
Label each region on the periodic table.
- Noble gases
- Period 3
- Group 4A
- s block elements
- alkaline earth elements
- f block elements
transition metals - group 10
(a)
Interpretation:
Theregion of noble gases on the periodic table is to be labeled.
Concept Introduction:
The elements are placed in periodic table according to their atomic numbers. They are arranged in increasing order of atomic numbers systematically. The study of elements and their properties can be done easily as the elements with similar properties fall in the same group.
Answer to Problem 2.47P
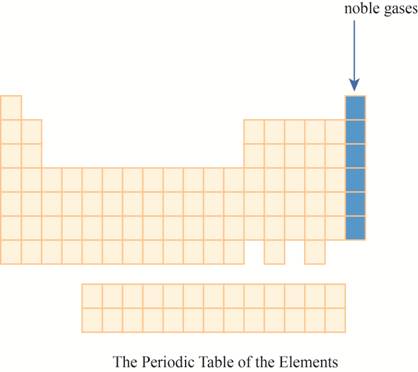
The noble gases are placed on the extreme right column of the periodic table as shown below.
Explanation of Solution
Theelements are organized on the basis of their increasing atomic number in periodic table.
These elements are organized in rows and columns. The rows are known as periods and columns as groups. Each period represents the outermost shell.
The noble gases have their outermost shell fully filled with electrons.Due to fully filled outer atomic orbital, they get the place on extreme right of the periodic table.
The region of noble gases on the periodic table is shown below.
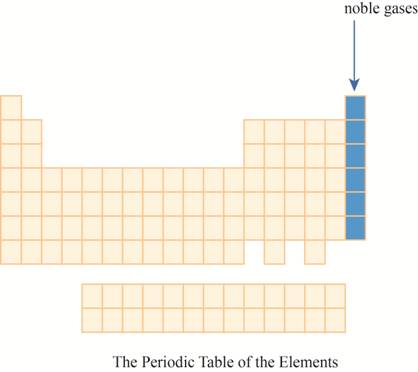
Figure 1
(b)
Interpretation:
The region of period
Concept Introduction:
The elements are placed in periodic table according to their atomic numbers. They are arranged in increasing order of atomic numbers systematically. The study of elements and their properties can be done easily as the elements with similar properties fall in the same group.
Answer to Problem 2.47P
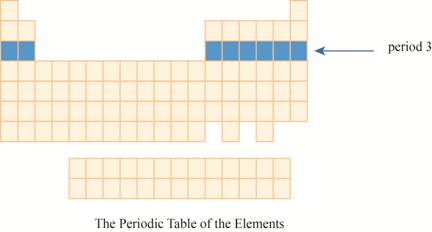
The period
Explanation of Solution
The elements are organized on the basis of their increasing atomic number in periodic table.
These elements are organized in rows and columns. The rows are known as periods and columns as groups. Each period represents the outermost shell. As this outermost shell is filled, the next atom goes to the next row or period.
The third row of the periodic table is known as third period. As the electron goes into third energy level or shell, they are placed in third row. The third shell has two orbitals
These elements are (sodium on the extreme left) to argon (on the extreme right) with atomic numbers,
The region of period
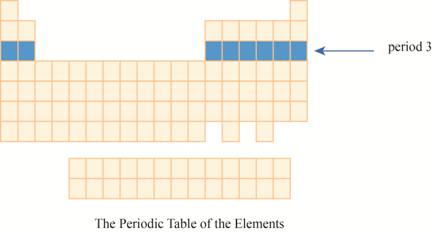
Figure 2
(c)
Interpretation:
The region of group
Concept Introduction:
The elements are placed in periodic table according to their atomic numbers. They are arranged in increasing order of atomic numbers systematically. The study of elements and their properties can be done easily as the elements with similar properties fall in the same group
Answer to Problem 2.47P
The group
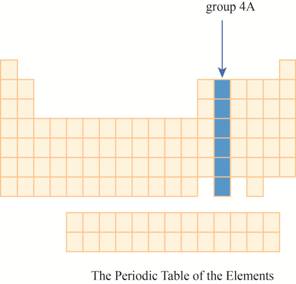
Explanation of Solution
The elements are organized on the basis of their increasing atomic number in periodic table.
These elements are organized in rows and columns. The rows are known as periods and columns as groups. Each period represents the outermost shell. As this outermost shell is filled the next atom goes to the next row or period.
The transition metals are given place in the middle of the periodic table and to its right, main group elements having valence electrons
The group
It has main group elements, carbon and its family. The region of group
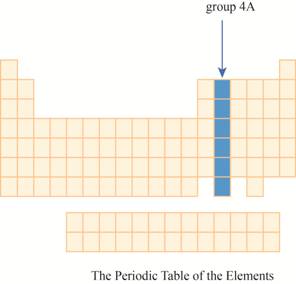
Figure 3
(d)
Interpretation:
The region of
Concept Introduction:
The elements are placed in periodic table according to their atomic numbers. They are arranged in an increasing order of the atomic numbers systematically. The study of elements and their properties can be done easily as the elements with similar properties fall in the same group
Answer to Problem 2.47P
The
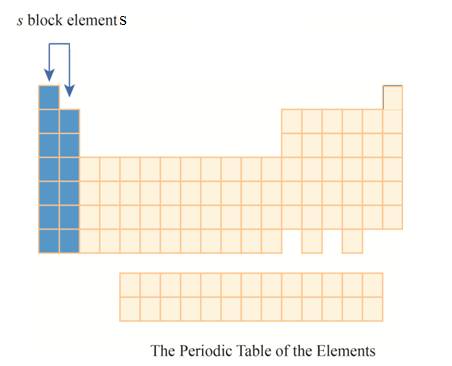
Explanation of Solution
The elements are organized on the basis of their increasing atomic number in periodic table.
These elements are organized in rows and columns. The rows are known as periods and columns as groups. Each period represents the outermost shell. As this outermost shell is filled the next atom goes to the next row or period.
The
The first column has elements with one electron in their outer
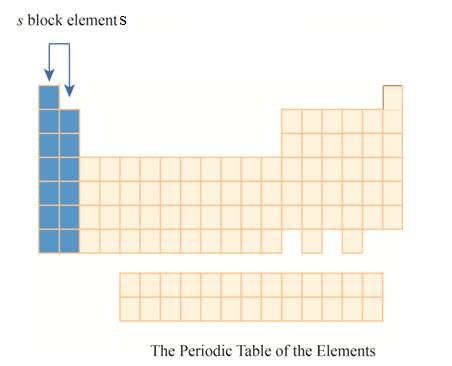
Figure 4
(e)
Interpretation:
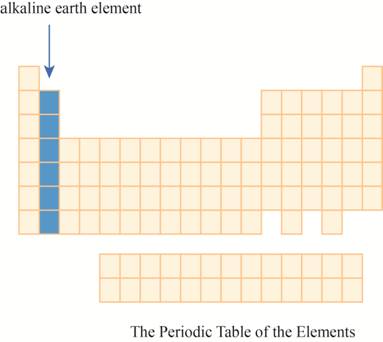
The region of alkaline earth elements on the periodic table is to be labeled.
Concept Introduction:
The elements are placed in periodic table according to their atomic numbers. They are arranged in increasing order of atomic numbers systematically. The study of elements and their properties can be done easily as the elements with similar properties fall in the same group
Answer to Problem 2.47P
The alkaline earth elements are kept in first two columns on the extreme left of periodic tableas shown below.
Explanation of Solution
The elements are organized on the basis of their increasing atomic number in periodic table.
These elements are organized in rows and columns. The rows are known as periods and columns as groups. Each period represents the outermost shell. As this outermost shell is filled the next atom goes to the next row or period.
These elements have two electrons in their outer
The alkaline earth elements are placed in the second columns on the left of periodic table. The elements of this column has electron in their outer
The region of alkaline earth elements on the periodic table are shown below.
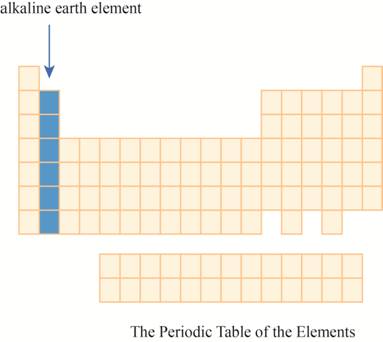
Figure 5
(f)
Interpretation:
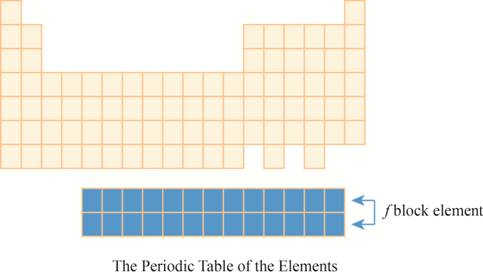
The region of
Concept Introduction:
The elements are placed in periodic table according to their atomic numbers. They are arranged in increasing order of atomic numbers systematically. The study of elements and their properties can be done easily as the elements with similar properties fall in the same group
Answer to Problem 2.47P
The
Explanation of Solution
The elements are organized on the basis of their increasing atomic number in periodic table.
These elements are organized in rows and columns. The rows are known as periods and columns as groups. Each period represents the outermost shell. As this outermost shell is filled the next atom goes to the next row or period.
The
The placement of these elements below the main periodic table is due to their electronic configuration. The
The region of
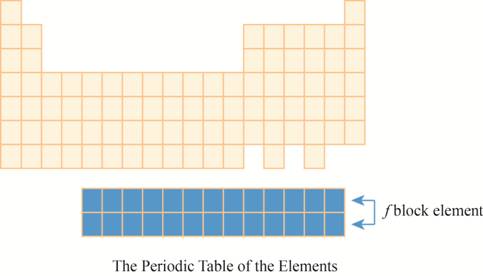
Figure 6
(g)
Interpretation:
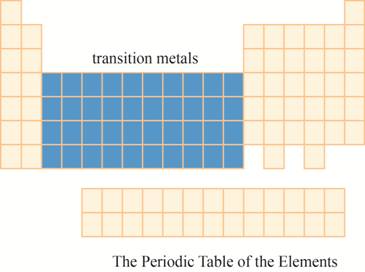
The region of transition metals on the periodic table is to be labeled.
Concept Introduction:
The elements are placed in periodic table according to their atomic numbers. They are arranged in increasing order of atomic numbers systematically. The study of elements and their properties can be done easily as the elements with similar properties fall in the same group.
Answer to Problem 2.47P
The transition metals are kept in ten columns in the middle of the main group elements on the periodic tableas shown below.
Explanation of Solution
The elements are organized on the basis of their increasing atomic number in periodic table.
These elements are organized in rows and columns. The rows are known as periods and columns as groups. Each period represents the outermost shell. As this outermost shell is filled the next atom goes to the next row or period.
In the transition metals the
The region of transition metals on the periodic table is shown below.
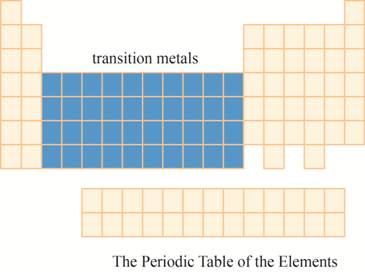
Figure 7
(h)
Interpretation:
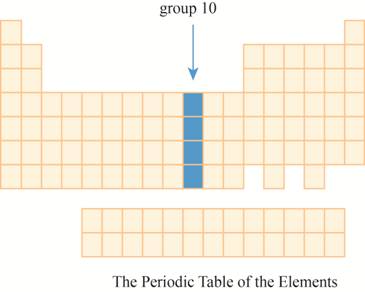
The region group
Concept Introduction:
The elements are placed in periodic table according to their atomic numbers. They are arranged in increasing order of atomic numbers systematically. The study of elements and their properties can be done easily as the elements with similar properties fall in the same group.
Answer to Problem 2.47P
This section has transition element.The region group
Explanation of Solution
The elements are organized on the basis of their increasing atomic number in periodic table.
These elements are organized in rows and columns. The rows are known as periods and columns as groups. Each period represents the outermost shell. As this outermost shell is filled the next atom goes to the next row or period.
The transition elements' inner shell gets filled. They have the electronic configuration of
The group
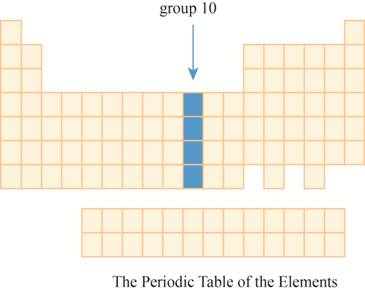
Figure 8
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Organic Chemistry
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
- Q5: Label each chiral carbon in the following molecules as R or S. Make sure the stereocenter to which each of your R/S assignments belong is perfectly clear to the grader. (8pts) R OCH 3 CI H S 2pts for each R/S HO R H !!! I OH CI HN CI R Harrow_forwardCalculate the proton and carbon chemical shifts for this structurearrow_forwardA. B. b. Now consider the two bicyclic molecules A. and B. Note that A. is a dianion and B. is a neutral molecule. One of these molecules is a highly reactive compound first characterized in frozen noble gas matrices, that self-reacts rapidly at temperatures above liquid nitrogen temperature. The other compound was isolated at room temperature in the early 1960s, and is a stable ligand used in organometallic chemistry. Which molecule is the more stable molecule, and why?arrow_forward
- A mixture of C7H12O2, C9H9OCl, biphenyl and acetone was put together in a gas chromatography tube. Please decide from the GC resutls which correspond to the peak for C7,C9 and biphenyl and explain the reasoning based on GC results. Eliminate unnecessary peaks from Gas Chromatography results.arrow_forwardIs the molecule chiral, meso, or achiral? CI .CH3 H₂C CIarrow_forwardPLEASE HELP ! URGENT!arrow_forward
- Identify priority of the substituents: CH3arrow_forwardHow many chiral carbons are in the molecule? OH F CI Brarrow_forwardA mixture of three compounds Phen-A, Acet-B and Rin-C was analyzed using TLC with 1:9 ethanol: hexane as the mobile phase. The TLC plate showed three spots of R, 0.1 and 0.2 and 0.3. Which of the three compounds (Phen-A; Acet-B or Rin-C) would have the highest (Blank 1), middle (Blank 2) and lowest (Blank 3) spot respectively? 0 CH: 0 CH, 0 H.C OH H.CN OH Acet-B Rin-C phen-A A A <arrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





