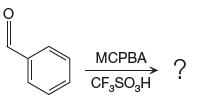
The ketone, substrate in the reaction, is asymmetrical ketone. carbonyl C is bonded to a H atom and an aryl group. According to the migratory aptitude, the H atom has greater migratory aptitude, so its bond will prefentially break.
In this reaction, an O atom from the acid is inserted between carbonyl C and the H atom, initially bonded to carbonyl C. C=O is activated by
The complete mechanism and the ester formed as a product for the reaction are:
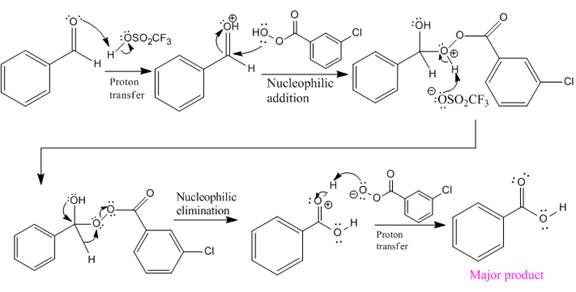
The mechanism and the product for the reaction are drawn on the basis of given reaction conditions.
(c)
Interpretation:
The mechanism and the major organic product for the given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Migratory Aptitude in a Baeyer–Villiger Oxidation:
Answer to Problem 21.60P
The mechanism and the major organic product for the given reaction are:
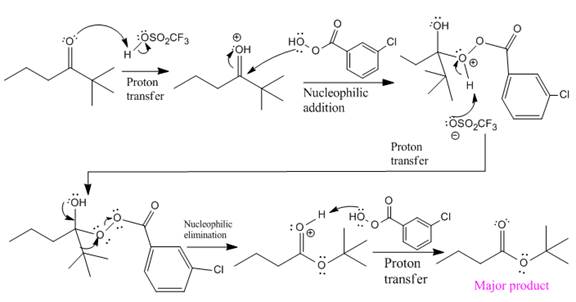
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is:
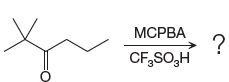
The ketone, substrate in the reaction, is asymmetrical ketone. carbonyl C is bonded to a primary alkyl group and tertiary alkyl group. According to migratory aptitude, the tertiary alkyl group has greater migratory aptitude, so its bond will prefentially break.
In this reaction an O atom from the acid is inserted between carbonyl C and the tertiary alkyl group, initially bonded to carbonyl C. C=O is activated by
The complete mechanism and the ester formed as a product for the reaction are:

The mechanism and the product for the reaction are drawn on the basis of given reaction conditions.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
EBK GET READY FOR ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- helparrow_forwardDone 11:14 ⚫ worksheets.beyondlabz.com 5 (a). Using the peak information you listed in the tables for both structures, assign each peak to that portion of the structure that produces the peak in the NMR spectrum. Draw this diagram on your own sheet of paper and attach the sketch of your drawing to this question. Question 6 5 (b). Using the peak information you listed in the tables for both structures, assign each peak to that portion of the structure that produces the peak in the NMR spectrum. Draw this diagram on your own sheet of paper and attach the sketch of your drawing to this question. Question 7 6. Are there any differences between the spectra you obtained in Beyond Labz and the predicted spectra? If so, what were the differences? <arrow_forward2. Predict the NMR spectra for each of these two compounds by listing, in the NMR tables below, the chemical shift, the splitting, and the number of hydrogens associated with each predicted peak. Sort the peaks from largest chemical shift to lowest. **Not all slots must be filled** Peak Chemical Shift (d) 5.7 1 Multiplicity multiplate .......... 5.04 double of doublet 2 4.98 double of doublet 3 4.05 doublet of quartet 4 5 LO 3.80 quartet 1.3 doublet 6 Peak Chemical Shift (d) Multiplicityarrow_forward
- Interpreting NMR spectra is a skill that often requires some amount of practice, which, in turn, necessitates access to a collection of NMR spectra. Beyond Labz Organic Synthesis and Organic Qualitative Analysis have spectral libraries containing over 700 1H NMR spectra. In this assignment, you will take advantage of this by first predicting the NMR spectra for two closely related compounds and then checking your predictions by looking up the actual spectra in the spectra library. After completing this assignment, you may wish to select other compounds for additional practice. 1. Write the IUPAC names for the following two structures: Question 2 Question 3 2. Predict the NMR spectra for each of these two compounds by listing, in the NMR tables below, the chemical shift, the splitting, and the number of hydrogens associated with each predicted peak. Sort the peaks from largest chemical shift to lowest. **Not all slots must be filled**arrow_forward11:14 ... worksheets.beyondlabz.com 3. To check your predictions, click this link for Interpreting NMR Spectra 1. You will see a list of all the - compounds in the spectra library in alphabetical order by IUPAC name. Hovering over a name in the list will show the structure on the chalkboard. The four buttons on the top of the Spectra tab in the tray are used to select the different spectroscopic techniques for the selected compound. Make sure the NMR button has been selected. 4. Scroll through the list of names to find the names for the two compounds you have been given and click on the name to display the NMR spectrum for each. In the NMR tables below, list the chemical shift, the splitting, and the number of hydrogens associated with each peak for each compound. Compare your answers to your predictions. **Not all slots must be filled** Peak Chemical Shift (d) Multiplicity 1 2 3 4 5arrow_forwardО δα HO- H -Br δα HO-- + + -Br [B] 8+ HO- -Br δα नarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





