
(a)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Chromic acid will oxidize a primary alcohol to a
Answer to Problem 19.56P
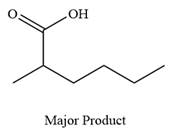
The product of the given reaction is
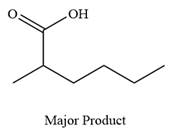
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
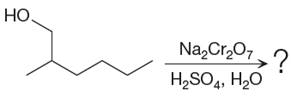
This is an example of an oxidation of a primary alcohol using sodium dichromate in aqueous acid. Chromic acid oxidizes a primary alcohol into corresponding carboxylic acid. The reaction is shown below:
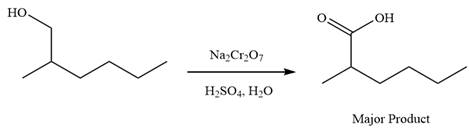
Thus, carboxylic acid is the major product of the reaction.
Chromic acid oxidizes a primary alcohol into corresponding carboxylic acid.
(b)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Chromic acid will oxidize a primary alcohol to a carboxylic acid or a secondary alcohol to a ketone. Chromic acid is prepared by dissolving sodium dichromate in an acidic solution.
Answer to Problem 19.56P
The product of the given reaction is
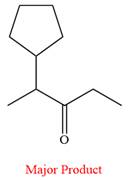
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
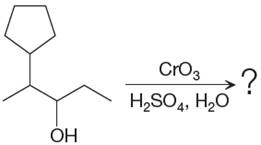
This is an example of an oxidation of a secondary alcohol using chromium trioxide in aqueous acid. Chromic acid oxidizes a secondary alcohol into corresponding ketone. The reaction is shown below:
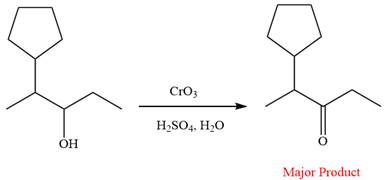
Thus, ketone is the major product of the reaction.
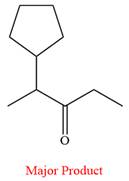
Chromic acid oxidizes a secondary alcohol into corresponding ketone.
(c)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Chromic acid will oxidize a primary alcohol to a carboxylic acid or a secondary alcohol to a ketone. Chromic acid is prepared by dissolving sodium dichromate in an acidic solution. Oxidation of chromic acid requires an
Answer to Problem 19.56P
There is no product of the given reaction, as chromic acid cannot oxidize tertiary alcohols.
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
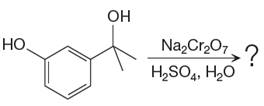
This is an example of an oxidation of a secondary alcohol using chromium trioxide in aqueous acid. Chromic acid oxidizes a secondary alcohol into corresponding ketone. Oxidation of chromic acid requires an
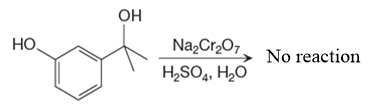
There is no product of the given reaction, as chromic acid cannot oxidize tertiary alcohols.
Chromic acid cannot oxidize tertiary alcohols as in tertiary alcohols carbon atom which is attached to the hydroxyl group does not have any hydrogen atom attached.
(d)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Chromic acid will oxidize a primary alcohol to a carboxylic acid or a secondary alcohol to a ketone.
Answer to Problem 19.56P
The product of the given reaction is
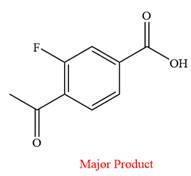
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
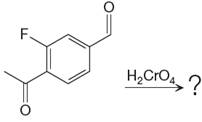
This is an example of an oxidation reaction using chromic acid. The reactant molecule has both an aldehyde and a ketone group. Chromic acid oxidizes an aldehyde group into carboxylic acid but is not a sufficiently strong oxidizing agent to oxidize ketones.
The reaction is shown below:
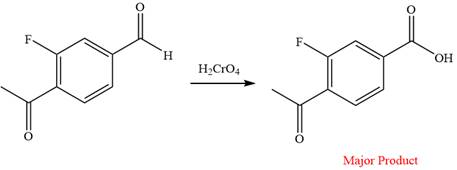
Thus, a carboxylic acid is the major product of the reaction.
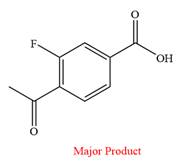
Chromic acid oxidizes an aldehyde to corresponding carboxylic acid but cannot oxidize a ketone.
(e)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Like chromic acid, potassium permanganate is also used as an oxidizing agent. When treated with a basic solution of potassium permanganate (
Answer to Problem 19.56P
The product of the given reaction is
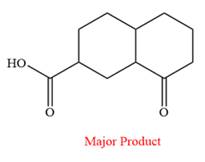
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
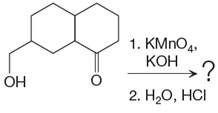
This is an example of an oxidation reaction using potassium permanganate. Like chromic acid, potassium permanganate is also used as an oxidizing agent. When treated with a basic solution of potassium permanganate (
The reaction is shown below:
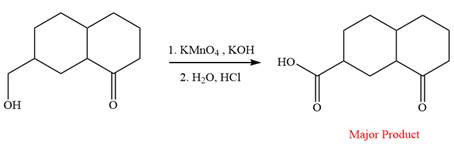
Thus, the major product of the given reaction is

When treated with a basic solution of potassium permanganate (
(f)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) is a partial oxidizing agent. Oxidation of a primary alcohol by pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) stops at the aldehyde because the reaction takes place in a nonaqueous medium. Pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) oxidizes a primary alcohol to an aldehyde and a secondary alcohol to a ketone.
Answer to Problem 19.56P
The product of the given reaction is
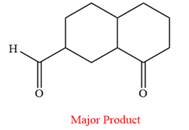
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
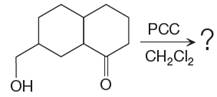
This is an example of an oxidation reaction using pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC). Like othe oxidizing agents, pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) oxidizes a primary alcohol to an aldehyde and a secondary alcohol to a ketone.
The reaction is shown below:
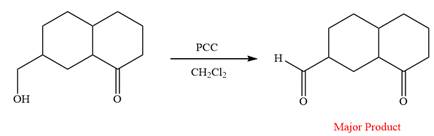
Thus, the major product of the given reaction is
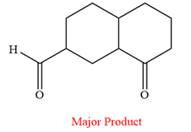
Pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) oxidizes a primary alcohol to an aldehyde and a secondary alcohol to a ketone.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
ORG CHEM W/ EBOOK & SW5 + STUDY GUIDE
- Recent advancements in liquid chromatography include the development of ultrahigh pressure liquid chromatography (UHPLC) and an increased use of capillary columns that had previously only been used with gas chromatography. Both of these advances have made the development of portable LC systems possible. For example, Axcend Corp. makes a portable system that uses a capillary column with an internal diameter of 150-μm-that is packed with 1.7-um stationary phase particles. In contrast, a traditional LC column has a 4.6 mm internal diameter and utilizes 5-um stationary phase particles. a) Explain one advantage that is afforded by the use of a capillary column in liquid chromatographic separation. Explain one disadvantage of capillary columns. b) Explain how the use of smaller stationary phase particles can improve the resolution of a separation. Include any relevant equations that support your explanation. c) A scientist at Rowan University is using the Axcend LC to conduct analyses of F…arrow_forwardThis paper describes the use of fullerene molecules, also known as buckyballs, as a stationary phase for liquid chromatography. The performance of the fullerene-modified stationary phase (FMS) is compared to that of a more common C18 stationary phase and to two other carbon-based stationary phases, PGC and COZ. A. 10A OM B. - Figure 1. Idealized drawing of the cross-section of a pore inside a silica particle, showing the relative densities of aminopropylsilyl (red/green) and fullerene (blue) groups: (A) full cross- section; (B) detailed view of covalent bonding of fullerene to the silica surface. Surface densities of silyl and fullerene groups were inferred from elemental composition results obtained at each stage of the synthesis (see Table 1). Absorbance (mAU, 220 nm) 700 600 500 400 300 200 100 a. Define selectivity, a, with words and an equation. b. Explain how the choice of stationary phase affects selectivity. c. Calculate the resolution of the nitrobenzene and toluene peaks in…arrow_forwardNormalized Intensity (a. u.) 0.5 1.0 A 3D-printed GC column (shown below) was created for use with "micro" gas chromatography applications. To prove its utility, it was used to separate a mixture of alkanes (C9-C18, C22, C24). For the separation shown below, the column temperature was ramped from 40 °C to 250 °C at a rate of 30 °C per minute. (a) 9 10 = 1 mm 12 13 15 22 0.0 0 100 200 300 400 Time (sec) a) What detector would you use for this analysis? Justify your selection. b) Explain how the chromatogram would change if the separation was run isothermally. c) Explain how the chromatogram would change if the temperature ramp were increased to 50 °C per minute.arrow_forward
- Devise a synthesis of each compound from the indicated starting material. You may also use any organic compounds with one or two carbons and any needed inorganic reagents. a. Brarrow_forwardPlease help me with #2b & #3 using the data.arrow_forwardHeparin is used as an anti-coagulant. A risk of heparin use is thrombocytopenia, or low platelet count. This risk is minimized with the use of low molecular weight heparins (LMWH), therefore it is desirable to separate LMWH from higher molecular weight heparins. The method of choice to do this is molecular exclusion chromatography. Below is a chromatogram from a molecular exclusion chromatographic run. Peaks ranging from A to J are clearly distinguishable. The heparin mixture that was analyzed had anywhere from 6 to 30 repeat units of monomer (where the heparin with 30 repeat units would be roughly five times the size of the heparin with six repeat units). a. Which letter most likely represents the peak with 6 repeat units given these heparin polymers were separated with molecular exclusion chromatography? b. Explain your reasoning describing the mechanism of retention in molecular exclusion chromatography. 100 80 60 60 Relative Abundance 40 40 E GH 20 20 B A 36 38 40 42 44 46 48 50 50…arrow_forward
- HELP NOW PLEASE ! ASAP! URGENT!arrow_forwardHELP NOW PLEASE ! ASAP! URGENT!arrow_forwardDraw a Newman projection for the molecule below from the perspective indicated. Which of the groups (letters A-H) are methyl groups? CH3 H H H A H B ☑ >> H. ABCDEFG I H -H CH3 G D CH F E Numeric 4 points How many gauche interactions exist in the conformation shown in the previous problem? 1arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





