
(a)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism and the overall product for the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The ester is hydrolyzed to the
Answer to Problem 21.14P
The mechanism and product for the given reaction is:
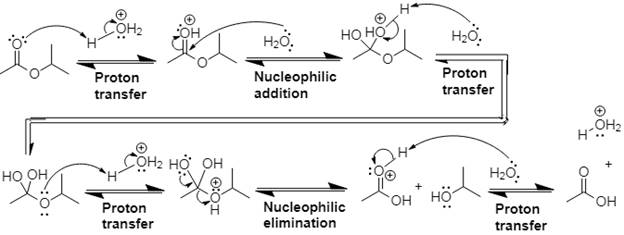
Explanation of Solution
In Step 1 of the mechanism, the acid protonates the ester’s carbonyl group, and in Step 2, water attacks the carbonyl
The complete, detailed mechanism and the overall product for the given reaction is drawn by acid-catalyzed ester hydrolysis.
(b)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism and the overall product for the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
This is an acid-catalyzed transesterification, and a new ester is formed.
Answer to Problem 21.14P
The mechanism and product for the given reaction is:
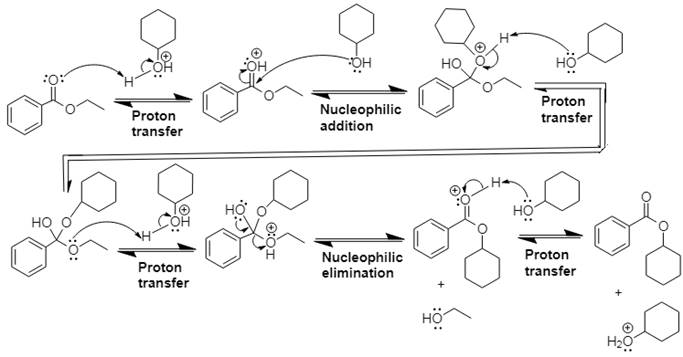
Explanation of Solution
In Step 1 of the mechanism, the acid protonates the ester’s carbonyl group, and in Step 2,
The complete, detailed mechanism and the overall product for the given reaction is drawn by acid-catalyzed transesterification.
(c)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism and the overall product for the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
This is an acid catalyzed amide hydrolysis which produces a carboxylic acid. Water acts as the nucleophile in this acid-catalyzed nucleophilic addition–elimination mechanism, and the leaving group is a molecule of
Answer to Problem 21.14P
The mechanism and product for the given reaction is:
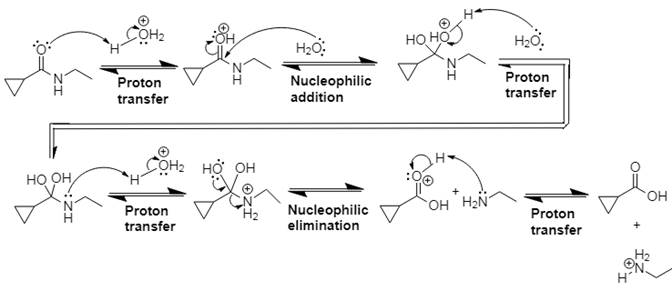
Explanation of Solution
In Step 1 of the mechanism, the acid protonates the ester’s carbonyl group, and in Step 2, water attacks the carbonyl
The complete, detailed mechanism and the overall product for the given reaction is drawn by acid-catalyzed amide hydrolysis.
(d)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism and the overall product for the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
This is an acid catalyzed ester hydrolysis which produces a carboxylic acid. Water acts as the nucleophile in this acid-catalyzed nucleophilic addition–elimination mechanism, and the leaving group is a molecule of alcohol. Proton transfer steps are incorporated to avoid the appearance of strong bases.
Answer to Problem 21.14P
The mechanism and product for the given reaction is:
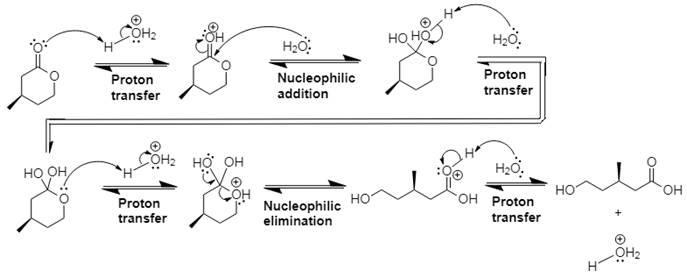
Explanation of Solution
In Step 1 of the mechanism, the acid protonates the ester’s carbonyl group, and in Step 2, water attacks the carbonyl
The complete, detailed mechanism and the overall product for the given reaction is drawn by acid-catalyzed ester hydrolysis.
(e)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism and the overall product for the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
This is Fischer esterification reaction.
Answer to Problem 21.14P
The mechanism and product for the given reaction is:
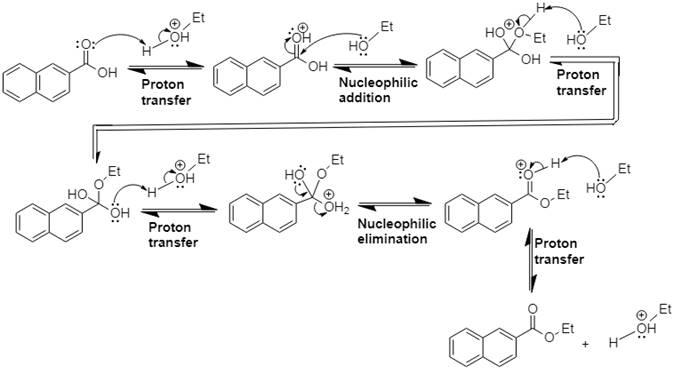
Explanation of Solution
In Step 1 of the mechanism, the acid protonates the acid’s carbonyl group, and in Step 2,
The complete, detailed mechanism and the overall product for the given reaction is drawn by Fischer esterification reaction.
(f)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism and the overall product for the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
This is an acid catalyzed amide hydrolysis which produces a carboxylic acid. Water acts as the nucleophile in this acid-catalyzed nucleophilic addition–elimination mechanism, and the leaving group is a molecule of amine. Proton transfer steps are incorporated to avoid the appearance of strong bases.
Answer to Problem 21.14P
The mechanism and product for the given reaction is:
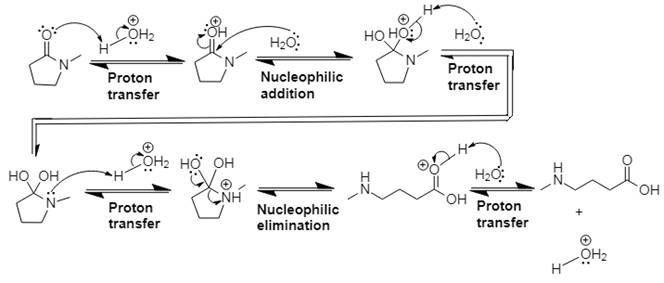
Explanation of Solution
In Step 1 of the mechanism, the acid protonates the ester’s carbonyl group, and in Step 2, water attacks the carbonyl
The complete, detailed mechanism and the overall product for the given reaction is drawn by acid-catalyzed amide hydrolysis.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
EBK GET READY FOR ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- In reactions whose kinetic equation is v = k[A]m, the rate coefficient k is always positive. Is this correct?arrow_forwardIf the concentration of A decreases exponentially with time, what is the rate equation? (A). -d[A] (B). dt d[A] = k[A] e-kt dtarrow_forwardGiven the first-order reaction: aA → products. State its kinetic equation.arrow_forward
- The following chemical structure represents a molecule of what molecular formula?arrow_forwardWhich region(s) of the following phospholipid is/are hydrophobic? RO I hydro-water phobic-dislikes = Hydrophobic dislikes water ○ I only Il only I and III only II and IV only O II, III, and IV only III || IVarrow_forwardPredict the product of the following reactions: O 0= excess Х Кон ОН H+ H+ Iarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
