
Concept explainers
The period
Answer to Problem 19.87P
The period
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The length of rod AB and CD is l.
The mass of the gear C is m.
The mass of the gear A is 4m.
The mass of rod AB
Assuming the acceleration due to gravity is g.
Calculation:
Show the position 1 and position 2 of the system with velocity as in Figure (1).
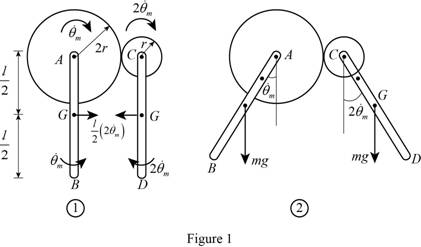
Write the kinematics relations of gear:
Let,
Substitute
For position 1:
Write the expression for centroidal mass moment of inertia gear C
Write the expression for centroidal mass moment of inertia of gear A
Write the expression for centroidal mass moment of inertia of rod AB
Write the expression for centroidal mass moment of inertia of rod CD
Write the expression the velocity of rod AB
Write the expression the velocity of rod CD
Write the expression for the kinetic energy
Substitute m for
Write the expression for the potential energy
For position 2:
Write the expression for the kinetic energy
Write the expression for the displacement
For small oscillation
Write the expression for the displacement
For small oscillation
Write the expression for the potential energy
Substitute
Express the term
Write the expression for the conservation of energy:
Substitute
Substitute
Calculate the period
Substitute
Therefore, the period
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
- Problem Statement A large plate of insulating material 8 cm thick has in it a 3 cm-diam hole, with axis normal to the surface. The temperature of the surroundings are 1800 K at one side of the plate and 400 K on the other side. Insulating plate D= 3 cm H= 8 cm Considering the sides of the hole to be black, (a) Draw a system of resistors that can be used to solve for the various heat transfer rates. For full credit you must label all "voltages", "currents," and resistances present. (b) Estimate the radiative heat transfer through the hole.arrow_forwardUsing MATLAB, plot the unit-step response curve for the following transfer function and Using MATLAB, obtain the rise time, peak time, maximum overshoot, and settling time. Auto Controls Provide codesarrow_forwardUse Routh's stability criterion to determine how many roots with positive real partsthe following equations have Auto Controls Show full solutionsarrow_forward
- Plot the unit step and unit ramp response curve for the following closed loop transferfunction using MATLAB. Indicate clearly the input and output in your plot Auto Controls provide matlab codearrow_forwardUsing a "for loop" in MATLAB program to obtain the unit-step response of thissystem for the following four cases in a single plot What can you observe from the plot? Auto Controls Provide matlab codearrow_forwardProblem 2 (40 Points) A particle of mass m is embedded at a distance a from the center of a massless circular disk of radius r. The disk rolls without slipping down a plane inclined at an angle a with the horizontal. A horizontal force of Ễ = −Fxî + Fyĵ resists motion of the disk down the plane by pushing on the disk at the axle that runs through the center of the disk. a) Find the kinetic energy T. (10 points) b) Find the potential energy V. (10 points) c) Write a position vector to the axle at the center of the wheel in terms of x and y. (10 points) d) Using virtual work, find the applied force Q₁ that would go in Lagrange's Equations. DO NOT WRITE OUT OR SOLVE LAGRANGES'S EQUATIONS. (10 points) x r m e 10 g F α HINTS 1) Consider using the STATIONARY red xy frame a reference frame from which to draw vectors 2) The red xy system DOES NOT move. It is stationary. 3) Consider that the disk rolls a distance of re down the ramparrow_forward
- Draw a counter balance circuit of a vertical cylinder. using counter balance valve and external load.arrow_forwardplease sketch a stress-strain diagram for a typical structural steel in tension and display all of the important features.arrow_forwardProblem 1 (30 Points) Consider the following 2 scenarios. In scenario 1, a mass m slides on a cylindrical surface of radius R. In scenario 2, a mass m hangs at the end of a thin massless rod of length R. In both scenarios, there is no friction either on the surface (scenario 1), or at the pivot point of the pendulum (scenario 2). Also in both scenarios, there is one generalized coordinate, . R Scenario 1 R m R g Scenario 2 m HINT: In both scenarios, it is much easier to choose your datum for potential energy as the center of the bowl (scenario 1), or the pivot point of the pendulum (scenario 2). Part I a) Determine the Lagrangian for each system. DO NOT FIND THE EQUATIONS OF MOTION (5 points) b) What can you say about the systems based on the Lagrangian? (2 points) c) Solve for the equations of motion for both systems. (8 points) Part II Now, for scenario 1, introduce an additional coordinate and treat it as a nonholonomic system to determine the normal force acting on the mass. a)…arrow_forward
- Consider 0.65 kg of N2 at 300 K, 1 bar contained in a rigid tank connected by a valve to another rigid tank holding 0.3 kg of CO2 at 300 K, 1 bar. The valve is opened and gases are allowed to mix, achieving an equilibrium state at 290 K. Determine: (a) the volume of each tank, in m³. (b) the final pressure, in bar. (c) the magnitude of the heat transfer to or from the gases during the process, in kJ. (d) the entropy change of each gas and of the overall system, in kJ/K.arrow_forward(Read Image) (Answer: ω = 1.10 rad/sec CW)arrow_forwardWhat is the configuration of the control loop if steam must be shut down in case of a problem? (I found this question on the internet and was wondering what the answer is) A.Valve is fail open, PIC is direct-acting, TIC is reverse acting, and controller algorithm is feed-forwarding.B. Valve is fail open, PIC is reverse-acting, TIC is direct acting, and controller algorithm is cascade.C. Valve is fail closed, PIC is direct-acting, TIC is reverse acting, and controller algorithm is feed-forward.D. Valve is fail closed, PIC is reverse-acting, TIC is reverse acting, and controller algorithm is cascade.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





