
Concept explainers
Prepare a statement of
• LO21–3, LO21–8
The comparative
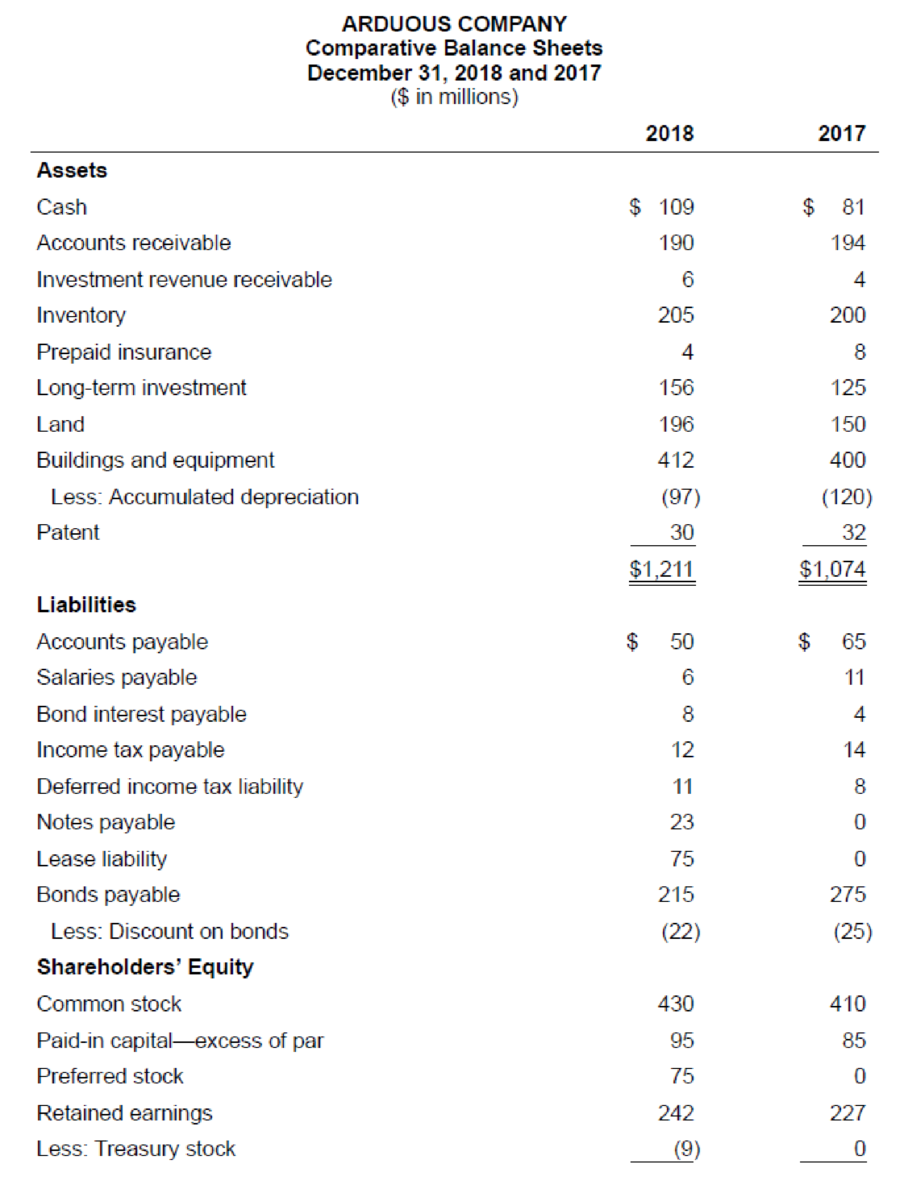
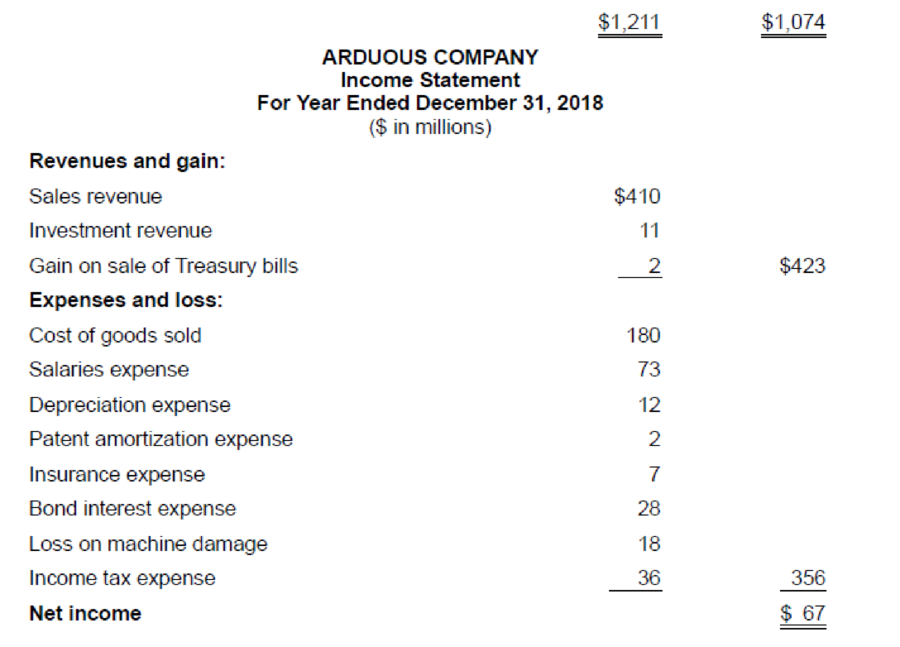
Additional information from the accounting records:
a. Investment revenue includes Arduous Company’s $6 million share of the net income of Demur Company, an equity method investee.
b. Treasury bills were sold during 2018 at a gain of $2 million. Arduous Company classifies its investments in Treasury bills as cash equivalents.
c. A machine originally costing $70 million that was one-half
d. Temporary differences between pretax accounting income and taxable income caused the
e. The
f. Land costing $46 million was acquired by issuing $23 million cash and a 15%, four-year, $23 million note payable to the seller.
g. The right to use a building was acquired with a 15-year lease agreement; present value of lease payments, $82 million. Annual lease payments of $7 million are paid at the beginning of each year starting January 1, 2018.
h. $60 million of bonds were retired at maturity.
i. In February, Arduous issued a 4% stock dividend (4 million shares). The market price of the $5 par value common stock was $7.50 per share at that time.
j. In April, 1 million shares of common stock were repurchased as
Required:
Prepare the statement of cash flows of Arduous Company for the year ended December 31, 2018. Present cash flows from operating activities by the direct method. (A reconciliation schedule is not required.)
Statement of cash flows: This statement reports all the cash transactions which are responsible for inflow and outflow of cash and result of these transactions is reported as ending balance of cash at the end of reported period.
To Prepare: The statement of cash flows of Company A.
Explanation of Solution
Spreadsheet: The spreadsheet is a supplementary device which helps to prepare the adjusting entries and the statement of cash flows easier. The spreadsheet is a working tool of the accountant but it is not a permanent accounting record.
The spreadsheet, for the statement of cash flow analysis, is shown below.
| Company A | ||||
| Spreadsheet for the Statement of Cash Flows | ||||
| Amount in Millions | ||||
| Particulars | December 31,2017 Amount ($) | Changes | December 31,2018 Amount ($) | |
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |||
| Assets | ||||
| Current Assets | ||||
| Cash | $81 | (21) $28 | $109 | |
| Accounts receivable | $194 | (1) $4 | $190 | |
| Investment revenue receivable | $4 | (2) $2 | $6 | |
| Inventory | $200 | (4) $5 | $205 | |
| Prepaid insurance | $8 | (8) $4 | $4 | |
| Long-term investment | $125 | (2) $6 (13) $25 | $156 | |
| Land | $150 | (14) $46* | $196 | |
| Buildings and equipment | $400 | (15) $82* | (10) $70 | $412 |
| Less: Depreciation | ($120) | (10) $35 | (6) $12 | ($97) |
| Patent | $32 | (7) $2 | $30 | |
| Total current assets | $1,074 | $1,211 | ||
| Liabilities and Stockholders’ Equity | ||||
| Liabilities | ||||
| Accounts payable | $65 | (4) $15 | $50 | |
| Salaries payable | $11 | (5) $5 | $6 | |
| Bond interest payable | $4 | (9) $4 | $8 | |
| Income tax payable | $14 | (11) $2 | $12 | |
| Deferred tax liability | $8 | (11) $3 | $11 | |
| Notes payable | $0 | (14) $23* | $23 | |
| Lease liability | $0 | (15) $7 | (15) $82* | $75 |
| Bonds payable | $275 | (16) $60 | $215 | |
| Less: Discount | ($25) | (9) $3 | ($22) | |
| Stockholders’ equity | ||||
| Common Stock | $410 | (17) $20 | $430 | |
| Paid-in capital—excess of par | $85 | (17) $10 | $95 | |
| Preferred stock | $0 | (18) $75 | $75 | |
| Retained Earnings | $227 | (17) $30/ (19) $22 | (12) $67 | $242 |
| Less: Treasury Stock | $0 | (20) $9 | ($9) | |
| Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity | $1,074 | $1,211 | ||
| Income Statement | ||||
| Revenues | ||||
| Sales revenue | (1) $410 | $410 | ||
| Investment revenue | (2) $11 | $11 | ||
| Gain on sale of treasury bills | (3) $2 | $2 | ||
| Expenses | ||||
| Cost of goods sold | (4) $180 | ($180) | ||
| Salaries expense | (5) $73 | ($73) | ||
| Depreciation expense | (6) $12 | ($12) | ||
| Patent amortization expense | (7) $2 | ($2) | ||
| Insurance expense | (8) $7 | ($7) | ||
| Bond interest expense | (9) $28 | ($28) | ||
| Loss on machine damage | (10) $18 | ($18) | ||
| Income tax expense | (11) $36 | ($36) | ||
| Net income | (12) $67 | $67 | ||
| Statement of Cash Flows | ||||
| Operating activities: | ||||
| Cash Inflows: | ||||
| From customers | (1) $414 | |||
| From investment revenue | (2) $3 | |||
| From sale of cash equivalents | (3) $2 | |||
| Cash Outflows: | ||||
| To suppliers of goods | (4) $200 | |||
| To employees | (5) $78 | |||
| For insurance | (8) $3 | |||
| For bond interest | (9) $21 | |||
| For income taxes | (11) $35 | |||
| Net cash flows | $82 | |||
| Investing activities: | ||||
| Sale of machine components | (10) $17 | |||
| Purchase of Long Term investment | (13) $25 | |||
| Purchase of land | (14) $23 | |||
| Net cash flows | ($31) | |||
| Financing activities: | ||||
| Payment on lease liability | (15) $7 | |||
| Retirement of bonds payable | (16) $60 | |||
| Sale of preferred stock | (18) $75 | |||
| Payment of cash dividends | (19) $22 | |||
| Purchase of treasury stock | (20) $9 | |||
| Net cash flows | ($23) | |||
| Net decrease in cash | (21) $28 | $28 | ||
| Total | $1,313 | $1,313 | ||
Table (1)
Operating activities: Operating activities refer to the normal activities of a company to carry out the business. The examples for operating activities are purchase of inventory, payment of salary, sales, and others.
Investing activities: Investing activities refer to the activities carried out by a company for acquisition of long term assets. The examples for investing activities are purchase of equipment, long term investment, sale of land, and others.
Financing activities: Financing activities refer to the activities carried out by a company to mobilize funds to carry out the business activities. The examples for financing activities are purchase of bonds, issuance of common shares, and others.
The spreadsheet of Company A shows the analysis of cash flows in the reporting year 2018.
| Company A | ||
| Statement of Cash Flows | ||
| For year ended December 31, 2018 | ||
| Amount in Millions | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Operating activities: | ||
| Cash Inflows: | ||
| From customers | $414 | |
| From investment revenue | $3 | |
| From sale of cash equivalents | $2 | |
| Cash Outflows: | ||
| To suppliers of goods | ($200) | |
| To employees | ($78) | |
| For insurance | ($3) | |
| For bond interest | ($21) | |
| For income taxes | ($35) | |
| Net cash flows from operating activities | $82 | |
| Investing activities: | ||
| Sale of machine components | $17 | |
| Purchase of Long Term investment | ($25) | |
| Purchase of land | ($23) | |
| Net cash flows from investing activities | ($31) | |
| Financing activities: | ||
| Payment on lease liability | ($7) | |
| Retirement of bonds payable | ($60) | |
| Sale of preferred stock | $75 | |
| Payment of cash dividends | ($22) | |
| Purchase of treasury stock | ($9) | |
| Net cash flows from financing activities | ($23) | |
| Net decrease in cash | $28 | |
| Cash balance, January 1, 2018 | $81 | |
| Cash balance, December 31, 2018 | $109 | |
Table (2)
The statement of cash flows of Company A, shows opening balance of cash flows for the reporting year 2018 as $81 million and the closing balance of cash as $109 million.
Note:
*Non Cash investing activity and financing activity:
- Company A acquired a building on 15 year lease for $82 million.
- Company A acquired a land for $46 million, by:
- Paying Cash of $23 million;
- Issuing 4-year note for $23 million.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
INTERMEDIATE ACCOUNTING (LL) W/CONNECT
- Give correct Answer! If image is blurr or data is unclear then plz comment i will write values or upload a new image. i will give unhelpful if you will use incorrect data.arrow_forwardAbbott Company uses the allowance method of accounting for uncollectible receivables. Abbott estimates that 3% of credit sales will be uncollectible. On January 1, Allowance for Doubtful Accounts had a credit balance of $3,300. During the year, Abbott wrote off accounts receivable totaling $2,100 and made credit sales of $113,000. After the adjusting entry, the December 31 balance in Bad Debt Expense will be .... a. 3300 b. 3390 c. 4590 d. 6690arrow_forwardDo fast answer of this accounting questionsarrow_forward
- Need help with this question solution general accountingarrow_forwardSunshine Blender Company sold 7,000 units in October at a sales price of $40 per unit. The variable cost is $25 per unit. Calculate the total contribution margin. OA. $280,000 OB. $105,000 OC. $87,500 OD. $175,000arrow_forwardI want to correct answer general accounting questionarrow_forward
- Five I + Beginning Work-in-Process Inventory Cost of Goods Manufactured Cost of Goods Sold Direct Labor Direct Materials Used Ending Work-in-Process Inventory Finished Goods Inventory 4 of 35 > manufactured. Use the followin Process Inventory, $32,800; an Total Manufacturing Costs Incurred during Period Total Manufacturing Costs to Account Forarrow_forwardDon't use ai given answer accounting questionsarrow_forwardRequirement 1. For a manufacturing company, identify the following as either a product cost or a period cost: Period cost Product cost a. Depreciation on plant equipment Depreciation on salespersons' automobiles Insurance on plant building Marketing manager's salary Direct materials used Manufacturing overhead g. Electricity bill for human resources office h. Production employee wagesarrow_forward
- I want to correct answer general accounting questionarrow_forwardTungsten, Inc. manufactures both normal and premium tube lights. The company allocates manufacturing over machine hours as the allocation base. Estimated overhead costs for the year are $108,000. Additional estimated information is given below. Machine hours (MHr) Direct materials Normal 23,000 $60,000 Premium 31,000 $480,000 Calculate the predetermined overhead allocation rate. (Round your answer to the nearest cent.) OA. $4.70 per direct labor hour OB. $3.48 per machine hour OC. $2.00 per machine hour OD. $0.20 per direct labor hourarrow_forward< Factory Utilities Indirect Materials Used $1,300 34,500 Direct Materials Used 301,000 Property Taxes on Factory Building 5,100 Sales Commissions 82,000 Indirect Labor Incurred 25,000 Direct Labor Incurred 150,000 Depreciation on Factory Equipment 6,300 What is the total manufacturing overhead?arrow_forward
 Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning


