
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The name of the following alkene is to be determined.
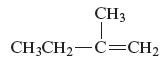
Concept Introduction :
The
(a)
Answer to Problem 163AE
The name of the given alkene is 2 − methyl − 1 butene.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the compound is given as follows:
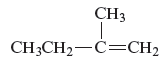
From the above structure, it can be seen that there are four carbon atoms present in the principle chain of the compound and the atoms are bonded with double bond. Hence, the compound is known as alkene. The double bond of the structure is present at the position one that is the lowest possible number. The substituent methyl of the structure is present at second carbon (C2). Therefore, the name of the compound is 2 − methyl − 1 butene. The representation of the carbon position in a structure is given below −
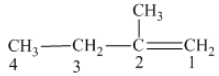
(b)
Interpretation:
The name of the following alkene is to be determined.
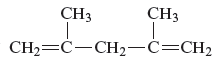
Concept Introduction :
The unsaturated hydrocarbon is a group of hydrocarbons and also known as alkenes or alkynes. They are unsaturated because of the presence of triple or double bonds. Alkynes or hydrocarbons consist of at least one triple bond while alkenes consist of at least one carbon-carbon double bond in the main chain.
(b)
Answer to Problem 163AE
The name of the given alkenes is 2, 4 − dimethyl − 1, 4 − pentadiene.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the given compound is −
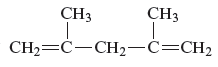
From the above structure, it can be seen that there are five carbon atoms are present in the principle chain of the compound and the atoms are bonded with two double bonds. Hence, the compound is known as alkene. The double of the structure is present at the position one and position four and these are the lowest possible numbers. The methyl substituent of the structure is present at second carbon (C2) and third carbon (C3). Therefore, the name of the compound is 2, 4 − dimethyl − 1, 4 − pentadiene. The representation of the carbon position in a structure is given below −
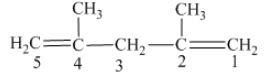
(c)
Interpretation:
The name of the following alkene is to be determined
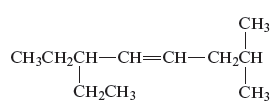
Concept Introduction :
The unsaturated hydrocarbon is a group of hydrocarbons and also known as alkenes or alkynes. They are unsaturated because of the presence of triple or double bonds. Alkynes or hydrocarbons consist of at least one triple bond while alkenes consist of at least one carbon-carbon double bond in the main chain.
(c)
Answer to Problem 163AE
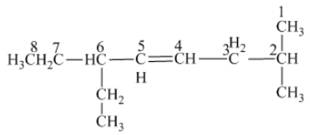
The name of the given alkene is 6 − ethyl − 2 − methyl − 4 octene.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the given compound is −
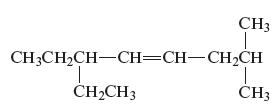
From the above structure, it can be seen that there are eight carbon atoms are present in the principle chain of the compound and there is a double bond in the main chain. Hence, the compound is known as alkene. The substituent ethyl is present at the sixth carbon (C6) atom and the substituent methyl is present at the second carbon atom (C2). Therefore, the name of the compound is 6 − ethyl − 2 − methyl − 4 octene. The representation of the carbon position in a structure is given below −
(d)
Interpretation:
The name of the following alkyne is to be determined.
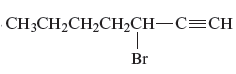
Concept Introduction :
The unsaturated hydrocarbon is a group of hydrocarbons and also known as alkenes or alkynes. They are unsaturated because of the presence of triple or double bonds. Alkynes or hydrocarbons consist of at least one triple bond while alkenes consist of at least one carbon-carbon double bond in the main chain.
(d)
Answer to Problem 163AE
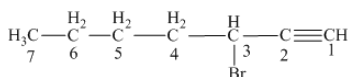
The name of the given alkyne is 3 − bromo-1-heptyne.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the given compound is −
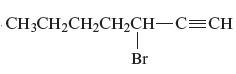
From the above structure, it can be seen that there are seven carbon atoms present in the principle chain of the compound and the atoms are bonded with triple bonds. Hence, the compound is known as alkyne. The triple bond of the structure is present at position one that is lowest possible number. The substituent bromine of the structure is present at third carbon (C3) position. Therefore, the name of the compound is 3 − bromo − 1 − heptyne. The representation of the carbon position in a structure is given below −
(e)
Interpretation:
The name of the following alkyne is to be determined
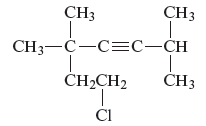
Concept Introduction :
The unsaturated hydrocarbon is a group of hydrocarbons and also known as alkenes or alkynes. They are unsaturated because of the presence of triple or double bonds. Alkynes or hydrocarbons consist of at least one triple bond while alkenes consist of at least one carbon-carbon double bond in the main chain.
(e)
Answer to Problem 163AE
The name of the given alkyne is 7 − chloro − 2, 5,5 − trimethyl − 3 − heptyne.
Explanation of Solution
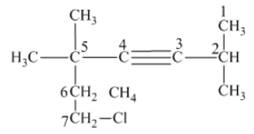
The structure of the given compound is −
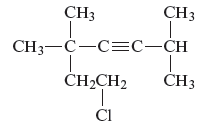
From the above structure, it can be seen that there are six carbon atoms are present in the principle chain of the compound and the atoms are bonded with triple bonds. Hence, the compound is known as alkynes. The triple bond of the structure is present at position three that is lowest possible number. The two methyl substituents of the structure are present at fifth carbon (C5) position and one methyl substituent is present at second carbon (C2) position. The other chlorine substituent is present at seventh carbon position (C7). Therefore, the name of the compound is 7 − chloro − 2, 5,5 − trimethyl − 3 − heptyne. The representation of the carbon position in a structure is given below −
(f)
Interpretation:
The name of the following alkyne is to be determined
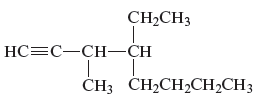
Concept Introduction:
The unsaturated hydrocarbon is a group of hydrocarbons and also known as alkenes or alkynes. This structure is formed because of the presence of triple or double bonds. Alkynes or hydrocarbons consists at least triple bond while alkynes consist at least one carbon-carbon double bon in the main chain.
(f)
Answer to Problem 163AE
The name of the given alkyne is 4 − ethyl − 3 − methyl − 1 − octyne.
Explanation of Solution
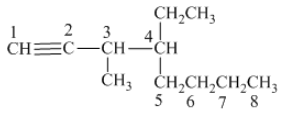
The structure of the given compound is −
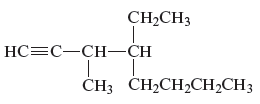
From the above structure, it can be seen that there are eight carbon atoms are present in the principle chain of the compound and the atoms are bonded with triple bonds. Hence, the compound is known as alkynes. The triple bond of the structure is present at position one that is lowest possible number. The methyl substituent of the structure is present at third carbon (C3) position and one ethyl substituent is present at fourth carbon (C4) position. Therefore, the name of the compound is 4 − ethyl − 3 − methyl − 1 − octyne. The representation of the carbon position in a structure is given below −
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
EBK WEBASSIGN FOR ZUMDAHL'S CHEMICAL PR
- Synthesize 2-Ethyl-3-methyloxirane from dimethyl(propyl)sulfonium iodide using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Synthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIf possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forwardSynthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forwardWe mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if (E)-2-butenal and 3-oxo-butanenitrile are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardQuestion 3 (4 points), Draw a full arrow-pushing mechanism for the following reaction Please draw all structures clearly. Note that this intramolecular cyclization is analogous to the mechanism for halohydrin formation. COH Br + HBr Brarrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning  Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning





