
Concept explainers
Consider a rigid body of arbitrary shape that is attached at its mass center O and subjected to no force other than its weight and the reaction of the support at O.
(a) Prove that the angular momentum HO of the body about the fixed point O is constant in magnitude and direction, that the kinetic energy T of the body is constant, and that the projection along HO of the angular velocity ω of the body is constant.
(b) Show that the tip of the
(c) Show that with respect to a frame of reference attached to the body and coinciding with its principal axes of inertia, the tip of the vector ω appears to describe a curve on an ellipsoid of equation
The ellipsoid (called the Poinsot ellipsoid) is rigidly attached to the body and is of the same shape as the ellipsoid of inertia, but of a different size.
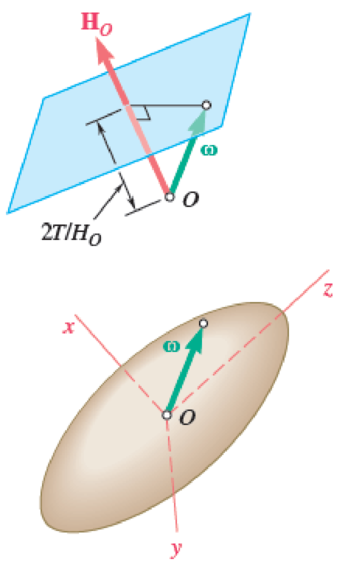
Fig. P18.143
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 18 Solutions
VECTOR MECH...,STAT.+DYN.(LL)-W/ACCESS
- 3. Determine the flow rate through the pipe line show in the figure in ft³/s, and determine the pressures at A and C, in psi. 5' B C 12° 20' D 6"d 2nd- Water Aarrow_forward5. A flow is field given by V = x²₁³+xy, and determine 3 ·y³j- (a) Whether this is a one, two- or three-dimensional flow (b) Whether it is a possible incompressible flow (c) Determine the acceleration of a fluid particle at the location (X,Y,Z)=(1,2,3) (d) Whether the flow is rotational or irrotational flow?arrow_forwardSolve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forward
- Solve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forwarddraw the pneumatic circuit to operate a double-acting cylinder with: 1. Extension: Any of two manual conditions plus cylinder fully retracted, → Extension has both meter-in and meter-out, 2. Retraction: one manual conditions plus cylinder fully extended, → Retraction is very fast using quick exhaust valve.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution with fbd only. I will upvote, thank you. Expert solution plsarrow_forward
- Correct answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution with fbd only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution with fbd only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution only with fbd. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forward
- Correct answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution with fbd only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





