
(a)
Interpretation:
Synthesis of the given compound is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
The acetic acid is treated with various reagents to form products that contain different
Answer to Problem 21.85P
The synthesis of the given compound is as follows:
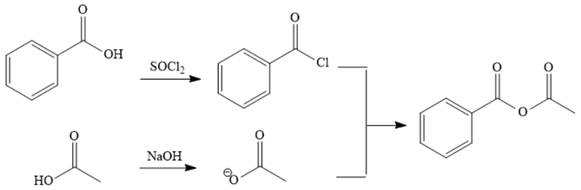
Explanation of Solution
The reaction requires converting a carboxylic acid to an acid anhydride, which represents going up the stability ladder. This is difficult to do directly but can be carried out by first producing an acid chloride. The acid chloride and the salt of acetic acid will make the desired anhydride.
The acetic acid is treated with various reagents to form products that contain different functional groups.
(b)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of the given compound is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
The acetic acid is treated with various reagents to form products that contain different functional groups. The new functional groups formed are anhydride, amine, ether, aldehyde, ketone, etc. When carboxylic acid converted to an acid anhydride, the stability ladder going up. When an anhydride reacted with ethanol to formed the ester, the stability ladder going down.
Answer to Problem 21.85P
The synthesis of the given compound is as follows:
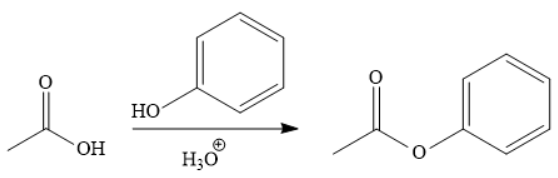
Explanation of Solution
The addition of phenol forms the ester under acidic condition, a Fischer esterification. This is a reversible reaction and can be carried out directly because the reactant and product species are on the same rung of the stability ladder.
The acetic acid is treated with various reagents to form products that contain different functional groups.
(c)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of the given compound is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
The acetic acid is treated with various reagents to form products that contain different functional groups. The new functional groups formed are anhydride, amine, ether, aldehyde, ketone, etc. When carboxylic acid converted to an acid anhydride, the stability ladder going up. When an anhydride reacted with ethanol to formed the ester, the stability ladder going down.
Answer to Problem 21.85P
The synthesis of the given compound is as follows,
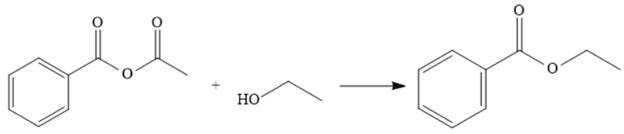
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of the anhydride from (a) with ethanol makes the ester. This represents going down the stability ladder and is done relatively easily.
The acetic acid is treated with various reagents to form products that contain different functional groups.
(d)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of the given compound is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
The acetic acid is treated with various reagents to form products that contain different functional groups. The new functional groups formed are anhydride, amine, ether, aldehyde, ketone, etc. When carboxylic acid converted to an acid anhydride, the stability ladder going up. When an anhydride reacted with ethanol to formed the ester, the stability ladder going down.
Answer to Problem 21.85P
The synthesis of the given compound is as follows:
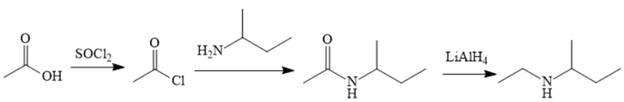
Explanation of Solution
The amine can be produced by reducing the corresponding amide. It is difficult to produce the amide directly from acetic acid because the amine that would be required for the nucleophile would deprotonate the carboxylic acid. The amide can be made relatively easily, however, by first converting acetic acid to acetyl chloride and then treating acetyl chloride with the amine.
The acetic acid is treated with various reagents to form products that contain different functional groups.
(e)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of the given compound is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
The acetic acid is treated with various reagents to form products that contain different functional groups. The new functional groups formed are anhydride, amine, ether, aldehyde, ketone, etc. When carboxylic acid converted to an acid anhydride, the stability ladder going up. When an anhydride reacted with ethanol to formed the ester, the stability ladder going down.
Answer to Problem 21.85P
The synthesis of the given compound is as follows,
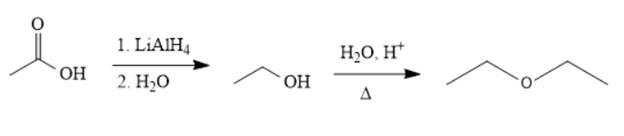
Explanation of Solution
Reducing the acid to an alcohol, followed by dehydration, leads to the ether. Alternatively, ethanol can be deprotonated by
The acetic acid is treated with various reagents to form products that contain different functional groups.
(f)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of the given compound is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
The acetic acid is treated with various reagents to form products that contain different functional groups. The new functional groups formed are anhydride, amine, ether, aldehyde, ketone, etc. When carboxylic acid converted to an acid anhydride, the stability ladder going up. When an anhydride reacted with ethanol to formed the ester, the stability ladder going down.
Answer to Problem 21.85P
The synthesis of the given compound is as follows,
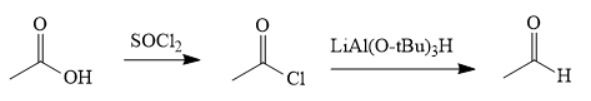
Explanation of Solution
First, acid is treated with
The acetic acid is treated with various reagents to form products which contain different functional groups.
(g)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of the given compound is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
The acetic acid is treated with various reagents to form products that contain different functional groups. The new functional groups formed are anhydride, amine, ether, aldehyde, ketone, etc. When carboxylic acid converted to an acid anhydride, the stability ladder going up. When an anhydride reacted with ethanol to formed the ester, the stability ladder going down.
Answer to Problem 21.85P
The synthesis of the given compound is as follows,
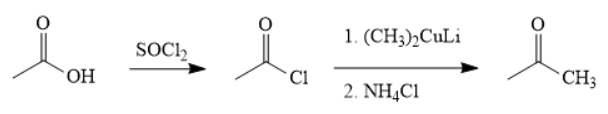
Explanation of Solution
First, acid is treated with
The acetic acid is treated with various reagents to form products which contain different functional groups.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
EBK GET READY FOR ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- Q Select to Edit NH3 (CH3)2CHCI (1 equiv) AICI 3 Select to Draw cat. H2SO4 SO3 (1 equiv) HO SOCl2 pyridine Select to Edit >arrow_forwardComplete and balance the following half-reaction in basic solution. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. Zn(s) → Zn(OH)₄²⁻(aq)arrow_forwardb. ὋΗ CH3CH2OH H2SO4arrow_forward
- For the reaction A (g) → 3 B (g), Kp = 0.379 at 298 K. What is the value of ∆G for this reaction at 298 K when the partial pressures of A and B are 5.70 atm and 0.250 atm?arrow_forward14. Calculate the concentrations of Ag+, Ag(S2O3), and Ag(S2O3)23- in a solution prepared by mixing 150.0 mL of 1.00×10-3 M AgNO3 with 200.0 mL of 5.00 M Na2S2O3 Ag+ + S20 Ag(S203)¯ K₁ = 7.4 × 108 Ag(S203)¯ + S20¯ = Ag(S203) K₂ = 3.9 x 104arrow_forwardΗΝ, cyclohexanone pH 4-5 Draw Enamine I I CH3CH2Br THF, reflux H3O+ I Drawing Draw Iminium Ionarrow_forward
- :0: :0: Select to Add Arrows :0: (CH3)2NH :0: ■ Select to Add Arrows :0: :0: (CH3)2NH ■ Select to Add Arrowsarrow_forwardDraw the product of the following H action sequence. Ignore any inorganic byproducts formed. 1. (CH3CH2)2CuLi, THF 2. CH3Br Q Atoms, Bonds and Rings H Charges ㅁarrow_forwardPlease help me with this the problem is so confusingarrow_forward
- 14 Question (1 point) Disiamylborane adds to a triple bond to give an alkenylborane. Upon oxidation with OH, H2O2, the alkenylborane will form an enol that tautomerizes to an aldehyde. In the first box below, draw the mechanism arrows for the reaction of disiamylborane with the alkyne, and in the last box draw the structure of the aldehyde. 4th attempt Feedback i > 3rd attempt OH, H2O2 i See Periodic Table See Hintarrow_forwardanswer with mechanisms and steps. handwritten please!arrow_forwardHello I need some help with Smartwork. For drawing structure B, I know the correct answer is CH₃B₂, but when I try to type it in, it keeps giving me CH₄BH₃ instead. Do you know how I should write it properly? Should I use a bond or something else?arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





