
Concept explainers
a.
Interpretation:
Classification of reaction below into oxidation and reduction has to be determined. Also, whether

Concept Introduction:
In
Oxidizing agent reduces to complete oxidation reaction while reducing agent oxidizes to complete reduction reaction.
More convenient way to spot
Coenzyme
b.
Interpretation:
Classification of reaction below into oxidation and reduction has to be determined. Also, whether
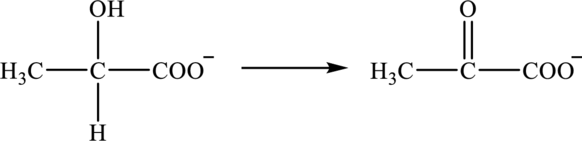
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part a.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 18 Solutions
Connect 1-Semester Online Access for Principles of General, Organic & Biochemistry
- 2-Cyclopentyl-2-methyl-1,3-dioxolane is reacted with H₂SO₄. Draw and name the structures of the products.arrow_forwardIndicate the products of the reaction of 1-cyclohexyl-2,2-dimethylpropan-1-one with CH3CO3H (). Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardWrite chemical equations for: the reaction of benzoic acid chloride with grignard reagent [CH3MgX] the reaction of butanoic acid with methyl amine [CH3NH2]arrow_forward
- 2-(3-Aminopropyl)cyclohexan-1-one is reacted with H₂SO₄. Draw the structures of the products.arrow_forwardPlease help me solve number 2arrow_forwardChoose the best reagents to complete the following reaction. 오 Na2Cr2O7 H2SO4, H2O Problem 22 of 35 A Na2Cr2O7 H2SO4, H2O H2/Pt B pressure OH 1. NaBH4 C 2. H3O+ D DMP (Dess-Martin Periodinane) CH2Cl2 CrO3 Done Dramabana_Minor Submitarrow_forward
- Indicate the products of the reaction of Cycloheptanone with pyrrolidine (cat. H+). Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIndicate the products of the reaction of 2-(3-aminopropyl)cyclohexan-1-one with H2SO4. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIndicate the products of the reaction of 2-cyclopentyl-2-methyl-1,3-dioxolane with H3O+. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Question 4 For the molecule shown below, (7 marks): A) Sketch the Newman projection for the view looking along the bond from the perspective of the arrow. B) Then, draw the Newman projection for each 60° rotation along the bond until it returns to the starting point. C) Clearly indicate which Newman projection is the one we see in the structure shown below, and clearly indicate which Newman projection is the highest in energy and which is the lowest in energy. H H Me 'H Me Mearrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts and the amine side product. 'N' 1. NaOH, heat 2. Neutralizing work-up Select to Drawarrow_forwardSubmit Problem 3 of 10 Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts and the amine side product. O 'N' NH 1. NaOH, heat 2. Neutralizing work-up Select to Drawarrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,





