
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Course List)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305251052
Author: Michael Cummings
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 19, Problem 25QP
Genomics and Human Evolution
The Denisovan genome contains sequences that originated from an unknown human species. Using Figure 19.11, speculate on which species this might be. Is it possible that there are other ancestral species that may remain to be discovered that would change the phylogeny presented in the figure?
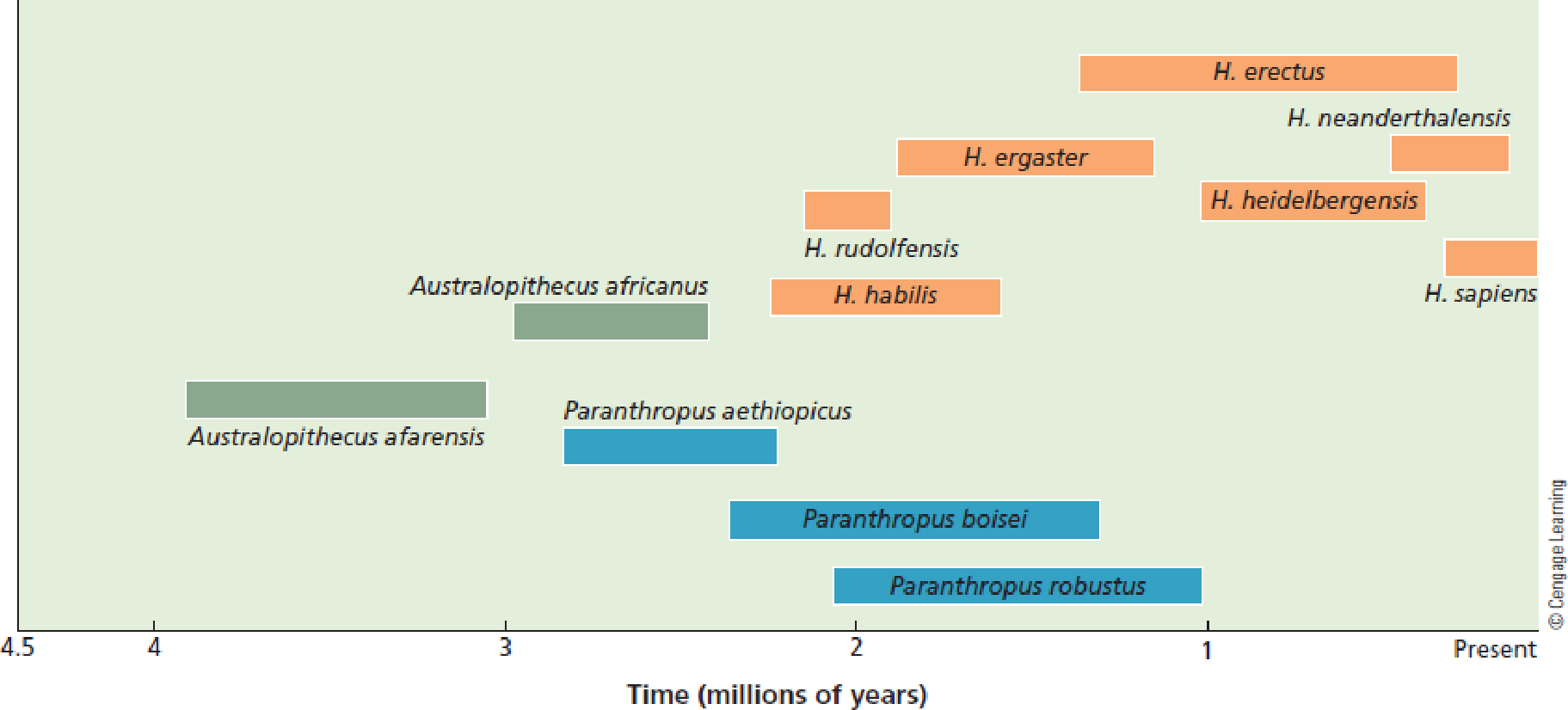
FIGURE 19.11 Estimates for the dates of origin and extinction for the three main groups of hominins (green, blue, and orange). The australopithecines split into two groups about 2.7 million years ago. One of those groups, the genus Homo, contains the ancestors to our species, H. sapiens.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
The hominid evolutionary tree (Figure 20.19)
Sahelanthropus tchadensis
Orrorin tugenensis
Ardipithecus ramidus
Ardipithecus
kadabba
Au. anamensis
Au. garhi
Au. afarensis
Au. africanus
P. boisel
- Homo
Paranthropus
= Australopithecus
= early hominids
= age of fossils
- inferred relationships between
hominid species
-- relationships of major groups
R aethiopicus
P robustus
H. ergaster
H. habilis
H. floresiensis
Hrectus
to
H. neanderthalensis
of hominids
H. heidelbergensis
H sapiens
miocene
pliocene
pleistocene
halocene
7.
5.
1.
millions of years ago
Figure 20.19 Evolutionary reconstruction of hominids; the human family tree. Age ranges of
fossils are shown by red lines, and tan lines represent inferred relationships based on fossil
evidence. Major groups are contained within colored boxes. Au. = Australopithecus; P. =
Paranthropus; H. = Homo.
%3D
%3D
%3D
suggests that the genus Homo evolved a little over 2 million years ago.
is reconstructed based on morphology and estimated age of…
Once nuclear DNA sequencing became fast and able to handle sequencing ancient DNA, living humans were found to have some Neanderthal genes. Is this finding clear evidence that some early modern humans did indeed hybridize with Neanderthals? Why?
20. The ~100 Neanderthal remains from the site Krapina, Czech Republic,
exhibit an abrupt change to a more modern appearance approximately 40,000 ybp, indicating that Neanderthals were completely replaced by Anatomically modern humans.
exhibit a slow transition from Neanderthals to more modern appearance over time.
were all slaughtered by an incoming hoard of Anatomically Modern Homo sapiens.
demonstrate that Neanderthal mitochondrial DNA is not found among any living human populations.
provide evidence for care of the elderly.
Chapter 19 Solutions
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Course List)
Ch. 19.8 - Why dont genetic markers on the Y chromosome...Ch. 19.8 - Prob. 2GRCh. 19 - If you suspected that heterozygous carriers of a...Ch. 19 - If allele frequencies in the hemoglobin gene are...Ch. 19 - Prob. 1QPCh. 19 - How Can We Measure Allele Frequencies in...Ch. 19 - How Can We Measure Allele Frequencies in...Ch. 19 - Prob. 4QPCh. 19 - Prob. 5QPCh. 19 - How Can We Measure Allele Frequencies in...
Ch. 19 - How Can We Measure Allele Frequencies in...Ch. 19 - How Can We Measure Allele Frequencies in...Ch. 19 - Using the HardyWeinberg Law in Human Genetics...Ch. 19 - Prob. 10QPCh. 19 - Using the HardyWeinberg Law in Human Genetics In a...Ch. 19 - Prob. 12QPCh. 19 - Measuring Genetic Diversity in Human Populations...Ch. 19 - Measuring Genetic Diversity in Human Populations...Ch. 19 - Prob. 15QPCh. 19 - Measuring Genetic Diversity in Human Populations...Ch. 19 - Prob. 17QPCh. 19 - Prob. 18QPCh. 19 - Measuring Genetic Diversity in Human Populations...Ch. 19 - Natural Selection Affects the Frequency of Genetic...Ch. 19 - Prob. 21QPCh. 19 - Prob. 22QPCh. 19 - The Evolutionary History and Spread of Our Species...Ch. 19 - Prob. 24QPCh. 19 - Genomics and Human Evolution The Denisovan genome...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The phylogenetic tree for vertebrates depicted below was constructed from sequence data for two rRNA mitochondrial genes (12S and 16S). How do the results of this analysis compare with the phylogenetic trees in Figures 32.10 and 32.24? Identify the major clades of vertebrates on the tree depicted below. Source: R. Zardoya and A. Meyer. 1998. Complete mitochondrial genome suggests diapsid affinities of turtles. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA 95:1422614231. Copyright 1998 National Academy of Sciences, U.S.A.arrow_forwardThe Evolutionary History and Spread of Our Species (Homo sapiens) a. Briefly describe the two major theories discussed in this chapter about the origin of modern humans. b. Which of these two theories would predict a closer relationship for the various modern human populations? c. Which of the two theories is best supported by the genetic evidence?arrow_forward)Approximately how far back in time does the fossil record extend? 3.5 million years 5.0 million years 3.5 billion years 5.0 billion years -) How could the duplication of the Hox gene complex help facilitate animal adaptive radiation? The new gene copies helped facilitate the evolution of more complex body plans. The new gene copies helped facilitate the evolution of smaller bodies. The new gene copies led to lower metabolic rates. It is unlikely that gene duplication events in the Hox complex played a role in the adaptive radiation animals. ) Whatever its ultimate cause(s), the Cambrian explosion is a prime example of mass extinction evolutionary stasis adaptive radiation a large meteor impactarrow_forward
- Homo floresiensis describe the fossil/ DNA etc. and where it comes from. Describe what makes this species different from previously discovered species. Describe one way it changes our understanding of human evolution.arrow_forwardWhen I first studied hominin evolution, they had found "Lucy", an Australopithecus afarensis, and everyone thought her species was an early ancestor of Homo sapien. The picture is much more complicated, with lots of hominins living in close proximity for millions of years...much different than our now singular species. Look at the phylogenetic tree and use it as a guide to briefly describe hominin lines in Africa up to Homo. Do not discuss Homo.Just discuss a sense that you generally can grasp what was going on in Africa with our Genus for 6 or 7 million years!arrow_forwardcreate a phylogeny of human evolution. It should include all known hominids beginning with the earliest and ending with modern Homo sapiens. In your version of a future, humans will create a phylogeny of human evolution. It should include all known hominids beginning with the earliest and ending with modern Homo sapiens and your version of a future human. The requirement is to put the genus and species name of the hominid, beginning with the earliest one, which is Sehelanthropus tchadensis, in the phylogeny along with its dating age.arrow_forward
- Which method provides the most accurate evidence for scientists to use when determining evolutionary relationships between two species of animals? identifying fossil patterns in rock strata where the animals live looking for similarities in the coloration and eating habits of the animals looking for similar vestigial structures in both species of animals comparing genetic sequences in the animals using samples of DNA 0000.arrow_forwardSpecies Embryo (A-F) Describe the Anatomical Changes from Early to Late Stages Human Chicken Rabbit Tortoise Salamander В Fish A Guide Questions: 1. Look again at the six embryos in their earliest stages. Describe the patterns you see. What physical similarities exist between each of the embryos? 2. Does this suggest an evolutionary relationship? Explain how these embryos can be used as evidence of a common ancestor between each of these six organisms.arrow_forwardA transitional fossil with traits intermediates between turtles and crocodilians Fossil evidence that the carapace (shell) of turtles is an exaptation Ankle bones from extinct turtles More DNA data from living turtles All of the optionsarrow_forward
- 43. Which of the following recent fossil discoveries dating between 4.4 – 5.8 mya was clearly bipedal as reflected by features of the hip and thigh bone, but still had long, curved toes and an opposable big toe set off to the side (i.e., with a saddle joint like a thumb), leading human paleontologists to suggest that the fossil species is relatively close to our last common ancestor with other African apes? Orrorin tugenensis Archaic Homo sapiens Homo sapiens neanderthalensis Homo habilis Homo erectusarrow_forwardEvolution in Humans 1) explain how fossil evidence is used to reconstruct the hominid history 2) explain how genetic evidence is used to document changes in species and populations over time 3) describe several techniques that paleontologists today use to establish fossil agearrow_forwardThe phylogenetic tree for 12 cat species (Felidae) reproduced at right was assembled from molecular sequence data. Which species is the domestic cats closest relative? Which clade is the sister taxon to tigers? Are bobcats more closely related to cougars or to ocelots? Source: From Warren E. Johnson et al. 2006. The late Miocene radiation of modern Felidae: A genetic assessment. Science 311:7377.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...
Biology
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781337392938
Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:Cengage Learning
The Evolution of Populations: Natural Selection, Genetic Drift, and Gene Flow; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SRWXEMlI0_U;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
The Evolution of Humans | Evolution | Biology | FuseSchool; Author: FuseSchool - Global Education;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Vf_dDp7drFg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY