
(a)
Interpretation:
The name of the given compound is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
• First, identify the longest carbon chain.
• The next step is to identify the groups attached to the longest chain.
• Identify the position, location, and a number of the substituents bonded to the carbon chain.
• Use prefix di, tri, tetra if the same type of substituents are present.
• Name the substituents in alphabetical order.
Answer to Problem 20.2P
The name of the given compound is
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the given compound is shown below.
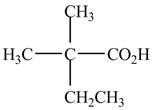
Figure 1
When a compound is named, the first thing is to identify the longest parent chain. If the parent chain is substituted, then it is numbered in such a manner so that the substituent gets the lowest locant number. In the given case, the structure is numbered as shown below.
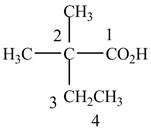
Figure 2
It contains a carboxyl group which is a higher priority
The given compound is named as
(b)
Interpretation:
The name of the given compound is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid is a class of organic compound that contains a
• First, identify the longest carbon chain.
• The next step is to identify the groups attached to the longest chain.
• Identify the position, location, and a number of the substituents bonded to the carbon chain.
• Use prefix di, tri, tetra if the same type of substituents are present.
• Name the substituents in alphabetical order.
Answer to Problem 20.2P
The name of the given compound is
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the given compound is shown as below.
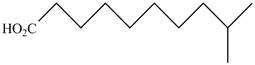
Figure 3
When a compound is named the first thing is to identify the longest parent chain. If the parent chain is substituted, then it is numbered in such a manner so that the substituent gets the lowest locant number. In the given case, the structure is numbered as shown below.
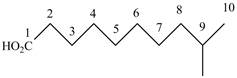
Figure 4
It contains a carboxyl group which is a higher priority functional group. The numbering is started from the carboxyl group. The parent chain is identified as decane. It is monosubstituted at
The given compound is named as
(c)
Interpretation:
The name of the given compound is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid is a class of organic compound that contains a
• First, identify the longest carbon chain.
• The next step is to identify the groups attached to the longest chain.
• Identify the position, location, and a number of the substituents bonded to the carbon chain.
• Use prefix di, tri, tetra if the same type of substituents are present.
• Name the substituents in alphabetical order.
Answer to Problem 20.2P
The name of the given compound is
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the given compound is shown as below.
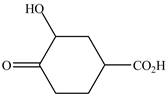
Figure 5
When a compound is named the first thing is to identify the longest parent chain. If the parent chain is substituted, then it is numbered in such a manner so that the substituent gets the lowest locant number. In the given case, the structure is numbered as shown below.
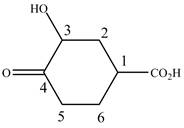
Figure 6
It contains a carboxyl group which is a higher priority functional group. The numbering is started from the carboxyl group. The parent chain is identified as cyclohexane. Cyclohexane is disubstituted at
The given compound is named as
(d)
Interpretation:
The name of the given compound is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid is a class of organic compound that contains a
• First, identify the longest carbon chain.
• The next step is to identify the groups attached to the longest chain.
• Identify the position, location, and a number of the substituents bonded to the carbon chain.
• Use prefix di, tri, tetra if the same type of substituents are present.
• Name the substituents in alphabetical order.
Answer to Problem 20.2P
The name of the given compound is
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the given compound is shown as below.
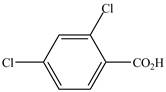
Figure 7
When a compound is named the first thing is to identify the longest parent chain. If the parent chain is substituted, then it is numbered in such a manner so that the substituent gets the lowest locant number. In the given case, the structure is numbered as shown below.
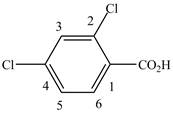
Figure 8
It contains a carboxyl group which is a higher priority functional group. The numbering is started from the carboxyl group. The parent chain is identified as benzene. Benzene is disubstituted at
The given compound is named as
(e)
Interpretation:
The name of the given compound is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid is a class of organic compound that contains a
• First, identify the longest carbon chain.
• The next step is to identify the groups attached to the longest chain.
• Identify the position, location, and a number of the substituents bonded to the carbon chain.
• Use prefix di, tri, tetra if the same type of substituents are present.
• Name the substituents in alphabetical order.
Answer to Problem 20.2P
The name of the given compound is
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the given compound is shown as below.
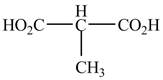
Figure 9
When a compound is named the first thing is to identify the longest parent chain. If the parent chain is substituted, then it is numbered in such a manner so that the substituent gets the lowest locant number. In the given case, the structure is numbered as shown below.
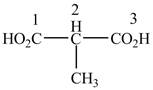
Figure 10
The numbering is started from the carboxyl group since the carboxyl group has higher priority over others. The parent chain is identified as propane. It contains two carboxyl groups named as a propanedioic acid. It is monosubstituted at
The given compound is named as
(f)
Interpretation:
The name of the given compound is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid is a class of organic compound that contains a
• First, identify the longest carbon chain.
• The next step is to identify the groups attached to the longest chain.
• Identify the position, location, and a number of the substituents bonded to the carbon chain.
• Use prefix di, tri, tetra if the same type of substituents are present.
• Name the substituents in alphabetical order.
Answer to Problem 20.2P
The name of the given compound is cyclopropanoic acid..
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the given compound is shown as below.
![]()
Figure 11
When a compound is named the first thing is to identify the longest parent chain. If the parent chain is substituted, then it is numbered in such a manner so that the substituent gets the lowest locant number. In the given case, the structure is numbered as shown below.
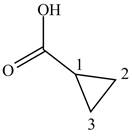
Figure 12
It contains a carboxyl group which is a higher priority functional group. The numbering is started from the carboxyl group. The parent chain is identified as cyclopropane. Therefore the given compound is named as cyclopropanoic acid
The given compound is named as cyclopropanoic acid.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Polymers may be composed of thousands of monomers. Draw three repeat units (trimer) of the polymer formed in this reaction. Assume there are hydrogen atoms there are hydrogen atoms on the two ends of the trimer. Ignore inorganic byproducts please.arrow_forwardi need help with the folarrow_forwardPLEASE HELP NOW! URGENT!arrow_forward
- a. Determine whether each of the Followery Molecules is in the R- On the y- Configuration 1-01"/ 1-6-4 Br 4 I el Br b. Draw The Fisher projection For all the Meso compounds that can exist FOR The Following molenlearrow_forward1- Refer to the monosaccharides below to answer each of the following question(s): CH₂OH CHO CH₂OH CH₂OH 0 H- OH 0 0 HO- H H- -OH HO H HO H H OH HO- H CH₂OH H. OH HO H HO- H CH₂OH CH₂OH CH3 a. Sorbose b. Rhamnose c. Erythrulose d. Xylulose Classify each sugar by type; for example, glucose is an aldohexose. a. Xylulose is .. b. Erythrulose is . c. Sorbose is .. d. Rhamnose is .. 2- Consider the reaction below to answer the following question(s). CHO H OH CH₂OH CH₂OH HO- H HO HO + H. -OH HO OH HO. H OH OH H -OH H OH CH₂OH Q Z a. Refer to Exhibit 25-11. Place a triangle around the anomeric carbon in compound Q. Compound Z is: b. 1. the D-anomer. 2. the a-anomer. 3. the ẞ-anomer. 4. the L-anomer. c. Which anomer is the LEAST stable? d. Q and Z are cyclic examples of: a. acetals b. hemiacetals c. alditols d. hemialditolsarrow_forwardi need help identifying the four carbon oxygen bonds in the following:arrow_forward
- Imagine each of the molecules shown below was found in an aqueous solution. Can you tell whether the solution is acidic, basic, or neutral? molecule HO H3N + The solution is... X O acidic OH O basic H3N-CH-C-O O neutral ○ (unknown) O acidic ○ basic CH2 CH 3-S-CH2 O neutral ○ (unknown) H3N O OH O acidic O basic Oneutral O (unknown) 0 H3N-CH-C-O CH3 CH CH3 O acidic O basic O neutral ○ (unknown) ? olo Ar BHarrow_forwardno Ai walkthroughs need other product (product in picture is wrong dont submit the same thing)arrow_forwardHow to solve this!arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





