
Label each region on the periodic table.
- Noble gases
- Period 3
- Group 4A
- s block elements
- alkaline earth elements
- f block elements
transition metals - group 10
(a)
Interpretation:
Theregion of noble gases on the periodic table is to be labeled.
Concept Introduction:
The elements are placed in periodic table according to their atomic numbers. They are arranged in increasing order of atomic numbers systematically. The study of elements and their properties can be done easily as the elements with similar properties fall in the same group.
Answer to Problem 33P
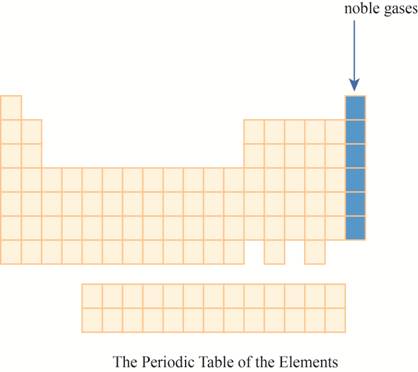
The noble gases are placed on the extreme right column of the periodic table as shown below.
Explanation of Solution
Theelements are organized on the basis of their increasing atomic number in periodic table.
These elements are organized in rows and columns. The rows are known as periods and columns as groups. Each period represents the outermost shell.
The noble gases have their outermost shell fully filled with electrons.Due to fully filled outer atomic orbital, they get the place on extreme right of the periodic table.
The region of noble gases on the periodic table is shown below.
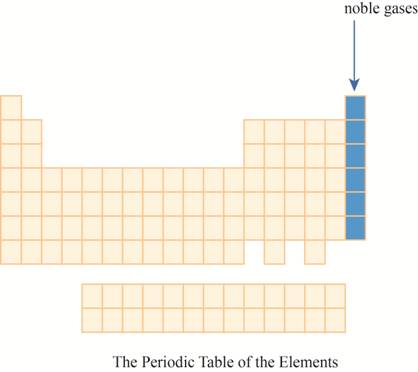
Figure 1
(b)
Interpretation:
The region of period
Concept Introduction:
The elements are placed in periodic table according to their atomic numbers. They are arranged in increasing order of atomic numbers systematically. The study of elements and their properties can be done easily as the elements with similar properties fall in the same group.
Answer to Problem 33P
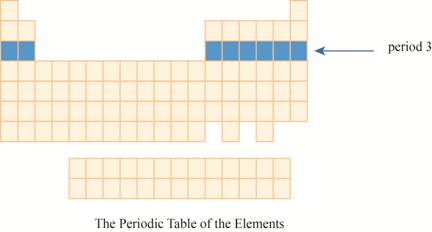
The period
Explanation of Solution
The elements are organized on the basis of their increasing atomic number in periodic table.
These elements are organized in rows and columns. The rows are known as periods and columns as groups. Each period represents the outermost shell. As this outermost shell is filled, the next atom goes to the next row or period.
The third row of the periodic table is known as third period. As the electron goes into third energy level or shell, they are placed in third row. The third shell has two orbitals
These elements are (sodium on the extreme left) to argon (on the extreme right) with atomic numbers,
The region of period
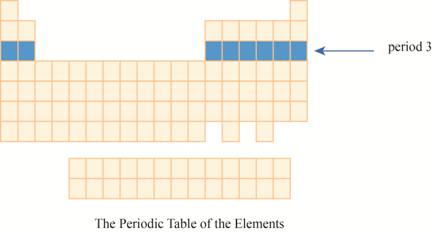
Figure 2
(c)
Interpretation:
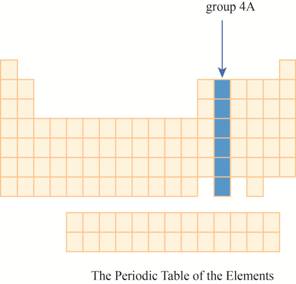
The region of group
Concept Introduction:
The elements are placed in periodic table according to their atomic numbers. They are arranged in increasing order of atomic numbers systematically. The study of elements and their properties can be done easily as the elements with similar properties fall in the same group
Answer to Problem 33P
The group
Explanation of Solution
The elements are organized on the basis of their increasing atomic number in periodic table.
These elements are organized in rows and columns. The rows are known as periods and columns as groups. Each period represents the outermost shell. As this outermost shell is filled the next atom goes to the next row or period.
The transition metals are given place in the middle of the periodic table and to its right, main group elements having valence electrons
The group
It has main group elements, carbon and its family. The region of group
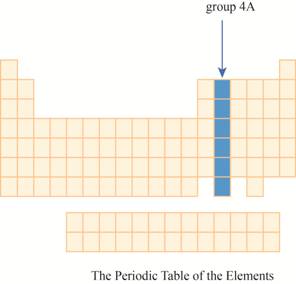
Figure 3
(d)
Interpretation:
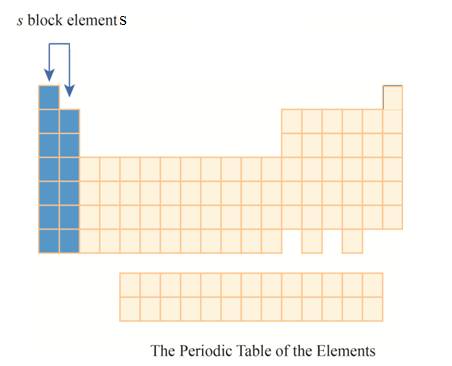
The region of
Concept Introduction:
The elements are placed in periodic table according to their atomic numbers. They are arranged in an increasing order of the atomic numbers systematically. The study of elements and their properties can be done easily as the elements with similar properties fall in the same group
Answer to Problem 33P
The
Explanation of Solution
The elements are organized on the basis of their increasing atomic number in periodic table.
These elements are organized in rows and columns. The rows are known as periods and columns as groups. Each period represents the outermost shell. As this outermost shell is filled the next atom goes to the next row or period.
The
The first column has elements with one electron in their outer
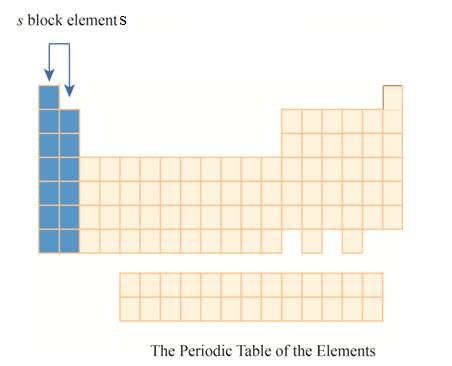
Figure 4
(e)
Interpretation:
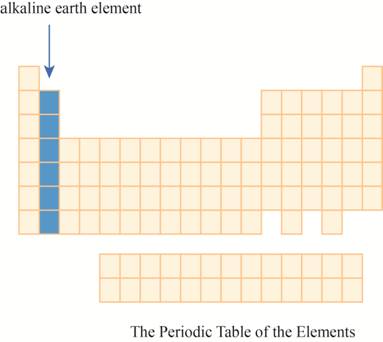
The region of alkaline earth elements on the periodic table is to be labeled.
Concept Introduction:
The elements are placed in periodic table according to their atomic numbers. They are arranged in increasing order of atomic numbers systematically. The study of elements and their properties can be done easily as the elements with similar properties fall in the same group
Answer to Problem 33P
The alkaline earth elements are kept in first two columns on the extreme left of periodic tableas shown below.
Explanation of Solution
The elements are organized on the basis of their increasing atomic number in periodic table.
These elements are organized in rows and columns. The rows are known as periods and columns as groups. Each period represents the outermost shell. As this outermost shell is filled the next atom goes to the next row or period.
These elements have two electrons in their outer
The alkaline earth elements are placed in the second columns on the left of periodic table. The elements of this column has electron in their outer
The region of alkaline earth elements on the periodic table are shown below.
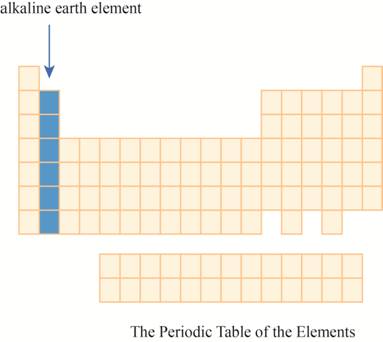
Figure 5
(f)
Interpretation:
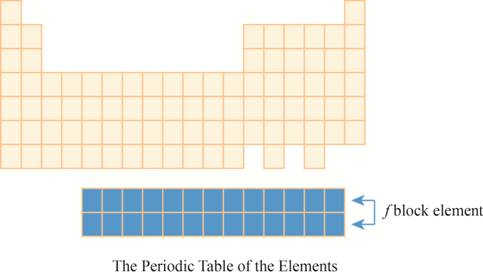
The region of
Concept Introduction:
The elements are placed in periodic table according to their atomic numbers. They are arranged in increasing order of atomic numbers systematically. The study of elements and their properties can be done easily as the elements with similar properties fall in the same group
Answer to Problem 33P
The
Explanation of Solution
The elements are organized on the basis of their increasing atomic number in periodic table.
These elements are organized in rows and columns. The rows are known as periods and columns as groups. Each period represents the outermost shell. As this outermost shell is filled the next atom goes to the next row or period.
The
The placement of these elements below the main periodic table is due to their electronic configuration. The
The region of
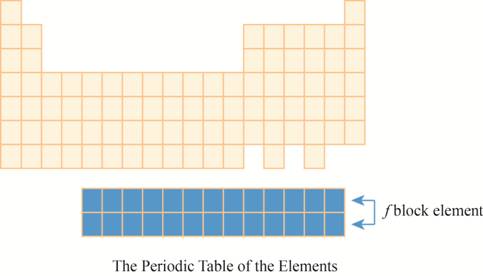
Figure 6
(g)
Interpretation:
The region of transition metals on the periodic table is to be labeled.
Concept Introduction:
The elements are placed in periodic table according to their atomic numbers. They are arranged in increasing order of atomic numbers systematically. The study of elements and their properties can be done easily as the elements with similar properties fall in the same group.
Answer to Problem 33P
The transition metals are kept in ten columns in the middle of the main group elements on the periodic tableas shown below.
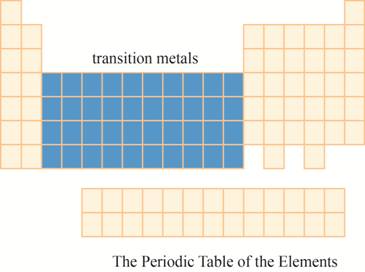
Explanation of Solution
The elements are organized on the basis of their increasing atomic number in periodic table.
These elements are organized in rows and columns. The rows are known as periods and columns as groups. Each period represents the outermost shell. As this outermost shell is filled the next atom goes to the next row or period.
In the transition metals the
The region of transition metals on the periodic table is shown below.
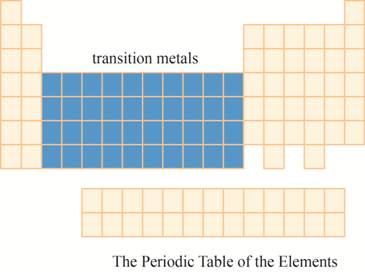
Figure 7
(h)
Interpretation:
The region group
Concept Introduction:
The elements are placed in periodic table according to their atomic numbers. They are arranged in increasing order of atomic numbers systematically. The study of elements and their properties can be done easily as the elements with similar properties fall in the same group.
Answer to Problem 33P
This section has transition element.The region group
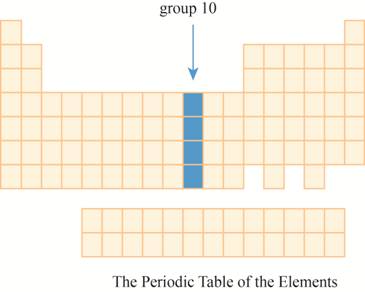
Explanation of Solution
The elements are organized on the basis of their increasing atomic number in periodic table.
These elements are organized in rows and columns. The rows are known as periods and columns as groups. Each period represents the outermost shell. As this outermost shell is filled the next atom goes to the next row or period.
The transition elements' inner shell gets filled. They have the electronic configuration of
The group
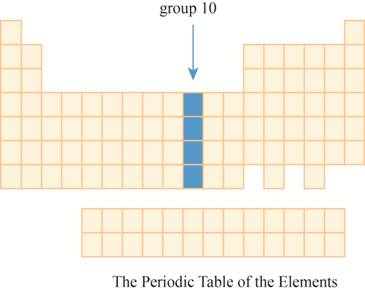
Figure 8
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
GENERAL,ORGANIC, & BIOLOGICAL CHEM-ACCES
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Organic Chemistry
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
- Which representation(s) show polymer structures that are likely to result in rigid, hard materials and those that are likely to result in flexible, stretchable, soft materials?arrow_forward3. Enter the molecular weight of the product obtained from the Williamson Ether Synthesis? OH OH & OH excess CH3l Ag₂Oarrow_forwardPlease answer 1, 2 and 3 on the endarrow_forward
- In the box below, specify which of the given compounds are very soluble in polar aprotic solvents. You may select more than one compound. Choose one or more: NaCl NH4Cl CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CN CH3CH2OH hexan-2-one NaOH CH3SCH3arrow_forwardOn the following structure, select all of the atoms that could ACCEPT a hydrogen bond. Ignore possible complications of aromaticity. When selecting be sure to click on the center of the atom.arrow_forwardRank the compounds below from lowest to highest melting point.arrow_forward
- 18 Question (1 point) Draw the line structure form of the given partially condensed structure in the box provided. :ÖH HC HC H2 ΙΩ Н2 CH2 CH3 CH3 partially condensed formarrow_forwardsomeone else has already submitted the same question on here and it was the incorrect answer.arrow_forwardThe reaction: 2NO2(g) ⇌ N2O4(g) is an exothermic reaction, ΔH=-58.0 kJ/molrxn at 0°C the KP is 58.If the initial partial pressures of both NO2(g) and N2O4(g) are 2.00 atm:A) Is the reaction at equilibrium? If not, what is the value of Q? B) Which direction will the reaction go to reach equilibrium? C) Use an ICE table to find the equilibrium pressures.arrow_forward
- The dissociation of the weak acid, nitrous acid, HNO2, takes place according to the reaction: HNO2 (aq) ⇌ H+(aq) + NO2–(aq) K=7.2 X 10-4 When 1.00 mole of HNO2 is added to 1.00 L of water, the H+ concentration at equilibrium is 0.0265 M.A) Calculate the value of Q if 1.00 L of water is added? B) How will reaction shift if 1.00 L of water is added?arrow_forwardSuppose a certain copolymer elastomeric material “styrene-butadiene rubber”) contains styrene ("S") monomers –(C8H8)– and butadiene ("B") monomers –(C4H6)– and that their numerical ratio S:B = 1:8. What is the mass ratio mS:mB of the two monomers in the material? What is the molecular mass M of a macromolecule of this copolymer with degree of polymerization n = 60,000? Data: AC = 12.01 u, AH = 1.008 u.arrow_forwardLab Questions from Lab: Gravimetric Determination of Calcium as CaC2O4•H2O What is the purpose of the methyl red indicator? Why does a color change to yellow tell you that the reaction is complete? Why is the precipitate rinsed with ice-cold water in step 4? Why not room temperature or hot water? Why is it important that the funnels be placed in a desiccator before weighing (steps 1 and 5)?arrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





