
You have 1.0 M solutions of Al(NO3)3 and AgNO3 along with Al and Ag electrodes to construct a voltaic cell. The salt bridge contains a saturated solution of KCl. Complete the picture associated with this problem by
- a writing the
symbols of the elements and ions in the appropriate areas (both solutions and electrodes). - b identifying the anode and cathode.
- c indicating the direction of electron flow through the external circuit.
- d indicating the cell potential (assume standard conditions, with no current flowing).
- e writing the appropriate half-reaction under each of the containers.
- f indicating the direction of ion flow in the salt bridge.
- g identifying the species undergoing oxidation and reduction.
- h writing the balanced overall reaction for the cell.
(a)
Interpretation:
Anode, cathode, direction of electron flow, symbols of elements and ions in cell, EMF of the cell and half cell and balanced overall cell reactions should be given.
Concept introduction:
Voltaic cell:
The device, which is converting the chemical energy into electrical energy, is called voltaic cell and this conversation is takes place by the redox reaction.
The oxidation half reaction takes place in anode and reduction half reaction takes place in cathode.
From the result of this redox reaction the electron flow is form anode to cathode direction in outer circuit.
Cell potential (EMF):
The maximum potential difference between two electrodes of voltaic cell is known as cell potential.
If standard reduction potentials of electrodes are given the cell potential (EMF) is given by,
Where,
The cell potential value is positive in spontaneous cell and negative in nu in spontaneous cell.
Answer to Problem 19.32QP
The symbols of elements and ions in cell are,
Symbols of Aluminium is Al, Silver is Ag, Aluminium ion is
Explanation of Solution
The symbols of elements and ions in cell are,
Symbol of Aluminium is Al and it is an anode
Symbol of Silver is Ag and it is an cathode
Symbol of Aluminium ion is
Symbol of Silver ion is
(b)
Interpretation:
Anode, cathode, direction of electron flow, symbols of elements and ions in cell, EMF of the cell and half cell and balanced overall cell reactions should be given.
Concept introduction:
Voltaic cell:
The device, which is converting the chemical energy into electrical energy, is called voltaic cell and this conversation is takes place by the redox reaction.
The oxidation half reaction takes place in anode and reduction half reaction takes place in cathode.
From the result of this redox reaction the electron flow is form anode to cathode direction in outer circuit.
Cell potential (EMF):
The maximum potential difference between two electrodes of voltaic cell is known as cell potential.
If standard reduction potentials of electrodes are given the cell potential (EMF) is given by,
Where,
The cell potential value is positive in spontaneous cell and negative in nu in spontaneous cell.
Answer to Problem 19.32QP
Silver rod in Silver nitrate is a cathode and Aluminium rod in Aluminium nitrate is an anode.
Explanation of Solution
In given cell, Silver rod in Silver nitrate is a cathode and Aluminium rod in Aluminium nitrate is an anode.
(c)
Interpretation:
Anode, cathode, direction of electron flow, symbols of elements and ions in cell, EMF of the cell and half cell and balanced overall cell reactions should be given.
Concept introduction:
Voltaic cell:
The device, which is converting the chemical energy into electrical energy, is called voltaic cell and this conversation is takes place by the redox reaction.
The oxidation half reaction takes place in anode and reduction half reaction takes place in cathode.
From the result of this redox reaction the electron flow is form anode to cathode direction in outer circuit.
Cell potential (EMF):
The maximum potential difference between two electrodes of voltaic cell is known as cell potential.
If standard reduction potentials of electrodes are given the cell potential (EMF) is given by,
Where,
The cell potential value is positive in spontaneous cell and negative in nu in spontaneous cell.
Answer to Problem 19.32QP
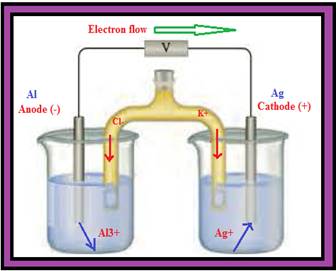
Figure 1
Explanation of Solution
(d)
Interpretation:
Anode, cathode, direction of electron flow, symbols of elements and ions in cell, EMF of the cell and half cell and balanced overall cell reactions should be given.
Concept introduction:
Voltaic cell:
The device, which is converting the chemical energy into electrical energy, is called voltaic cell and this conversation is takes place by the redox reaction.
The oxidation half reaction takes place in anode and reduction half reaction takes place in cathode.
From the result of this redox reaction the electron flow is form anode to cathode direction in outer circuit.
Cell potential (EMF):
The maximum potential difference between two electrodes of voltaic cell is known as cell potential.
If standard reduction potentials of electrodes are given the cell potential (EMF) is given by,
Where,
The cell potential value is positive in spontaneous cell and negative in nu in spontaneous cell.
Answer to Problem 19.32QP
The cell potential (EMF) of given voltaic cell is
Explanation of Solution
The standard reduction potentials of (SRQ) of half cell reactions are record from standard reduction potentials table and they are,
The most positive SQR is considering as cathode potential.
The SQR of electrodes are plugged in the bellow equation to give cell potential of given voltaic cell.
The cell potential (EMF) of given voltaic cell is
(e)
Interpretation:
Anode, cathode, direction of electron flow, symbols of elements and ions in cell, EMF of the cell and half cell and balanced overall cell reactions should be given.
Concept introduction:
Voltaic cell:
The device, which is converting the chemical energy into electrical energy, is called voltaic cell and this conversation is takes place by the redox reaction.
The oxidation half reaction takes place in anode and reduction half reaction takes place in cathode.
From the result of this redox reaction the electron flow is form anode to cathode direction in outer circuit.
Cell potential (EMF):
The maximum potential difference between two electrodes of voltaic cell is known as cell potential.
If standard reduction potentials of electrodes are given the cell potential (EMF) is given by,
Where,
The cell potential value is positive in spontaneous cell and negative in nu in spontaneous cell.
Answer to Problem 19.32QP
The Oxidation half cell reaction is,
The reduction half cell reaction is,
Explanation of Solution
The Oxidation half cell reaction is,
The reduction half cell reaction is,
(f)
Interpretation:
Anode, cathode, direction of electron flow, symbols of elements and ions in cell, EMF of the cell and half cell and balanced overall cell reactions should be given.
Concept introduction:
Voltaic cell:
The device, which is converting the chemical energy into electrical energy, is called voltaic cell and this conversation is takes place by the redox reaction.
The oxidation half reaction takes place in anode and reduction half reaction takes place in cathode.
From the result of this redox reaction the electron flow is form anode to cathode direction in outer circuit.
Cell potential (EMF):
The maximum potential difference between two electrodes of voltaic cell is known as cell potential.
If standard reduction potentials of electrodes are given the cell potential (EMF) is given by,
Where,
The cell potential value is positive in spontaneous cell and negative in nu in spontaneous cell.
Answer to Problem 19.32QP
Explanation of Solution
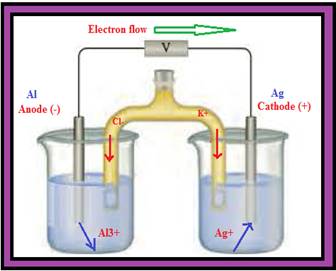
Figure 1
(g)
Interpretation:
Anode, cathode, direction of electron flow, symbols of elements and ions in cell, EMF of the cell and half cell and balanced overall cell reactions should be given.
Concept introduction:
Voltaic cell:
The device, which is converting the chemical energy into electrical energy, is called voltaic cell and this conversation is takes place by the redox reaction.
The oxidation half reaction takes place in anode and reduction half reaction takes place in cathode.
From the result of this redox reaction the electron flow is form anode to cathode direction in outer circuit.
Cell potential (EMF):
The maximum potential difference between two electrodes of voltaic cell is known as cell potential.
If standard reduction potentials of electrodes are given the cell potential (EMF) is given by,
Where,
The cell potential value is positive in spontaneous cell and negative in nu in spontaneous cell.
Answer to Problem 19.32QP
Explanation of Solution
The Oxidation half cell reaction is,
The reduction half cell reaction is,
Hence,
(h)
Interpretation:
Anode, cathode, direction of electron flow, symbols of elements and ions in cell, EMF of the cell and half cell and balanced overall cell reactions should be given.
Concept introduction:
Voltaic cell:
The device, which is converting the chemical energy into electrical energy, is called voltaic cell and this conversation is takes place by the redox reaction.
The oxidation half reaction takes place in anode and reduction half reaction takes place in cathode.
From the result of this redox reaction the electron flow is form anode to cathode direction in outer circuit.
Cell potential (EMF):
The maximum potential difference between two electrodes of voltaic cell is known as cell potential.
If standard reduction potentials of electrodes are given the cell potential (EMF) is given by,
Where,
The cell potential value is positive in spontaneous cell and negative in nu in spontaneous cell.
Answer to Problem 19.32QP
The balanced overall cell reaction is,
Explanation of Solution
The Oxidation half cell reaction is,
The reduction half cell reaction is,
To sum the two half cell reactions and remove a electron to give a balanced overall cell reaction.
The balanced overall cell reaction is,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Course List)
- Provide steps and explanation please.arrow_forwardDraw a structural formula for the major product of the acid-base reaction shown. H 0 N + HCI (1 mole) CH3 N' (1 mole) CH3 You do not have to consider stereochemistry. ● • Do not include counter-ions, e.g., Na+, I, in your answer. . In those cases in which there are two reactants, draw only the product from 989 CH3 344 ? [Farrow_forwardQuestion 15 What is the major neutral organic product for the following sequence? 1. POCI₂ pyridine ? 2. OsO4 OH 3. NaHSO Major Organic Product ✓ OH OH 'OH OH 'OH 'CIarrow_forward
- Could you please solve the first problem in this way and present it similarly but color-coded or step by step so I can understand it better? Thank you!arrow_forwardCould you please solve the first problem in this way and present it similarly but color-coded or step by step so I can understand it better? Thank you!arrow_forwardCould you please solve the first problem in this way and present it similarly but (color-coded) and step by step so I can understand it better? Thank you! I want to see what they are doingarrow_forward
 General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning





