1 Units, Physical Quantities, And Vectors 2 Motion Along A Straight Line 3 Motion In Two Or Three Dimensions 4 Newton’s Laws Of Motion 5 Applying Newton’s Laws 6 Work And Kinetic Energy 7 Potential Energy And Energy Conservation 8 Momentum, Impulse, And Collisions 9 Rotation Of Rigid Bodies 10 Dynamics Of Rotational Motion 11 Equilibrium And Elasticity 12 Fluid Mechanics 13 Gravitation 14 Periodic Motion 15 Mechanical Waves 16 Sound And Hearing 17 Temperature And Heat 18 Thermal Properties Of Matter 19 The First Law Of Thermodynamics 20 The Second Law Of Thermodynamics 21 Electric Charge And Electric Field 22 Gauss’s Law 23 Electric Potential 24 Capacitance And Dielectrics 25 Current, Resistance, And Electromotive Force 26 Direct-current Circuits 27 Magnetic Field And Magnetic Forces 28 Sources Of Magnetic Field 29 Electromagnetic Induction 30 Inductance 31 Alternating Current 32 Electromagnetic Waves 33 The Nature And Propagation Of Light 34 Geometric Optics 35 Interference 36 Diffraction 37 Relativity 38 Photons: Light Waves Behaving As Particles 39 Particles Behaving As Waves 40 Quantum Mechanics I: Wave Functions 41 Quantum Mechanics Ii: Atomic Structure 42 Molecules And Condensed Matter 43 Nuclear Physics 44 Particle Physics And Cosmology expand_more
2.1 Displacement, Time, And Average Velocity 2.2 Instantaneous Velocity 2.3 Average And Instantaneous Acceleration 2.4 Motion With Constant Acceleration 2.5 Freely Falling Bodies 2.6 Velocity And Position By Integration Chapter Questions expand_more
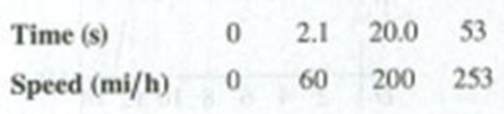
Problem 2.1DQ: Does the speedometer of a car measure speed or velocity? Explain. Problem 2.2DQ: The black dots at the top of Fig. Q2.2 represent a series of high-speed photographs of an insect... Problem 2.3DQ: Can an object with constant acceleration reverse its direction of travel? Can it reverse its... Problem 2.4DQ: Under what conditions is average velocity equal to instantaneous velocity? Problem 2.5DQ: Is it possible for an object to be (a) slowing down while its acceleration is increasing in... Problem 2.6DQ: Under what conditions does the magnitude of the average velocity equal the average speed? Problem 2.7DQ: When a Dodge Viper is at Elwoods Car Wash, a BMW Z3 is at Elm and Main. Later, when the Dodge... Problem 2.8DQ: A driver in Massachusetts was sent to traffic court for speeding. The evidence against the driver... Problem 2.9DQ: Can you have zero displacement and nonzero average velocity? Zero displacement and nonzero velocity?... Problem 2.10DQ: Can you have zero acceleration and nonzero velocity? Use a xt graph to explain. Problem 2.11DQ: Can you have zero velocity and nonzero average acceleration? Zero velocity and nonzero acceleration?... Problem 2.12DQ: An automobile is traveling west. Can it have a velocity toward the west and at the same time have an... Problem 2.13DQ: The officials truck in Fig. 2.2 is at x1 = 277 m at t1 = 16.0 s and is at x2 = 19 m at t2 = 25.0 s.... Problem 2.14DQ: Under constant acceleration the average velocity of a particle is half the sum of its initial and... Problem 2.15DQ: You throw a baseball straight up in the air so that it rises to a maximum height much greater than... Problem 2.16DQ: Prove these statements: (a) As long as you can ignore the effects of the air, if you throw anything... Problem 2.17DQ: A dripping water faucet steadily releases drops 1.0 s apart. As these drops fall, does the distance... Problem 2.18DQ: If you know the initial position and initial velocity of a vehicle and have a record of the... Problem 2.19DQ: From the top of a tall building, you throw one ball straight up with speed 0 and one bal1 straight... Problem 2.20DQ: You run due cast at a constant speed of 3.00 m/s for a distance of 120.0 m and then continue running... Problem 2.21DQ: An object is thrown straight up into the air and feels no air resistance. How can the object have an... Problem 2.22DQ: When you drop an object from a certain height, it takes time T to reach the ground with no air... Problem 2.1E: A car travels in the +x-direction on a straight and level road. For the first 4.00 s of its motion,... Problem 2.2E: In an experiment, a shearwater (a seabird) was taken from its nest, flown 5150 km away, and... Problem 2.3E: Trip Home. You normally drive on the freeway between San Diego and Los Angeles at an average speed... Problem 2.4E: From Pillar to Post. Starting from a pillar, you run 200 m cast (the +x-direction) at an average... Problem 2.5E: Starting from the front door of a ranch house, you walk 60.0 m due east to a windmill, turn around,... Problem 2.6E: A Honda Civic travels in a straight line along a road. The cars distance x from a stop sign is given... Problem 2.7E: CALC A car is stopped at a traffic light. It then travels along a straight road such that its... Problem 2.8E: CALC A bird is flying due east. Its distance from a tall building is given by x(t) = 28.0 m + (12.4... Problem 2.9E: A ball moves in a straight line (the x-axis). The graph in Fig. E2.9 shows this balls velocity as a... Problem 2.10E: A physics professor leaves her house and walks along the sidewalk toward campus. After 5 min it... Problem 2.11E: A test car travels in a straight line along the x-axis. The graph in Fig. E2.11 shows the cars... Problem 2.12E: Figure E2.12 shows the velocity of a solar-powered car as a function of time. The driver accelerates... Problem 2.13E: The Fastest (and Most Expensive) Car! The table shows test data for the Bugatti Veyron Super Sport,... Problem 2.14E: CALC A race car starts from rest and travels east along a straight and level track. For the first... Problem 2.15E: CALC A turtle crawls along a straight line, which we will call the x-axis with the positive... Problem 2.16E: An astronaut has left the International Space Station to test a new space scooter. Her partner... Problem 2.17E: CALC A cars velocity as a function of time is given by x(t) = + t2, where = 3.00m/s and = 0.100... Problem 2.18E: CALC The position of the front bumper of a test car under microprocessor control is given by x(t) =... Problem 2.19E: An antelope moving with constant acceleration covers the distance between two points 70.0 m apart in... Problem 2.20E: BIO Blackout? A jet fighter pilot wishes to accelerate from rest at a constant acceleration of 5g to... Problem 2.21E: A Fast Pitch. The fastest measured pitched baseball left the pitchers hand at a speed of 45.0 m/s.... Problem 2.22E: A Tennis Serve. In the fastest measured tennis serve, the ball left the racquet at 73.14 m/s. A... Problem 2.23E: BIO Automobile Air Bags. The human body can survive an acceleration trauma incident (sudden stop) if... Problem 2.24E: BIO A pilot who accelerates at more than 4g begins to gray out but doesnt completely lose... Problem 2.25E: BIO Air-Bag Injuries. During an auto accident, the vehicles air bags deploy and slow down the... Problem 2.26E: BIO Prevention of Hip Fractures. Falls resulting in hip fractures are a major cause of injury and... Problem 2.27E: BIO Are We Martians? It has been suggested, and not facetiously, that life might have originated on... Problem 2.28E: Entering the Freeway. A car sits on an entrance ramp to a freeway, waiting for a break in the... Problem 2.29E: At launch a rocket ship weighs 4.5 million pounds. When it is launched from rest, it takes 8.00 s to... Problem 2.30E: A cat walks in a straight line, which we shall call the x-axis, with the positive direction to the... Problem 2.31E: The graph in Fig. E2.31 shows the velocity of a motorcycle police officer plotted as a function of... Problem 2.32E: Two cars, A and B, move along the x-axis. Figure F.2.32 is a graph of the positions of A and B... Problem 2.33E: A small block has constant acceleration as it slides down a frictionless incline. The block is... Problem 2.34E: At the instant the traffic light turns green, a car that has been waiting at an intersection starts... Problem 2.35E: (a) If a flea can jump straight up to a height of 0.440 m, what is its initial speed as it leaves... Problem 2.36E: A small rock is thrown vertically upward with a speed of 22.0 m/s from the edge of the roof of a... Problem 2.37E: A juggler throws a bowling pin straight up with an initial speed of 8.20 m/s. How much time elapses... Problem 2.38E: You throw a glob of putty straight up toward the ceiling, which is 3.60 m above the point where the... Problem 2.39E: A tennis ball on Mars, where the acceleration due to gravity is 0.379g and air resistance is... Problem 2.40E: Touchdown on the Moon. A lunar lander is making its descent to Moon Base I (Fig. E2.40). The lander... Problem 2.41E: A Simple Reaction-Time Test. A meter stick is held vertically above your hand, with the lower end... Problem 2.42E: A brick is dropped (zero initial speed) from the roof of a building. The brick strikes the ground in... Problem 2.43E: Launch Failure. A 7500-kg rocket blasts off vertically from the launch pad with a constant upward... Problem 2.44E: A hot-air balloonist, rising vertically with a constant velocity of magnitude 5.00 m/s, releases a... Problem 2.45E: BIO The rocket-driven sled Sonic Wind No. 2, used for investigating the physiological effects of... Problem 2.46E: An egg is thrown nearly vertically upward from a point near the cornice of a tall building. The egg... Problem 2.47E: A 15-kg rock is dropped from rest on the earth and reaches the ground in 1.75 s. When it is dropped... Problem 2.48E: A large boulder is ejected vertically upward from a volcano with an initial speed of 40.0 m/s.... Problem 2.49E: You throw a small rock straight up front the edge of a highway bridge that crosses a river. The rock... Problem 2.50E: CALC A small object moves along the x-axis with acceleration ax(t) = (0.0320 m/s3)(15.0 s t). At t... Problem 2.51E: CALC A rocket starts from rest and moves upward from the surface of the earth. For the first 10.0 s... Problem 2.52E: CALC The acceleration of a bus is given by ax(t) = t, where = 1.2 m/s3. (a) If the buss velocity at... Problem 2.53E: CALC The acceleration of a motorcycle is given by ax(t) = At Bt2, where A = 1.50 m/s3 and B = 0.120... Problem 2.54E: BIO Flying Leap of the Flea. High-speed motion pictures (3500 frames/second) of a jumping, 210-g... Problem 2.55P: BIO A typical male sprinter can maintain his maximum acceleration for 2.0 s. and his maximum speed... Problem 2.56P: CALC A lunar lander is descending toward the moons surface. Until the lander reaches the surface,... Problem 2.57P: Earthquake Analysis. Earthquakes produce several types of shock waves. The most well known are the... Problem 2.58P: A brick is dropped from the roof of a tall building. After it has been falling for a few seconds, it... Problem 2.59P: A rocket carrying a satellite is accelerating straight up from the earths surface. At 1.15 s after... Problem 2.60P: A subway train starts from rest at a station and accelerates at a rate of 1.60 m/s2 for 14.0 s. It... Problem 2.61P: A gazelle is running in a straight line (the x-axis). The graph in Fig. P2.61 shows this animals... Problem 2.62P: Collision. The engineer of a passenger train traveling at 25.0 m/s sights a freight train whose... Problem 2.63P: A ball starts from rest and rolls down a hill with uniform acceleration, traveling 200 m during the... Problem 2.64P: Two cars start 200 m apart and drive toward each other at a steady 10 m/s. On the front of one of... Problem 2.65P: A car and a truck start from rest at the same instant, with the car initially at some distance... Problem 2.66P: You are standing at rest at a bus stop. A bus moving at a constant speed of 5.00 m/s passes you.... Problem 2.67P: Passing. The driver of a car wishes to pass a truck that is traveling at a constant speed of 20.0... Problem 2.68P: CALC An objects velocity is measured to be vx(t) = t2, where = 4.00 m/s and = 2.00 m/s3, At t =... Problem 2.69P: CALC The acceleration of a particle is given by ax(t) = 2.00 m/s2 + (3.00 m/s3)t. (a) Find the... Problem 2.70P: Egg Drop. You are on the roof of the physics building, 46.0 m above the ground (Fig. P2.70). Your... Problem 2.71P: A certain volcano on earth can eject rocks vertically to a maximum height H. (a) How high (in terms... Problem 2.72P: An entertainer juggles balls while doing other activities. In one act, she throws a ball vertically... Problem 2.73P: Look Out Below. Sam heaves a 16-lb shot straight up, giving it a constant upward acceleration from... Problem 2.74P: A flowerpot falls off a windowsill and passes the window of the story below. Ignore air resistance.... Problem 2.75P: Two stones are thrown vertically upward from the ground, one with three times the initial speed of... Problem 2.76P: A Multistage Rocket. In the first stage of a two-stage rocket, the rocket is fired from the launch... Problem 2.77P: During your summer internship for an aerospace company, you are asked to design a small research... Problem 2.78P: A physics teacher performing an outdoor demonstration suddenly falls from rest off a high cliff and... Problem 2.79P: A helicopter carrying Dr. Evil takes off with a constant upward acceleration of 5.0 m/s2. Secret... Problem 2.80P: Cliff Height. You are climbing in the High Sierra when you suddenly find yourself at the edge of a... Problem 2.81P: CALC An object is moving along the x-axis. At t = 0 it has velocity 0x = 20.0 m/s. Starting at time... Problem 2.82P: A ball is thrown straight up from the ground with speed 0. At the same instant, a second ball is... Problem 2.83P: CALC Cars A and B travel in a straight line. The distance of A from the starting point is given as a... Problem 2.84P: DATA In your physics lab you release a small glider from rest at various points on a long,... Problem 2.85P: DATA In a physics lab experiment, you release a small steel ball at various heights above the ground... Problem 2.86P: DATA A model car starts from rest and travels in a straight line. A smartphone mounted on the car... Problem 2.87CP: In the vertical jump, an athlete starts from a crouch and jumps upward as high as possible. Even the... Problem 2.88CP: Catching the Bus. A student is running at her top speed of 5.0 m/s to catch a bus, which is stopped... Problem 2.89CP: A ball is thrown straight up from the edge of the roof of a building. A second ball is dropped from... Problem 2.90PP: BIO BLOOD FLOW IN THE HEART. The human circulatory system is closedthat is. the blood pumped out of... Problem 2.91PP: BIO BLOOD FLOW IN THE HEART. The human circulatory system is closedthat is. the blood pumped out of... Problem 2.92PP: BIO BLOOD FLOW IN THE HEART. The human circulatory system is closedthat is. the blood pumped out of... format_list_bulleted


 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON




