
Applied Statics and Strength of Materials (6th Edition)
6th Edition
ISBN: 9780133840544
Author: George F. Limbrunner, Craig D'Allaird, Leonard Spiegel
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 19, Problem 19.16SP
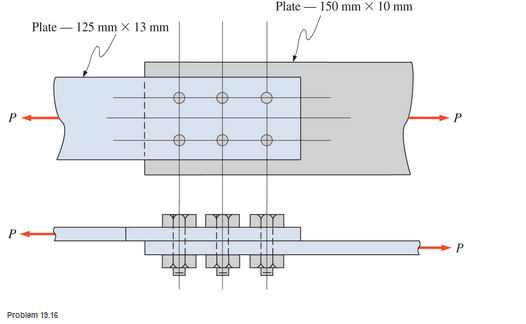
Calculate the allowable tensile load for the lap joint shown. The fasteners are 25-mm-diameter A325-X high-strength bolts. The plates are ASTM A36 steel.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
An airplane lands on the straight runaway, originally travelling at 110 ft/s when s = 0. If it is
subjected to the decelerations shown, determine the time t' needed to stop the plane and construct the s -t graph for the motion.
draw a graph and show all work step by step
dny
dn-1y
dn-1u
dn-24
+a1
+
+ Any
=
bi
+b₂-
+ +bnu.
dtn
dtn-1
dtn-1
dtn-2
a) Let be a root of the characteristic equation
1
sn+a1sn-
+
+an
= : 0.
Show that if u(t) = 0, the differential equation has the solution y(t) = e\t.
b) Let к be a zero of the polynomial
b(s) = b₁s-1+b2sn−2+
Show that if the input is u(t)
equation that is identically zero.
=
..
+bn.
ekt, then there is a solution to the differential
B
60 ft
WAB
AB
30%
:
The crane's telescopic boom rotates with the angular velocity w = 0.06 rad/s and
angular acceleration a = 0.07 rad/s². At the same instant, the boom is extending
with a constant speed of 0.8 ft/s, measured relative to the boom. Determine the
magnitude of the acceleration of point B at this instant.
Chapter 19 Solutions
Applied Statics and Strength of Materials (6th Edition)
Ch. 19 - Prob. 19.1PCh. 19 - Rework Problem 19.1 assuming a bearing-type...Ch. 19 - Rework Problem 19.1 assuming a bearing-type...Ch. 19 - Compute the allowable tensile load for the...Ch. 19 - Rework Problem 19.4 assuming a bearing-type...Ch. 19 - Rework Problem 19.4 assuming that the bolts are 34...Ch. 19 - Select the number and arrangement of 34 in....Ch. 19 - Calculate the allowable tensile load for the...Ch. 19 - In the connection shown, 14 in. side and end...Ch. 19 - Design the fillet welds parallel to the applied...
Ch. 19 - A fillet weld between two steel plates...Ch. 19 - Design an end connection using longitudinal welds...Ch. 19 - Calculate the allowable tensile load for the butt...Ch. 19 - Calculate the allowable tensile load for the lap...Ch. 19 - Calculate the allowable tensile load for the butt...Ch. 19 - Rework Problem 19.10 assuming that both plates are...Ch. 19 - Rework Problem 19.12 assuming that the angle is an...Ch. 19 - Two ASTM A36 steel plates, each 12 in. by 12 in. ,...Ch. 19 - Rework Problem 19.20 changing the fasteners to 34...Ch. 19 - Calculate the minimum main plate thickness for the...Ch. 19 - A roof truss tension member is made up of 2L6412...Ch. 19 - Rework Problem 19.23 changing the fasteners to six...Ch. 19 - Determine the allowable tensile load that can be...Ch. 19 - The welded connection shown is subjected to an...Ch. 19 - In Problem 19.26, use a 38 in. fillet weld, change...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The motion of peg P is constrained by the lemniscate curved slot in OB and by the slotted arm OA. (Figure 1) If OA rotates counterclockwise with a constant angular velocity of 0 = 3 rad/s, determine the magnitude of the velocity of peg P at 0 = 30°. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Determine the magnitude of the acceleration of peg P at 0 = 30°. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. 0 (4 cos 2 0)m² B Aarrow_forward5: The structure shown was designed to support a30-kN load. It consists of a boom AB with a 30 x 50-mmrectangular cross section and a rod BC with a 20-mm-diametercircular cross section. The boom and the rod are connected bya pin at B and are supported by pins and brackets at A and C,respectively.1. Calculate the normal stress in boom AB and rod BC,indicate if in tension or compression.2. Calculate the shear stress of pins at A, B and C.3. Calculate the bearing stresses at A in member AB,and in the bracket.arrow_forward4: The boom AC is a 4-in. square steel tube with a wallthickness of 0.25 in. The boom is supported by the 0.5-in.-diameter pinat A, and the 0.375-in.-diameter cable BC. The working stresses are 25ksi for the cable, 18 ksi for the boom, and 13.6 ksi for shear in the pin.Neglect the weight of the boom.1. Calculate the maximum value of P (kips) based on boom compression and the maximum value of P (kips) based on tension in the cable.2. Calculate the maximum value of P (kips) based on shear in pin.arrow_forward
- 3: A steel strut S serving as a brace for a boat hoist transmits a compressive force P = 54 kN to the deck of a pier as shown in Fig. STR-08. The strut has a hollow square cross section with a wall thickness t =12mm and the angle θ between the strut and the horizontal is 40°. A pin through the strut transmits the compressive force from the strut to two gusset plates G that are welded to the base plate B. Four anchor bolts fasten the base plate to the deck. The diameter of the pin is 20mm, the thickness of the gusset plates is 16mm, the thickness of the base plate is 8mm, and the diameter of the anchor bolts is 12mm. Disregard any friction between the base plate and the deck.1. Determine the shear stress in the pin, in MPa and the shear stress in the anchor bolts, in MPa.2. Determine the bearing stress in the strut holes, in MPa.arrow_forward1. In the figure, the beam, W410x67, with 9 mm web thicknesssubjects the girder, W530x109 with 12 mm web thickness to a shear load,P (kN). 2L – 90 mm × 90 mm × 6 mm with bolts frame the beam to thegirder.Given: S1 = S2 = S5 = 40 mm; S3 = 75 mm; S4 = 110 mmAllowable Stresses are as follows:Bolt shear stress, Fv = 125 MPaBolt bearing stress, Fp = 510 MPa1. Determine the allowable load, P (kN), based on the shearcapacity of the 4 – 25 mm diameter bolts (4 – d1) and calculate the allowable load, P (kN), based on bolt bearing stress on the web of the beam.2. If P = 450 kN, determine the minimum diameter (mm) of 4 – d1based on allowable bolt shear stress and bearing stress of thebeam web.arrow_forward6: The 6-kN load P is supported by two wooden members of 75 x 125-mm uniform cross section that are joined by the simple glued scarf splice shown.1. Calculate the normal stress in the glue, in MPa.2. Calculate the shear stress in the glue, in MPa.arrow_forward
- Using Matlab calculate the following performance characteristics for a Tesla Model S undergoing the 4506 drive cycle test Prated Trated Ebat 80kW 254 Nm 85kWh/1645kg MUEH A rwheel 0.315M 133.3 C 0.491 Ng ng 7g 8.190.315 8.19 0.315 7ed= 85% Ebpt 35-956 DRIVE AXLE Ebfb chę =85% V Minverter H/A Battery Charger En AC Pry 9) required energy output from the motor to drive this cycle Cassume no regenerative braking) b) range of the Tesla Model S for this drive cycle (assume no regenerative breaking c) estimated mpge cycle of the Tesla Model S for this drive Cassume no regenerative breaking) d) Recalculate parts abc now assuming you can regenerate returns correctly due to inefficiency. from braking. Be careful to handle the diminishing energy braking makes in terms of required e) Quantify the percentage difference that regenerative required energy, range and mpge, DI L Ta a ra OLarrow_forwardHW.5.1 Determine the vertical displacement of joint C on the truss as shown by using Castigliano's theorem. Let E = 200(109) GPa and A = 300 mm² 4 m E 20 kN 3 m 3 m B D 30 kN Carrow_forward3-55 A multifluid container is connected to a U-tube, as shown in Fig. P3–55. For the given specific gravities and fluid column heights, determine the gage pressure at A. Also determine the height of a mercury column that would create the same pressure at A. Answers: 0.415 kPa, 0.311 cmarrow_forward
- I need help answering parts a and barrow_forwardRequired information Water initially at 200 kPa and 300°C is contained in a piston-cylinder device fitted with stops. The water is allowed to cool at constant pressure until it exists as a saturated vapor and the piston rests on the stops. Then the water continues to cool until the pressure is 100 kPa. NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. Water 200 kPa 300°C On the T-V diagram, sketch, with respect to the saturation lines, the process curves passing through the initial, intermediate, and final states of the water. Label the T, P, and V values for end states on the process curves. Please upload your response/solution by using the controls provided below.arrow_forwardA piston-cylinder device contains 0.87 kg of refrigerant-134a at -10°C. The piston that is free to move has a mass of 12 kg and a diameter of 25 cm. The local atmospheric pressure is 88 kPa. Now, heat is transferred to refrigerant-134a until the temperature is 15°C. Use data from the tables. R-134a -10°C Determine the change in the volume of the cylinder of the refrigerant-134a if the specific volume and enthalpy of R-134a at the initial state of 90.4 kPa and -10°C and at the final state of 90.4 kPa and 15°C are as follows: = 0.2418 m³/kg, h₁ = 247.77 kJ/kg 3 v2 = 0.2670 m³/kg, and h₂ = 268.18 kJ/kg The change in the volume of the cylinder is marrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Welding: Principles and Applications (MindTap Cou...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305494695Author:Larry JeffusPublisher:Cengage Learning
Welding: Principles and Applications (MindTap Cou...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305494695Author:Larry JeffusPublisher:Cengage Learning

Welding: Principles and Applications (MindTap Cou...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305494695
Author:Larry Jeffus
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Differences between Temporary Joining and Permanent Joining.; Author: Academic Gain Tutorials;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PTr8QZhgXyg;License: Standard Youtube License