
(a)
Interpretation:
The major advantage and disadvantages of two dimensional NMR methods over conventional one-dimensional techniques are to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy is a method used to determine the physical and chemical nature of atoms in different compounds. In two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy information about atoms is plotted in two frequency axes.
Answer to Problem 19.42QAP
The major advantage of two dimensional NMR method is that chemical shift and coupling constants are obtained and disadvantage is the complex analysis of two dimensional NMR method.
Explanation of Solution
The advantages and disadvantages of two dimensional NMR methods over conventional one-dimensional techniques are as mentioned below.
| S. No. | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| 1 | One dimensional NMR gives information about simple organic compounds while two dimensional NMR gives information about complex organic compounds. | The two dimensional NMR consists of different phases of cross and diagonal peak multi-pet. |
| 2 | Two dimensional NMR gives information about the chemical shift, coupling constant and signals of compounds. | The analysis of two dimensional NMR is complex as compared to one dimensional NMR. |
| 3 | The spectrum of complex compounds like proteins, heterocyclic compounds can only found by two dimensional NMR. | The intense peak may get obscured by cross-peaks in two dimensional NMR. |
(b)
Interpretation:
The pulse sequence used in COSY and HETCOR experiments and behavior of magnetization vector
Concept introduction:
The structure of heterocyclic complex compounds is determined by two dimensional NMR. The two dimensional NMR involves the techniques COSY and HETCOR. In the HETCOR experiment, the behavior of a single bond between two different nucleoli is observed. The COSY experiment interprets the resonance of correlating protons when there is spin-spin bond coupling in protons.
Answer to Problem 19.42QAP
The pulse sequence used in COSY and HETCOR experiments explains the single bond coupling between two different nucleoli and resonance in the compound. The magnetizing behavior of vector
Explanation of Solution
The COSY and HETCOR are two pulse sequence experiments. There is an evolution period between two pulses. The evolution period is the difference between time periods of pulses. In the chemical shift, coupling constant arises between this evolution period. The COSY and HETCOR experiments give the spectrum of the complex compound. The two pulses are applied with some time duration on a sample of the compound. This process is applied again after the sample of the compound achieves equilibrium. The spectrum of a compound is obtained by repeating this process several times. The chemical shift, coupling constant and signals are obtained by analyzing the spectrum.
The behavior of the magnetization, vector
(c)
Interpretation:
The identification of resonances in
Concept introduction:
The resonances in the compound are found by the spectrum of the compound.
Answer to Problem 19.42QAP
The resonances in atom
Explanation of Solution
The resonance in the compound is found by the environment of
The below figure represents the proton NMR of
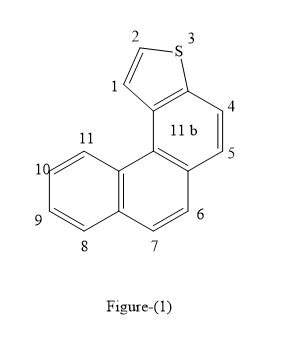
The
The double bond is also present between atoms
(d)
Interpretation:
The differences in the resonance of atoms
Concept introduction:
The resonance in different atoms can be distinguished by chemical shift, coupling constant and signal of pulses.
Answer to Problem 19.42QAP
The resonance of atoms
Explanation of Solution
The atom
On the basis of chemical shift resonance of atoms
(e)
Interpretation:
The resonances in
Concept introduction:
The resonance of different atoms in a compound is explained on the basis of chemical shift. The chemical shift is the resonate frequency of the nucleus in the magnetic field applied. On the basis of the position and chemical shift of nucleus resonance in the compound can be explained.
Answer to Problem 19.42QAP
The atoms
Explanation of Solution
The peaks of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Principles of Instrumental Analysis, 6th Edition
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing 2,2-dimethylpropanal with acetaldehyde and sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Ethyl-3-methyloxirane from dimethyl(propyl)sulfonium iodide using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Synthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIf possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forward
- Synthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forwardWe mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if (E)-2-butenal and 3-oxo-butanenitrile are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forward
 Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning,
Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning, Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning




