
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The correct name should be given for the incorrectly named organic compound 2,4,6-tribromobenzene.
Concept Introduction:
Nomenclature of benzene and its derivative compounds:
Monosubstituted alkylbenzenes are named as derivatives of benzene; for example butylbenzene.
When one of the special case compounds (example aniline, toluene, phenol) is involved, the compound is named as a derivative of the special compound.
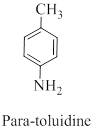
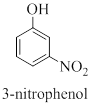
Nomenclature of benzene compound with more substituents,
If one of the substituents imparts a special name, name the molecule as a derivative of that parent.
If none of the substituents imparts a special name, number the substituents to give the smallest set of numbers, and list them in alphabetical order before the ending “benzene”.
Example:
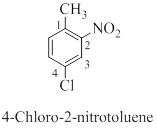
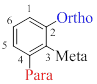
To indicate relative position on a benzene ring, three terms are mainly used and they are,
- (1) Ortho-(o): On adjacent carbons (1,2)
- (2) Meta-(m): Separated by one carbon (1,3)
- (3) Para-(p): Separated by two carbons (1,4)
(b)
Interpretation: The correct name should be given for the incorrectly named organic compound 3-hydroxynitrobenzene.
Concept introduction:
Nomenclature of benzene and its derivative compounds:
Monosubstituted alkylbenzenes are named as derivatives of benzene; for example butylbenzene.
When one of the special case compounds (example aniline, toluene, phenol…) is involved, the compound is named as a derivative of the special compound.
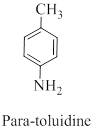

Nomenclature of benzene compound with more substituents,
If one of the substituents imparts a special name, name the molecule as a derivative of that parent.
If none of the substituents imparts a special name, number the substituents to give the smallest set of numbers, and list them in alphabetical order before the ending “benzene”.
Example:
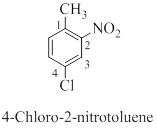
To indicate relative position on a benzene ring, three terms are mainly used and they are,
- (1) Ortho-(o): On adjacent carbons (1,2)
- (2) Meta-(m): Separated by one carbon (1,3)
- (3) Para-(p): Separated by two carbons (1,4)

(c)
Interpretation: The correct name should be given for the incorrectly named organic compound
Concept introduction:
Nomenclature of benzene and its derivative compounds:
Monosubstituted alkylbenzenes are named as derivatives of benzene; for example butylbenzene.
When one of the special case compounds (example aniline, toluene, phenol…) is involved, the compound is named as a derivative of the special compound.
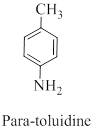

Nomenclature of benzene compound with more substituents,
If one of the substituents imparts a special name, name the molecule as a derivative of that parent.
If none of the substituents imparts a special name, number the substituents to give the smallest set of numbers, and list them in alphabetical order before the ending “benzene”.
Example:
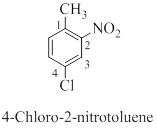
To indicate relative position on a benzene ring, three terms are mainly used and they are,
- (1) Ortho-(o): On adjacent carbons (1,2)
- (2) Meta-(m): Separated by one carbon (1,3)
- (3) Para-(p): Separated by two carbons (1,4)

(d)
Interpretation: The correct name should be given for the incorrectly named organic compound 1,6-dichlorobenzene.
Concept introduction:
Nomenclature of benzene and its derivative compounds:
Monosubstituted alkylbenzenes are named as derivatives of benzene; for example butylbenzene.
When one of the special case compounds (example aniline, toluene, phenol…) is involved, the compound is named as a derivative of the special compound.
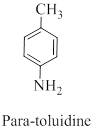

Nomenclature of benzene compound with more substituents,
If one of the substituents imparts a special name, name the molecule as a derivative of that parent.
If none of the substituents imparts a special name, number the substituents to give the smallest set of numbers, and list them in alphabetical order before the ending “benzene”.
Example:
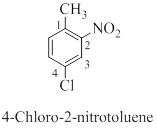
To indicate relative position on a benzene ring, three terms are mainly used and they are,
- (1) Ortho-(o): On adjacent carbons (1,2)
- (2) Meta-(m): Separated by one carbon (1,3)
- (3) Para-(p): Separated by two carbons (1,4)

Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 19 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- In intercalation compounds, their sheets can be neutral or have a negative or positive charge, depending on the nature of the incorporated species and its structure. Is this statement correct?arrow_forwardThis thermodynamic cycle describes the formation of an ionic compound MX2 from a metal element M and nonmetal element X in their standard states. What is the lattice enthalpy of MX2 ? What is the enthalpy formation of MX2 ? Suppose both the heat of sublimation of M and the ionization enthalpy of M were smaller. Would MX2 be more stable? Or less? or impossible to tell without more information?arrow_forward7. Draw the mechanism to describe the following transformation: Note: This is a base catalyzed reaction. So, the last steps must make [OH]- OH [OH]¯ OH Heat Oarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





