
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Mass number for the given atom need to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The total number of protons in an atom is said to be its
The total number of neutrons and protons of an atom is said to be its mass number. By using the total number of protons and neutrons all the atoms can be identified. Mass number is denoted by “A”.
Atomic number does not change for atoms present in an element while mass number can change due to difference in number of neutrons. These are known as isotopes.
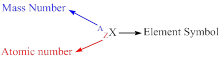
Total number of neutrons present in an atom can be found out of finding the difference between mass number and atomic number.
(b)
Interpretation:
Mass number for the given atom need to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The total number of protons in an atom is said to be its atomic number. By using the total number of protons and neutrons all the atoms can be identified. Atomic number is denoted by “Z”. Atomic number is a characteristic of each and every atom in an element.
The total number of neutrons and protons of an atom is said to be its mass number. By using the total number of protons and neutrons all the atoms can be identified. Mass number is denoted by “A”.
Atomic number does not change for atoms present in an element while mass number can change due to difference in number of neutrons. These are known as isotopes.

Total number of neutrons present in an atom can be found out of finding the difference between mass number and atomic number.
(c)
Interpretation:
Mass number for the given set of atoms needs to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The total number of protons in an atom is said to be its atomic number. By using the total number of protons and neutrons all the atoms can be identified. Atomic number is denoted by “Z”. Atomic number is a characteristic of each and every atom in an element.
The total number of neutrons and protons of an atom is said to be its mass number. By using the total number of protons and neutrons all the atoms can be identified. Mass number is denoted by “A”.
Atomic number does not change for atoms present in an element while mass number can change due to difference in number of neutrons. These are known as isotopes.

Total number of neutrons present in an atom can be found out of finding the difference between mass number and atomic number.
(d)
Interpretation:
Mass number for the given atom need to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The total number of protons in an atom is said to be its atomic number. By using the total number of protons and neutrons all the atoms can be identified. Atomic number is denoted by “Z”. Atomic number is a characteristic of each and every atom in an element.
The total number of neutrons and protons of an atom is said to be its mass number. By using the total number of protons and neutrons all the atoms can be identified. Mass number is denoted by “A”.
Atomic number does not change for atoms present in an element while mass number can change due to difference in number of neutrons. These are known as isotopes.

Total number of neutrons present in an atom can be found out of finding the difference between mass number and atomic number.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 2 Solutions
Chemistry: Atoms First V1
- A mixture of C7H12O2, C9H9OCl, biphenyl and acetone was put together in a gas chromatography tube. Please decide from the GC resutls which correspond to the peak for C7,C9 and biphenyl and explain the reasoning based on GC results. Eliminate unnecessary peaks from Gas Chromatography results.arrow_forwardIs the molecule chiral, meso, or achiral? CI .CH3 H₂C CIarrow_forwardPLEASE HELP ! URGENT!arrow_forward
- Identify priority of the substituents: CH3arrow_forwardHow many chiral carbons are in the molecule? OH F CI Brarrow_forwardA mixture of three compounds Phen-A, Acet-B and Rin-C was analyzed using TLC with 1:9 ethanol: hexane as the mobile phase. The TLC plate showed three spots of R, 0.1 and 0.2 and 0.3. Which of the three compounds (Phen-A; Acet-B or Rin-C) would have the highest (Blank 1), middle (Blank 2) and lowest (Blank 3) spot respectively? 0 CH: 0 CH, 0 H.C OH H.CN OH Acet-B Rin-C phen-A A A <arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co





