
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The density of the electrons in the atom to be calculated.
Concept Introduction:
Atoms: Atoms consist of tiny particles called protons, neutrons and electrons. Proton and neutrons are present in the nucleus and the electron resides around the nucleus. The protons number will be same as the electrons count in the atom.
Nuclear stability: The nucleus is composed of protons and neutrons. The strongest nuclear force binds the particles tightly. Though the protons repel each other due to no attraction between similar charges, possess short-range attractions made the attraction possible between proton and proton, proton and neutron, neutron and neutron.
The stability of any element is determined by the difference between coulombic repulsion and the short-range attraction. If repulsion outweighs the attraction, the disintegration of nucleus occurs by producing the daughter nuclides. If the attractive forces prevail, the nucleus is stable.
(a)
Answer to Problem 2.82QP
The atom consists of concentrated mass called nucleus at the center and surrounded by the electrons.
Explanation of Solution
Every atom contains a nucleus in which all of its positive charge and most of its mass are concentrated is proven by the experiment.
Experiment: Allowing alpha-particles (positively charged) to bombard with the gold foil, expected all the rays to pass through. In contrast, the rays are deflected with angles is observed.
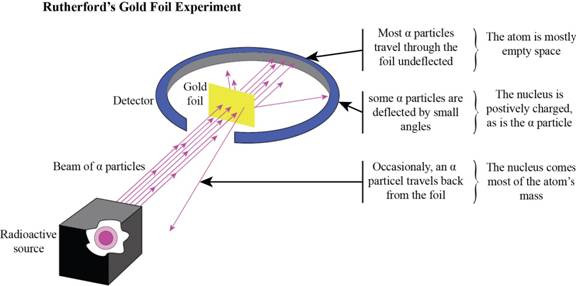
Rutherford’s Experiment evidences about:
- 1. The atom is mostly consist of empty space (due to most of the rays went through the foil).
- 2. Very solid particles; presence of nucleus is revealed by the rays were bounced back.
- 3. The nucleus consist of positive charge is confirmed by the rays deflected at an angle. The similar charges have no attraction and are deflected away.
(b)
Interpretation: The density of the electrons in the atom to be calculated.
Concept Introduction:
Atoms: Atoms consist of tiny particles called protons, neutrons and electrons. Proton and neutrons are present in the nucleus and the electron resides around the nucleus. The protons number will be same as the electrons count in the atom.
Nuclear stability: The nucleus is composed of protons and neutrons. The strongest nuclear force binds the particles tightly. Though the protons repel each other due to no attraction between similar charges, possess short-range attractions made the attraction possible between proton and proton, proton and neutron, neutron and neutron.
The stability of any element is determined by the difference between coulombic repulsion and the short-range attraction. If repulsion outweighs the attraction, the disintegration of nucleus occurs by producing the daughter nuclides. If the attractive forces prevail, the nucleus is stable.
(b)
Answer to Problem 2.82QP
The density of the electrons is
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the density of the nucleus.
Consider, the nucleus is spherical, and the volume of the nucleus is:
In order to calculate the density, the value of volume is must; which is calculated as shown above by considering the nucleus is spherical.
Calculate the density of space occupied by electrons in sodium atom.
To be required: The mass of
The volume occupied by the electron is obtained by the differences between the volume of the atom and volume of nucleus.
The volume of atom is:
Hence, the required terms are sufficient to calculate the density of the electrons:
The density of the electrons is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Chemistry: Atoms First V1
- Predict the major products of this organic reaction. Be sure you use dash and wedge bonds to show stereochemistry where it's important. + ☑ OH 1. TsCl, py .... 文 P 2. t-BuO K Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardConsider this organic reaction: ( Draw the major products of the reaction in the drawing area below. If there won't be any major products, because this reaction won't happen at a significant rate, check the box under the drawing area instead. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Х : а ค 1arrow_forwardIn the drawing area below, draw the major products of this organic reaction: If there are no major products, because nothing much will happen to the reactant under these reaction conditions, check the box under the drawing area instead. 1. NaH 2. CH3Br ? Click and drag to start drawing a structure. No reaction. : ☐ Narrow_forward
- + Predict the major product of the following reaction. : ☐ + ☑ ค OH H₂SO4 Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardConsider this organic reaction: ... OH CI Draw the major products of the reaction in the drawing area below. If there won't be any major products, because this reaction won't happen at a significant rate, check the box under the drawing area instead. ☐ No Reaction. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. : аarrow_forwardConsider the following reactants: Br Would elimination take place at a significant rate between these reactants? Note for advanced students: by significant, we mean that the rate of elimination would be greater than the rate of competing substitution reactions. yes O no If you said elimination would take place, draw the major products in the upper drawing area. If you said elimination would take place, also draw the complete mechanism for one of the major products in the lower drawing area. If there is more than one major product, you may draw the mechanism that leads to any of them. Major Products:arrow_forward
- Draw one product of an elimination reaction between the molecules below. Note: There may be several correct answers. You only need to draw one of them. You do not need to draw any of the side products of the reaction. OH + ! : ☐ + Х Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardFind one pertinent analytical procedure for each of following questions relating to food safety analysis. Question 1: The presence of lead, mercury and cadmium in canned tuna Question 2: Correct use of food labellingarrow_forwardFormulate TWO key questions that are are specifically in relation to food safety. In addition to this, convert these questions into a requirement for chemical analysis.arrow_forward
- What are the retrosynthesis and forward synthesis of these reactions?arrow_forwardWhich of the given reactions would form meso product? H₂O, H2SO4 III m CH3 CH₂ONa CH3OH || H₂O, H2SO4 CH3 1. LiAlH4, THF 2. H₂O CH3 IVarrow_forwardWhat is the major product of the following reaction? O IV III HCI D = III ა IVarrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning





