
Concept explainers
The Islander Fishing Company purchases clams for
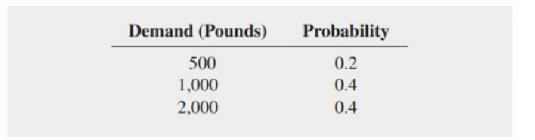
a. For each possible purchase level (500, 1,000, or 2,000 pounds). compute the profit (or loss) for each level of demand.
b. Determine the optimal action based on the maximax criterion.
c. Determine the optimal action based on the maximax criterion.
d. Using the expected monetary value (EMV) criterion, determine the optimal number of pounds of clams the company should purchase from the fishermen. Discuss.
e. Compute the standard deviation for each possible purchase level.
f. Compute the expected opportunity loss (EOL) for purchasing 500, 1,000, and 2,000 pounds of clams.
g. Explain the meaning of the
h. Compute the coefficient of variation for purchasing 500, 1,000, and 2,000 pounds of clams. Discuss.
i. Compute the return-to-risk ratio (RTRR) for purchasing 500, 1,000, and 2,000 pounds of clams. Discuss.
j. Based on (d) and (1). would you choose to purchase 500, 1,000, or 2,000 pounds of claims? Why?
k. Compare the results of (d), (f), (h), and (i) and explain any differences.
l. Suppose that clams can be sold to restaurants for
m. What would he the effect on the results in (a) through (k) if the probability of the demand for 500, 1,000, and 2,000 clams were 0.4, 0.4, and 0.2, respectively?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 20 Solutions
Student Solutions Manual for Basic Business Statistics
- A well-known company predominantly makes flat pack furniture for students. Variability with the automated machinery means the wood components are cut with a standard deviation in length of 0.45 mm. After they are cut the components are measured. If their length is more than 1.2 mm from the required length, the components are rejected. a) Calculate the percentage of components that get rejected. b) In a manufacturing run of 1000 units, how many are expected to be rejected? c) The company wishes to install more accurate equipment in order to reduce the rejection rate by one-half, using the same ±1.2mm rejection criterion. Calculate the maximum acceptable standard deviation of the new process.arrow_forward5. Let X and Y be independent random variables and let the superscripts denote symmetrization (recall Sect. 3.6). Show that (X + Y) X+ys.arrow_forward8. Suppose that the moments of the random variable X are constant, that is, suppose that EX" =c for all n ≥ 1, for some constant c. Find the distribution of X.arrow_forward
- 9. The concentration function of a random variable X is defined as Qx(h) = sup P(x ≤ X ≤x+h), h>0. Show that, if X and Y are independent random variables, then Qx+y (h) min{Qx(h). Qr (h)).arrow_forward10. Prove that, if (t)=1+0(12) as asf->> O is a characteristic function, then p = 1.arrow_forward9. The concentration function of a random variable X is defined as Qx(h) sup P(x ≤x≤x+h), h>0. (b) Is it true that Qx(ah) =aQx (h)?arrow_forward
- 3. Let X1, X2,..., X, be independent, Exp(1)-distributed random variables, and set V₁₁ = max Xk and W₁ = X₁+x+x+ Isk≤narrow_forward7. Consider the function (t)=(1+|t|)e, ER. (a) Prove that is a characteristic function. (b) Prove that the corresponding distribution is absolutely continuous. (c) Prove, departing from itself, that the distribution has finite mean and variance. (d) Prove, without computation, that the mean equals 0. (e) Compute the density.arrow_forward1. Show, by using characteristic, or moment generating functions, that if fx(x) = ½ex, -∞0 < x < ∞, then XY₁ - Y2, where Y₁ and Y2 are independent, exponentially distributed random variables.arrow_forward
- 1. Show, by using characteristic, or moment generating functions, that if 1 fx(x): x) = ½exarrow_forward1990) 02-02 50% mesob berceus +7 What's the probability of getting more than 1 head on 10 flips of a fair coin?arrow_forward9. The concentration function of a random variable X is defined as Qx(h) sup P(x≤x≤x+h), h>0. = x (a) Show that Qx+b(h) = Qx(h).arrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





