
Concept explainers
A thin plate moves between two parallel, horizontal, stationary flat surfaces at a constant velocity of 5 m/s. The two stationary surfaces are spaced 4 cm apart, and the medium between them is filled with oil whose viscosity is
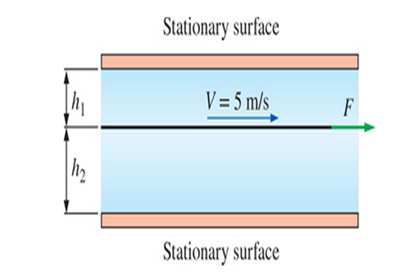
FIGURE P247
The force required maintain motion at
The force on the plate at
Answer to Problem 87P
The force required maintain motion at
The force on the plate at
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The moving velocity of the thin plate is
Write the expression for area of the plate.
Here the length of the plate is
Write the expression for shear force acting on the upper side of the plate.
Here, force acting on the upper side of the plate is
Write the expression for shear force acting on the lower side of the plate.
Here, shear force acting on the lower side of the plate is
Write the expression for force required to maintain the motion
Here force required to maintain the motion is
Write the expression for shear force acting on the upper side of the plate.
Here, force acting on the upper side of the plate is
Write the expression for shear force acting on the lower side of the plate.
Write the expression for force required to maintain the motion
Calculation:
Write the height of the plate from upper surface when the plate is between the mid of the surfaces.
Here, height of the plate from upper surface is
Write the height of the plate from bottom surface when the plate is between the mid of the surfaces.
Here, height of the plate from bottom surface is
Write the height of the plate from upper surface.
Here, the height of the plate from upper surface is
Write the height of the plate from bottom surface.
Here, the height of the plate from bottom surface is
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
The force required maintain motion at
The force on the plate at
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
FLUID MECHANICS FUNDAMENTALS+APPS
- Solve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardreading is 0.4 mas SHOWN. Assume h₁ = 0.4 m, h₂ = 0.5 m. (a) Do you know the specific weight of mercury? (b) Do you know the specific weight of gasoline? (c) Do you know the specific weight of oil? (a) YHg = 133,000 (b) Ygas = 6867 (c) Yoil = 8829 eTextbook and Media Part 2 N/m³ N/m³ N/m³ A+ Gasoline t +B Oil -Mercury Attempts: unlimited Did you calculate the pressure difference between two locations using the correct specific weight? Did you assume that the pressures in fluid are the same in a horizontal plane even though they are in different tubes? Are the calculated pressures in a column of fluid always higher at lower elevations? Did you account for the fact that the two horizontal tubes of the U-tube are above the ground? Concepts: The pressure in a fluid is a function of the specific weight of the fluid and the height relative to a reference. Pressure is constant in a horizontal plane of a continuous mass of fluid. (a) What is the initial pressure difference? (PA-PB) (b) What is…arrow_forward
- Find the solution of the following Differential Equations 1) "-4y+3y=0 3) "+16y=0 2) y"-16y=0 4) y"-y-6y=0 5) y"+2y=0 7) y"+y=0, (#0) 9) y"-y=0, y(0) = 6, y'(0) = -4 11) y"-4y+3y=0, y(0)=-1, 13) y'(0) = -5 "+2y+2y=0 15) y"-9y=0 17) y"-4y=0 6) y"-2y+2y=0 8) "+4y+5y=0 10) y"-9y=0, y(0) = 2, y'(0) = 0 12) y"-3y+2y= 0, y(0)=-1, y'(0) = 0 14) 4y+4y+y=0 16) "+6y+12y=0 18) 4y+4y+17y=0arrow_forwardAccess Pearson Mastering Engineering Back to my courses Course Home Course Home Scoresarrow_forwardAccess Pearson Mastering Engineering Back to my courses Course Home Course Home Scores Review Next >arrow_forward
- Access Pearson Course Home Scoresarrow_forwardAccess Pearson Mastering Engineering Back to my courses Course Home Course Home Scoresarrow_forwardAccess Pearson Mastering Engineering Back to my courses Course Home Course Home Scores ■Review Next >arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





