
Concept explainers
Statement of
• LO21–4, LO21–8
Refer to the data provided in the P 21–11 for Arduous Company.
Required:
Prepare the statement of cash flows for Arduous Company using the indirect method. (Note: The following problems use the technique learned in Appendix 21B.)
P 21–11 Prepare a statement of cash flows; direct method
• LO21–3, LO21–8
The comparative balance sheets for 2018 and 2017 and the income statement for 2018 are given below for Arduous Company. Additional information from Arduous’s accounting records is provided also.
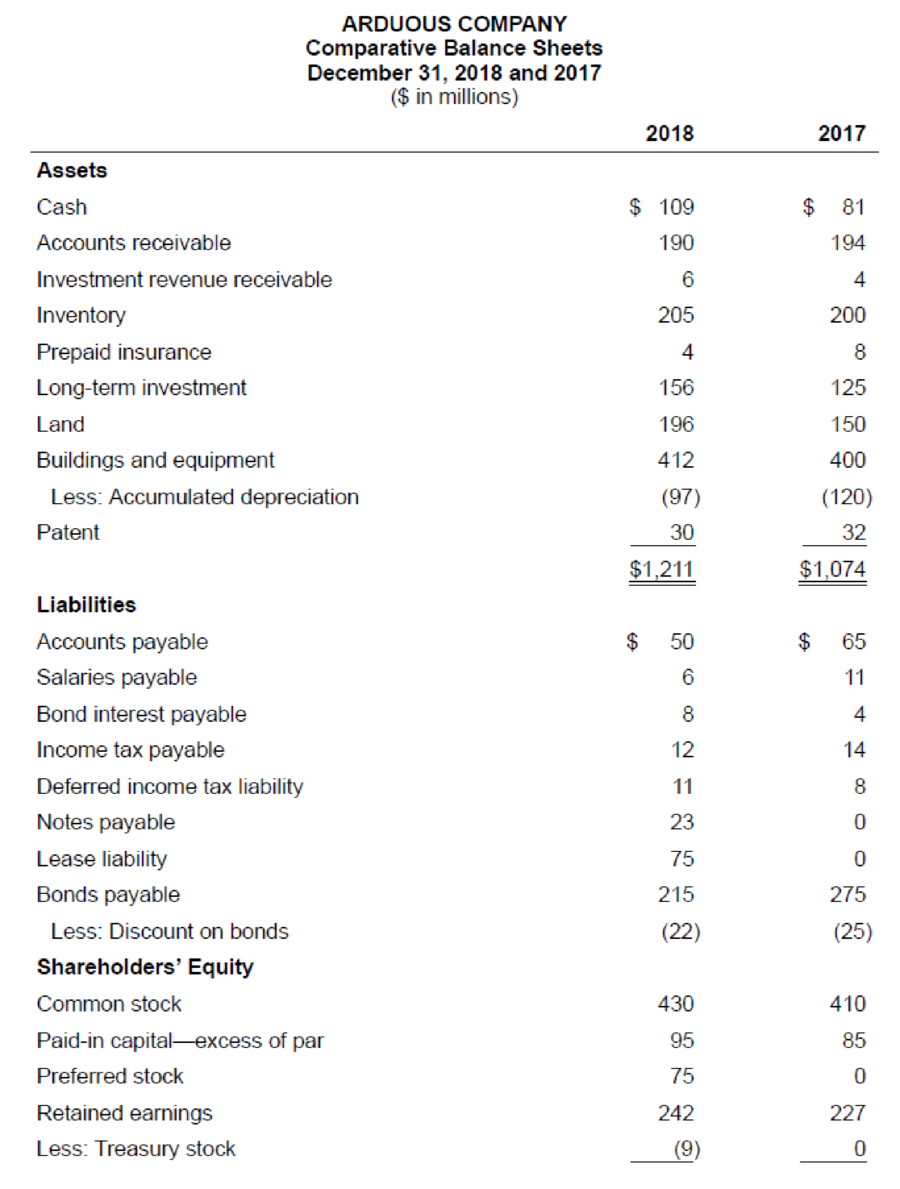
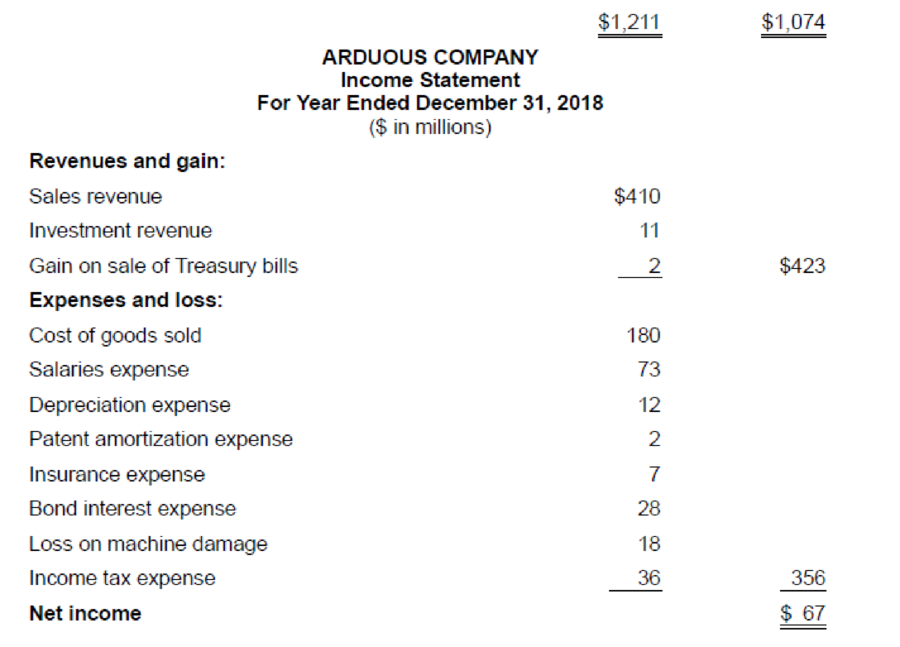
Additional information from the accounting records:
- a. Investment revenue includes Arduous Company’s $6 million share of the net income of Demur Company, an equity method investee.
- b. Treasury bills were sold during 2018 at a gain of $2 million. Arduous Company classifies its investments in Treasury bills as cash equivalents.
- c. A machine originally costing $70 million that was one-half
depreciated was rendered unusable by a flood. Most major components of the machine were unharmed and were sold for $17 million. - d. Temporary differences between pretax accounting income and taxable income caused the
deferred income tax liability to increase by $3 million. - e. The
preferred stock of Tory Corporation was purchased for $25 million as a long-term investment. - f. Land costing $46 million was acquired by issuing $23 million cash and a 15%, four-year, $23 million note payable to the seller.
- g. The right to use a building was acquired with a 15-year lease agreement; present value of lease payments, $82 million. Annual lease payments of $7 million are paid at the beginning of each year starting January 1, 2018.
- h. $60 million of bonds were retired at maturity.
- i. In February, Arduous issued a 4% stock dividend (4 million shares). The market price of the $5 par value common stock was $7.50 per share at that time.
- j. In April, 1 million shares of common stock were repurchased as
treasury stock at a cost of $9 million.
Required:
Prepare the statement of cash flows of Arduous Company for the year ended December 31, 2018. Present cash flows from operating activities by the direct method. (A reconciliation schedule is not required.)
Statement of cash flows: This statement reports all the cash transactions which are responsible for inflow and outflow of cash and result of these transactions is reported as ending balance of cash at the end of reported period.
To Prepare: The statement of cash flows of Company A.
Explanation of Solution
Spreadsheet: The spreadsheet is a supplementary device which helps to prepare the adjusting entries and the statement of cash flows easier. The spreadsheet is a working tool of the accountant but it is not a permanent accounting record.
The spreadsheet, for the statement of cash flow analysis, is shown below.
| Company A | ||||
| Spreadsheet for the Statement of Cash Flows | ||||
| Amount in Millions | ||||
| Particulars | December 31,2017 Amount ($) | Changes | December 31,2018 Amount ($) | |
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |||
| Assets | ||||
| Current Assets | ||||
| Cash | $81 | (21) $28 | $109 | |
| Accounts receivable | $194 | (1) $4 | $190 | |
| Investment revenue receivable | $4 | (2) $2 | $6 | |
| Inventory | $200 | (4) $5 | $205 | |
| Prepaid insurance | $8 | (8) $4 | $4 | |
| Long-term investment | $125 | (2) $6 (13) $25 | $156 | |
| Land | $150 | (14) $46* | $196 | |
| Buildings and equipment | $400 | (15) $82* | (10) $70 | $412 |
| Less: Depreciation | ($120) | (10) $35 | (6) $12 | ($97) |
| Patent | $32 | (7) $2 | $30 | |
| Total current assets | $1,074 | $1,211 | ||
| Liabilities and Stockholders’ Equity | ||||
| Liabilities | ||||
| Accounts payable | $65 | (4) $15 | $50 | |
| Salaries payable | $11 | (5) $5 | $6 | |
| Bond interest payable | $4 | (9) $4 | $8 | |
| Income tax payable | $14 | (11) $2 | $12 | |
| Deferred tax liability | $8 | (11) $3 | $11 | |
| Notes payable | $0 | (14) $23* | $23 | |
| Lease liability | $0 | (15) $7 | (15) $82* | $75 |
| Bonds payable | $275 | (16) $60 | $215 | |
| Less: Discount | ($25) | (9) $3 | ($22) | |
| Stockholders’ equity | ||||
| Common Stock | $410 | (17) $20 | $430 | |
| Paid-in capital—excess of par | $85 | (17) $10 | $95 | |
| Preferred stock | $0 | (18) $75 | $75 | |
| Retained Earnings | $227 | (17) $30/ (19) $22 | (12) $67 | $242 |
| Less: Treasury Stock | $0 | (20) $9 | ($9) | |
| Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity | $1,074 | $1,211 | ||
| Statement of Cash Flows | ||||
| Net income | (1) $67 | |||
| Adjustments for noncash effects: | ||||
| Depreciation expense | (2) $12 | |||
| Patent amortization expense | (3) $2 | |||
| Amortization of discount | (4) $3 | |||
| Decrease in accounts receivable | (5) $4 | |||
| Increase in investment revenue receivable | (6) $2 | |||
| Equity method income | (7) $6 | |||
| Decrease in prepaid insurance | (8) $4 | |||
| Increase in inventory | (9) $5 | |||
| Decrease in accounts payable | (10) $15 | |||
| Decrease in salaries payable | (11) $5 | |||
| Increase in interest payable | (12) $4 | |||
| Decrease in tax payable | (13) $2 | |||
| Increase in deferred tax liability | (14) $3 | |||
| Loss on machine damage | (15) $18 | |||
| Net cash flows | $82 | |||
| Investing activities: | ||||
| Sale of machine components | (15) $17 | |||
| Purchase of Long Term investment | (16) $25 | |||
| Purchase of land | (17) $23 | |||
| Net cash flows | ($31) | |||
| Financing activities: | ||||
| Payment on lease liability | (15) $7 | |||
| Retirement of bonds payable | (19) $60 | |||
| Sale of preferred stock | (21) $75 | |||
| Payment of cash dividends | (22) $22 | |||
| Purchase of treasury stock | (23) $9 | |||
| Net cash flows | ($23) | |||
| Net decrease in cash | (24) $28 | $28 | ||
| Total | $588 | $588 | ||
Table (1)
Operating activities: Operating activities refer to the normal activities of a company to carry out the business. The examples for operating activities are purchase of inventory, payment of salary, sales, and others.
Investing activities: Investing activities refer to the activities carried out by a company for acquisition of long term assets. The examples for investing activities are purchase of equipment, long term investment, sale of land, and others.
Financing activities: Financing activities refer to the activities carried out by a company to mobilize funds to carry out the business activities. The examples for financing activities are purchase of bonds, issuance of common shares, and others.
The spreadsheet of Company A shows the analysis of cash flows in the reporting year 2018.
| Company R | ||
| Statement of Cash Flows | ||
| For year ended December 31, 2018 | ||
| Amount in Millions | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Net income | $67 | |
| Adjustments for non-cash effects: | ||
| Depreciation expense | $12 | |
| Patent amortization expense | $2 | |
| Amortization of discount | $3 | |
| Decrease in accounts receivable | $18 | |
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | ||
| Decrease in accounts receivable | $4 | |
| Increase in investment revenue receivable | ($2) | |
| Equity method income | ($6) | |
| Decrease in prepaid insurance | $4 | |
| Increase in inventory | ($5) | |
| Decrease in accounts payable | ($15) | |
| Decrease in salaries payable | ($5) | |
| Increase in interest payable | $4 | |
| Decrease in tax payable | ($2) | |
| Increase in deferred tax liability | $3 | |
| Net cash outflow from operating activities | $82 | |
| Investing activities: | ||
| Sale of machine components | $17 | |
| Purchase of Long Term investment | ($25) | |
| Purchase of land | ($23) | |
| Net cash flows from investing activities | ($31) | |
| Financing activities: | ||
| Payment on lease liability | ($7) | |
| Retirement of bonds payable | ($60) | |
| Sale of preferred stock | $75 | |
| Payment of cash dividends | ($22) | |
| Purchase of treasury stock | ($9) | |
| Net cash flows from financing activities | ($23) | |
| Net decrease in cash | $28 | |
| Cash balance, January 1, 2018 | $81 | |
| Cash balance, December 31, 2018 | $109 | |
Table (2)
The statement of cash flows of Company A, shows opening balance of cash flows for the reporting year 2018 as $81 million and the closing balance of cash as $109 million.
Note:
*Non Cash investing activity and financing activity:
- Company A acquired a building on 15 year lease for $82 million.
- Company A acquired a land for $46 million, by:
- Paying Cash of $23 million;
- Issuing 4-year note for $23 million.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Intermediate Accounting
- Ivanhoe Equipment Company sells computers for $1,620 each and also gives each customer a 2-year warranty that requires the company to perform periodic services and to replace defective parts. In 2025, the company sold 860 computers on account. Based on experience, the company has estimated the total 2-year warranty costs as $40 for parts and $60 for labor per unit. (Assume sales all occur at December 31, 2025.) In 2026, Ivanhoe incurred actual warranty costs relative to 2025 computer sales of $13,200 for parts and $19,800 for labor. Record the entries to reflect the above transactions (accrual method) for 2025 and 2026. (Credit account titles are automatically indented when the amount is entered. Do not indent manually. If no entry is required, select "No Entry" for the account titles and enter O for the amounts. List all debit entries before credit entries.) Date Account Titles and Explanation 2025 2026 2025 Cash Sales Revenue (To record sale of computers) Warranty Expense Warranty…arrow_forwardNeed Answer of this Accounting Subject Relevant Questionarrow_forwardHellow Dear Teacher Please Help to Solve This Financial Accounting Problemarrow_forward
- Walthaus Corporation's standard cost sheet is as follows: Direct material 4 feet at $ 5.00 per foot Direct labor 3 hours at $ 10.00 per hour Variable overhead 3 hours at $ 2.00 per hour Fixed overhead 3 hours at $ 1.00 per hour Additional information: Actual results: purchased 30,000 feet of material at $5.25 per foot. (there were no beginning or ending material inventories); direct labor cost incurred was 26,000 hours at $9.75 per hour; actual variable overhead incurred, $50,000; and actual fixed overhead incurred $43,000. Overhead is applied to work-in-process on the basis of direct labor hours. The company produced 8,000 units of product during the period. The number of estimated hours for computing the fixed overhead application rate totaled 45,000 hours. What are the fixed overhead price and production volume variances? Multiple Choice $2,000 F; $23,000 U. $4,000 F; $25,000 U. $2,000 U; $23,000 F. None of the choices is correct.…arrow_forwardNo Ai 3. What is the purpose of depreciation?A. Track the market value of assetsB. Match the cost of an asset to the periods it benefitsC. Allocate cash flowsD. Record the decrease in asset liquidity need helparrow_forwardFinancial Accounting Question Solution with Detailed Explanation and Correct Answerarrow_forward
- I need help 3. What is the purpose of depreciation?A. Track the market value of assetsB. Match the cost of an asset to the periods it benefitsC. Allocate cash flowsD. Record the decrease in asset liquidityarrow_forwardImpact Window Company makes storm-resistant windows. The company's sales manager estimated the sales volume to be 160,000 windows. Due to the increased hurricane activity this year, the total demand for this type of window increased from 800,000 windows to 1,000,000 windows. At the same time the company's market share fell from 20 percent to 15 percent. The company's standard contribution margin is $15.00 per window. What is the company's market share variance? Multiple Choice $740,000 favorable $740,000 unfavorable $750,000 unfavorable None of these. $750,000 favorablearrow_forwardNo chatgpt 3. What is the purpose of depreciation?A. Track the market value of assetsB. Match the cost of an asset to the periods it benefitsC. Allocate cash flowsD. Record the decrease in asset liquidityarrow_forward
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning



