
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781118230725
Author: David Halliday, Robert Resnick, Jearl Walker
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2, Problem 23P
SSM An electron with an initial velocity v0 = 1.50 ×105 m/s enters a region of length L = 1.00 cm where it is electrically accelerated (Fig. 2-26). It emerges with v = 5.70 ×106 m/s. What is its acceleration, assumed constant?
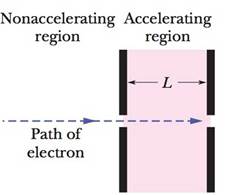
Figure 2-26 Problem 23.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
75. ssm A speed ramp at an airport is basically a large conveyor belt on
which you can stand and be moved along. The belt of one ramp moves at
a constant speed such that a person who stands still on it leaves the ramp
64 s after getting on. Clifford is in a real hurry, however, and skips the
speed ramp. Starting from rest with an acceleration of 0.37 m/s², he cov-
ers the same distance as the ramp does, but in one-fourth the time. What
is the speed at which the belt of the ramp is moving?
14 A proton initially has = 4.01 - 2.0j +
4.0 s later has = -2.0i- 2.0j + 5.0k (in meters per second). For
that 4.0 s, what are (a) the proton's average acceleration aw in unit-
vector notation, (b) the magnitude of av, and (c) the angle between
a and the positive direction of the x axis?
3.0k and then
avg
arg
ave
A particle moves along a horizontal path with a velocity of
v = (31²-61) m/s, where is the time in seconds. If it is initially
located at the origin O, determine the distance traveled in 3.5 s, and the
particle's average velocity and average speed during the time interval.
Chapter 2 Solutions
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Ch. 2 - Figure 2-16 gives the velocity of a particle...Ch. 2 - Figure 2-17 gives the acceleration at of a...Ch. 2 - Figure 2-18 shows four paths along which objects...Ch. 2 - Figure 2-19 is a graph of a particles position...Ch. 2 - Figure 2-20 gives the velocity of a particle...Ch. 2 - At t = 0, a particle moving along an x axis is at...Ch. 2 - Hanging over the railing of a bridge, you drop an...Ch. 2 - The following equations give the velocity vt of a...Ch. 2 - In Fig. 2-22, a cream tangerine is thrown directly...Ch. 2 - Suppose that a passenger intent on lunch during...
Ch. 2 - Figure 2-23 shows that a particle moving along an...Ch. 2 - While driving a car at 90 km/h, how far do you...Ch. 2 - Compute your average velocity in the following two...Ch. 2 - SSM WWW An automobile travels on a straight road...Ch. 2 - A car moves uphill at 40 km/h and then back...Ch. 2 - SSM The position of an object moving along an x...Ch. 2 - The 1992 world speed record for a bicycle...Ch. 2 - Two trains, each having a speed of 30 km/h, are...Ch. 2 - GO Panic escape. Figure 2-24 shows a general...Ch. 2 - ILW In 1 km races, runner 1 on track 1with time 2...Ch. 2 - To set a speed record in a measured straight-line...Ch. 2 - GO You are to drive 300 km to an interview. The...Ch. 2 - Traffic shock wave. An abrupt slowdown in...Ch. 2 - ILW You drive on Interstate 10 from San Antonio to...Ch. 2 - GO An electron moving along the x axis has a...Ch. 2 - GO a If a particles position is given by x = 4 ...Ch. 2 - The position function xt of a particle moving...Ch. 2 - The position of a particle moving along the x axis...Ch. 2 - The position of a particle moving along an x axis...Ch. 2 - SSM At a certain time a particle had a speed of 18...Ch. 2 - a If the position of a particle is given by x =...Ch. 2 - From t = 0 to t = 5.00 min, a man stands still,...Ch. 2 - The position of a particle moving along the x axis...Ch. 2 - SSM An electron with an initial velocity v0 = 1.50...Ch. 2 - Catapulting mushrooms. Certain mushrooms launch...Ch. 2 - An electric vehicle starts from rest and...Ch. 2 - A muon an elementary particle enters a region with...Ch. 2 - An electron has a constant acceleration of 3.2...Ch. 2 - On a dry road, a car with good tires may be able...Ch. 2 - ILW A certain elevator cab has a total run of 190...Ch. 2 - The brakes on your car can slow you at a rate of...Ch. 2 - SSM Suppose a rocket ship in deep space moves with...Ch. 2 - A worlds land speed record was set by Colonel...Ch. 2 - SSM ILW A car traveling 56.0 km/h is 24.0 m from a...Ch. 2 - GO In Fig. 2-27, a red car and a green car,...Ch. 2 - Figure 2-27 shows a red car and a green car that...Ch. 2 - A car moves along an x axis through a distance of...Ch. 2 - Figure 2-29 depicts the motion of a particle...Ch. 2 - a If the maximum acceleration that is tolerable...Ch. 2 - Cars A and B move in the same direction in...Ch. 2 - You are driving toward a traffic signal when it...Ch. 2 - GO As two trains move along a track, their...Ch. 2 - GO You are arguing over a cell phone while...Ch. 2 - GO When a high-speed passenger train traveling at...Ch. 2 - When startled, an armadillo will leap upward....Ch. 2 - SSM WWWa With what speed must a ball be thrown...Ch. 2 - Raindrops fall 1700 m from a cloud to the ground....Ch. 2 - SSMAt a construction site a pipe wrench struck the...Ch. 2 - A hoodlum throws a stone vertically downward with...Ch. 2 - SSM A hot-air balloon is ascending at the rate of...Ch. 2 - At time t = 0, apple 1 is dropped from a bridge...Ch. 2 - As a runaway scientific balloon ascends at 19.6...Ch. 2 - GO A bolt is dropped from a bridge under...Ch. 2 - SSM ILW A key falls from a bridge that is 45 m...Ch. 2 - GO A stone is dropped into a river from a bridge...Ch. 2 - SSM A ball of moist clay falls 15.0 m to the...Ch. 2 - GO Figure 2-35 shows the speed v versus height y...Ch. 2 - To test the quality of a tennis ball, you drop it...Ch. 2 - An object falls a distance h from rest. If it...Ch. 2 - Water drips from the nozzle of a shower onto the...Ch. 2 - GO A rock is thrown vertically upward from ground...Ch. 2 - GO A steel ball is dropped from a buildings roof...Ch. 2 - A basketball player grabbing a rebound jumps76.0...Ch. 2 - GO A drowsy cat spots a flowerpot that sails first...Ch. 2 - A ball is shot vertically upward from the surface...Ch. 2 - Figure 2-15a gives the acceleration of a...Ch. 2 - In a forward punch in karate, the fist begins at...Ch. 2 - When a soccer ball is kicked toward a player and...Ch. 2 - A salamander of the genus Hydromantes capturesprey...Ch. 2 - ILW How far does the runner whose velocitytime...Ch. 2 - Two particles move along an x axis. The position...Ch. 2 - In an arcade video game, a spot is programmed to...Ch. 2 - A rock is shot vertically upward from the edge of...Ch. 2 - GO At the instant the traffic light turns green,...Ch. 2 - A pilot flies horizontally at 1300 km/h, at height...Ch. 2 - GO To stop a car, first you require a certain...Ch. 2 - GO Figure 2-42 shows part of a street where...Ch. 2 - SSM A hot rod can accelerate from 0 to 60 km/h in...Ch. 2 - GO A red train traveling at 72 km/h and a green...Ch. 2 - GO At time t = 0, a rock climber accidentally...Ch. 2 - A train started from rest and moved with constant...Ch. 2 - SSM A particles acceleration along an x axis is a...Ch. 2 - Figure 2-44 gives the acceleration a versus time t...Ch. 2 - Figure 2-45 shows a simple device for measuring...Ch. 2 - A rocket-driven sled running on a straight, level...Ch. 2 - A mining cart is pulled up a hill at 20 km/h and...Ch. 2 - A motorcyclist who is moving along an x axis...Ch. 2 - SSM When the legal speed limit for the New York...Ch. 2 - A car moving with constant acceleration covered...Ch. 2 - SSM A certain juggler usually tosses balls...Ch. 2 - A particle starts from the origin at t = 0 and...Ch. 2 - A rock is dropped from a 100-m-high cliff. How...Ch. 2 - Two subway stops are separated by 1100 m. If a...Ch. 2 - A stone is thrown vertically upward. On its way up...Ch. 2 - A rock is dropped from rest from the top of a...Ch. 2 - SSM An iceboat has a constant velocity toward the...Ch. 2 - A lead ball is dropped in a lake from a diving...Ch. 2 - The single cable supporting an unoccupied...Ch. 2 - Two diamonds begin a free fall from rest from the...Ch. 2 - A ball is thrown vertically downward from the top...Ch. 2 - A parachutist bails out and freely falls 50 m....Ch. 2 - A ball is thrown down vertically with an initial...Ch. 2 - The sport with the fastest moving ball is jai...Ch. 2 - If a baseball pitcher throws a fastball at a...Ch. 2 - A proton moves along the x axis according to the...Ch. 2 - A motorcycle is moving at 30 m/s when the rider...Ch. 2 - A shuffleboard disk is accelerated at a constant...Ch. 2 - The head of a rattlesnake can accelerate at 50...Ch. 2 - A jumbo jet must reach a speed of 360 km/h on the...Ch. 2 - An automobile driver increases the speed at a...Ch. 2 - On average, an eye blink lasts about 100 ms. How...Ch. 2 - A certain sprinter has a top speed of 11.0 m/s. If...Ch. 2 - The speed of a bullet is measured to be 640 m/s as...Ch. 2 - The Zero Gravity Research Facility at the NASA...Ch. 2 - A car can be braked to a stop from the...Ch. 2 - In 1889, at Jubbulpore, India, a tug-of-war was...Ch. 2 - Most important in an investigation of an airplane...Ch. 2 - From January 26, 1977, to September 18, 1983,...Ch. 2 - The wings on a stonefly do not flap, and thus the...Ch. 2 - The position of a particle as it moves along a y...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
3. What is free-fall, and why does it make you weightless? Briefly describe why astronauts are weightless in th...
The Cosmic Perspective (8th Edition)
a. Draw the mechanism for the following reaction if it a involves specific-base catalysis. b. Draw the mechanis...
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Use the key to classify each of the following described tissue types into one of the four major tissue categori...
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
41. What is multiple-allele inheritance? Give an example.
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
Choose the best answer to each of the following. Explain your reasoning. A collision between two large spiral g...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
In a rapidly changing environment, which bacterial population would likely be more successful: one that has ind...
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 25. ssm A jogger accelerates from rest to 3.0 m/s in 2.0 s. A car accelerates from 38.0 to 41.0 m/s also in 2.0 s. (a) Find the acceleration (magnitude only) of the jogger. (b) Determine the acceleration (magnitude only) of the car. (c) Does the car travel farther than the jogger during the 2.0 s? If so, how much farther?arrow_forwardA car uniformly increases it's speed from 40 mi /h to 60 mi/h while going from A to B. Determine the magnitude of it's total acceleration at (a) 120 feet from A (b) 160 ft from A.arrow_forwardThe velocity of a particle moving along a straight line is given by v = 25t²- 80t -200 where v is measured in meters per second and t in seconds. It is given that the object is located 100 m to the left of the origin at t = 0s. Compute velocity when acceleration is zero position(s) the object changes direction.arrow_forward
- A treasure hunter follows a map moving 25 km [N], 37 km [W 37 degrees S], 63 km [E 65 degrees S] and finally 15 km [N 17 degrees E]. If his average for the entire trip was 45 km/hr, calculate: a. The total time for the trip; and b. The average velocity of the triparrow_forward(c) Find, to the nearest metre, the distance between points P and R. A car is travelling on a straight horizontal road. The velocity of the car, vms ', at time t secondsm it travels past three points, P, Q and R, is modelled by the equation -1 v = at +bt+c, where a, b and c are constants. The car passes P at time t = 0 with velocity 8 ms. (a) State the value of c. The car passes Q at time t = 5 and at that instant its deceleration is 0.12 ms2. The car passes R at time t = 18 with velocity 2.96 ms-1. %3D (b) Determine the values of a and b. (e) Find, to the nearest metre, the distance between points P and Rarrow_forwardA man starts walking north at 4f t/s from a point P. Five minutes later a woman starts walking southat 5f t/s from a point 500f t due east of P. At what rate are the people moving apart 15m after the womanstarts walking.arrow_forward
- ▶2/56 The preliminary design for a rapid-transit sys- tem calls for the train velocity to vary with time as shown in the plot as the train runs the 3.2 km between stations A and B. The slopes of the cubic transition curves (which are of form a + bt + ct² + dt³) are zero at the end points. Determine the total run time t between the stations and the maximum acceleration. A 3.2 km U, km/h Cubic functions 130 15 At 15 B B .arrow_forward31. ssm mmh A cart is driven by a large propeller or fan, which can ac- celerate or decelerate the cart. The cart starts out at the position x = 0 m, with an initial velocity of +5.0 m/s and a constant acceleration due to the fan. The direction to the right is positive. The cart reaches a maximum position of x = +12.5 m, where it begins to travel in the negative direc- tion. Find the acceleration of the cart.arrow_forwardA bus drives 40.0 km [E] from town A to town B, then another 30.0 km [N] to town C in a total time of 1.00 h. What are the values of its average speed and average velocity, respectively? a) 70 km/h, 70 km/h [37° S of E] d) 70 km/h, 50 km/h [37° N of E] b) 70 km/h, 50 km/h [37° S of E] e) 50 km/h [37° S of E], 70 km/h c) 50 km/h, 50 km/h [37° S of E] A student in a lab exerts a 25 N force to pull a block a distance of 48 cm. If a total of 10 J of work is done, the angle between the force and the displacement is a) 89° b) 66° c) 61° d) 24° e) none of these A book is at rest on a desk. Which of the following statements concerning the book is correct? a) The book exerts no force on the desk. b) The forces acting on the book are balanced. c) There are no forces acting on the book. d) The desk exerts no force on the book. e) None of the above statements is correct. Consider the following observations: Two point charges (with the same magnitude) are labeled A and B. Charge A is due south of…arrow_forward
- (a) Can a particle moving with instantaneous speed 5.00 m/s on a path with radius of curvature 3.00 m have an acceleration of magnitude 11.00 m/s²? O Yes O No If the answer is yes, explain how it can happen; if the answer is no, explain why not. This answer has not been graded yet. (b) Can it have an acceleration of magnitude 7.00 m/s²? O Yes O No If the answer is yes, explain how it can happen; if the answer is no, explain why not. This answer has not been graded yet. Need Help? Submit Answer Read Itarrow_forwardSituation 3: Two automobile Aand B are approaching each other in adjacent highway lanes. At t=Osec., A and B are 1km apart, their speeds are va = 110kph and v, = 60kph and they are at points P and Q respectively. Knowing that A passes point Q, 40 sec after B was there and that B passes point P, 42 sec. after A was there. (a) Determine the acceleration of A. (b) Determine the speed of B when they pass each other.arrow_forwardTraffic shock wave. An abrupt slowdown in concentratedtraffic can travel as a pulse, termed a shock wave, along theline of cars, either downstream (in the traffic direction) or upstream,or it can be stationary shows a uniformlyspaced line of cars moving at speed v = 25.0 m/s toward a uniformlyspaced line of slow cars moving at speed vs = 5.00 m/s.Assume that each faster car adds length L = 12.0 m (car lengthplus buffer zone) to the line of slow cars when it joins the line, and assumeit slows abruptly at the last instant. (a) For what separation distanced between the faster cars does the shock wave remainstationary? If the separation is twice that amount, what are the (b)speed and (c) direction (upstream or downstream) of the shock wave?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Kinematics Part 3: Projectile Motion; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aY8z2qO44WA;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY