
DRAW IT Show where the following antibiotics work: ciprofloxacin, tetracvcline, streptomycin, vancomycin, polymyxin B, sulfanilamide, rifampin, erythromycin.
To review:
Themode of action of given antibiotics in a bacterial cell.
Concept introduction:
The antibiotics can either act as a bacteriostatic (prevent growth of bacteria) or bactericidal (kill bacteria) agents. These drugs with a specific mode of action inhibits the essential biological processes of the target pathogen, including disruption of plasma membrane permeability, inhibition of cell wall, protein and nucleic acid synthesis, and inhibition of essential metabolites synthesis.
Answer to Problem 1R
Correct answer:
| ANTIBIOTICS | MODE OF ACTION |
| Ciprofloxacin | Inhibition of the nucleic acid replication |
| Tetracycline | Inhibition of the protein synthesis |
| Streptomycin | Inhibition of the protein synthesis |
| Vancomycin | Inhibition of the cell wall synthesis |
| Polymyxin B | Injury to the plasma membrane |
| Sulfanilamide | Inhibition of the essential metabolite synthesis |
| Rifampin | Inhibition of the nucleic acid transcription |
| Erythromycin | Inhibition of the protein synthesis |
Explanation of Solution
Diagram:
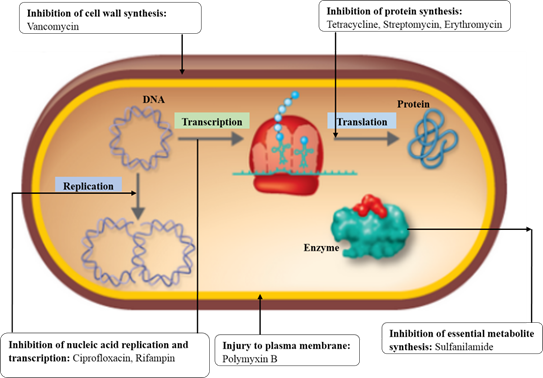
Explanation:
The mechanism of action of the given antibacterial drugs:
Ciprofloxacin – A broad spectrum of the bactericidal agent inhibits the bacterial enzyme DNA gyrase and blocks DNA synthesis. The DNA gyrase is an essential enzyme which is specifically involved in the introduction of negative supercoiling.
Tetracycline – A broad spectrum of the bacteriostatic agent prevents the attachment of aminoacyl tRNA from binding to bacterial 30S ribosome. By binding to the 30S subunit of bacterial ribosome, the tetracycline blocks the association of aminoacyl tRNA with the acceptor site.
Streptomycin – A broad spectrum of the bactericidal agent by acting on 70S ribosome inhibits the protein synthesis. It binds to the 30S subunit of bacterial ribosome and disrupts the protein synthesis (initiation and elongation step).
Vancomycin – A broad spectrum of the antibacterial agent inhibits the assembly of cell wall of bacteria. The N-acetylmuramic acid (NAG) and N-acetylglucosamine (NAM) monomers are the the building blocks of peptidoglycan cell wall. By binding to NAG and NAM, the vancomycin prevents the action of transpeptidase enzyme which is involved in the cross-linking of peptidoglycan.
Polymyxin B – A broad spectrum of the bactericidal agent with a cationic detergent action disrupts the permeability of the plasma membrane.
Sulfanilamide – A broad spectrum of the bacteriostatic agent acts as a competitive inhibitor of p-aminobenzoic acid (PABA). The sulfanilamide with a similar chemical structure competitively prevents the action of PABA and inhibits the folic acid biosynthesis. This arrests the bacterial growth and ultimately results in the elimination of the bacteria.
Rifampin – A broad spectrum of the bactericidal agent specifically inhibits the function of RNA polymerase in the bacteria. Rifampin forms a stable complex with the enzyme, thereby inhibits its activity in the nucleic acid transcription.
Erythromycin – A broad spectrum of the antibacterial agent inhibits the protein synthesis by binding to the bacterial 50S ribosome. It inhibits the activity of peptidyl transferase and intervenes with the amino acid translocation and protein assembly.
The specific site of action of the given antibacterial agents, namely cell wall synthesis (vancomycin), protein synthesis (tetracycline, streptomycin, erythromycin), essential metabolite synthesis (sulfanilamide), nucleic acid synthesis (ciprofloxacin), nucleic acid transcription (rifampin), and plasma membrane integrity (polymyxin B) is shown.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
Microbiology: An Introduction
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Microbiology Fundamentals: A Clinical Approach
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
- A loss of function mutation in Pitx1 enhancers can cause (blank) Removal of Pitx1 exons and growth of ectopic hindlimbs, growth of extra ectopic forelimbs, loss of forelimb specification and development, and loss of hindlimb specification and developmentarrow_forwardHox1a most likely contributes to (blank) patterning in the developing embryo? Ventral, posterior, limb or anteriorarrow_forwardSelect all of the following that can help establish Hox gene expression boundaries (things that affect Hox and not things that Hox affects). Retinoic acid, anterior/posterior axis, fibroblast growth factors, vagal neural crest, and enhancersarrow_forward
- Ectopic expression of Hox often results in (blank) phenotypes. (Blank) transformations are characterized by the replacement of one body part/structure with another. Hoxeotic, homealoneotic, joexotic, or homeoticarrow_forwardWhat's the difference when drawing omega-6 and omega-3?arrow_forward. Consider a base substitution mutation that occurred in a DNA sequence that resulted in a change in the encoded protein from the amino acid glutamic acid to aspartic acid. Normally the glutamic acid amino acid is located on the outside of the soluble protein but not near an active site. O-H¨ A. What type of mutation occurred? O-H B. What 2 types of chemical bonds are found in the R-groups of each amino acid? The R groups are shaded. CH2 CH2 CH2 H2N-C-COOH H2N-C-COOH 1 H Glutamic acid H Aspartic acid C. What 2 types of bonds could each R-group of each of these amino acids form with other molecules? D. Consider the chemical properties of the two amino acids and the location of the amino acid in the protein. Explain what effect this mutation will have on this protein's function and why.arrow_forward
- engineered constructs that consist of hollow fibers are acting as synthetic capillaries, around which cells have been loaded. The cellular space around a single fiber can be modeled as if it were a Krogh tissue cylinder. Each fiber has an outside “capillary” radius of 100 µm and the “tissue” radius can be taken as 200 µm. The following values apply to the device:R0 = 20 µM/secaO2 = 1.35 µM/mmHgDO2,T = 1.67 x 10-5 cm2/secPO2,m = 4 x 10-3 cm/secInstead of blood inside the fibers, the oxygen transport and tissue consumption are being investigated by usingan aqueous solution saturated with pure oxygen. As a result, there is no mass transfer resistance in the synthetic“capillary”, only that due to the membrane itself. Rather than accounting for pO2 variations along the length ofthe fiber, use an average value in the “capillary” of 130 mmHg.Is the tissue fully oxygenated?arrow_forwardMolecular Biology Please help with question. thank you You are studying the expression of the lac operon. You have isolated mutants as described below. In the presence of glucose, explain/describe what would happen, for each mutant, to the expression of the lac operon when you add lactose AND what would happen when the bacteria has used up all of the lactose (if the mutant is able to use lactose).5. Mutations in the lac operator that strengthen the binding of the lac repressor 200 fold 6. Mutations in the promoter that prevent binding of RNA polymerase 7. Mutations in CRP/CAP protein that prevent binding of cAMP8. Mutations in sigma factor that prevent binding of sigma to core RNA polymerasearrow_forwardMolecular Biology Please help and there is an attached image. Thank you. A bacteria has a gene whose protein/enzyme product is involved with the synthesis of a lipid necessary for the synthesis of the cell membrane. Expression of this gene requires the binding of a protein (called ACT) to a control sequence (called INC) next to the promoter. A. Is the expression/regulation of this gene an example of induction or repression?Please explain:B. Is this expression/regulation an example of positive or negative control?C. When the lipid is supplied in the media, the expression of the enzyme is turned off.Describe one likely mechanism for how this “turn off” is accomplished.arrow_forward
- Molecular Biology Please help. Thank you. Discuss/define the following:(a) poly A polymerase (b) trans-splicing (c) operonarrow_forwardMolecular Biology Please help with question. Thank you in advance. Discuss, compare and contrast the structure of promoters inprokaryotes and eukaryotes.arrow_forwardMolecular Biology Please help with question. Thank you You are studying the expression of the lac operon. You have isolated mutants as described below. In the absence of glucose, explain/describe what would happen, for each mutant, to the expression of the lac operon when you add lactose AND what would happen when the bacteria has used up all of the lactose (if the mutant is able to use lactose).1. Mutations in the lac repressor gene that would prevent the binding of lactose2. Mutations in the lac repressor gene that would prevent release of lactose once lactose hadbound3. Normally the lac repressor gene is located next to (a few hundred base pairs) and upstreamfrom the lac operon. Mutations in the lac repressor gene that move the lac repressor gene 100,000base pairs downstream.4. Mutations in the lac operator that would prevent binding of lac repressorarrow_forward
- Essentials of Pharmacology for Health ProfessionsNursingISBN:9781305441620Author:WOODROWPublisher:Cengage
 Microbiology for Surgical Technologists (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781111306663Author:Margaret Rodriguez, Paul PricePublisher:Cengage LearningBasic Clinical Lab Competencies for Respiratory C...NursingISBN:9781285244662Author:WhitePublisher:Cengage
Microbiology for Surgical Technologists (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781111306663Author:Margaret Rodriguez, Paul PricePublisher:Cengage LearningBasic Clinical Lab Competencies for Respiratory C...NursingISBN:9781285244662Author:WhitePublisher:Cengage





