
(a)
Interpretation:
The given amine needs to be labeled as 10, 20 or 30.
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 74P
A tertiary (3o) amine.
Explanation of Solution
Amines are derivatives which are derived from ammonia, wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group. They can be called as alkylamines and arylamines.
Whether an amine is primary (1o), secondary (2o) or tertiary (3o) depends on the number of hydrogen atoms replaced by an alkyl or aryl group in ammonia. The amine is a primary amine if one hydrogen atom is replaced, it is a secondary amine if 2 hydrogen atoms are replaced and if three hydrogen atoms are replaced it is known as a tertiary amine.
The given compound is as follows:
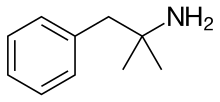
Here, only one hydrogen atom is replaced and therefore this amine called as a primary (1o) amine.
(b)
Interpretation:
The molecular shape around each atom of phentermine needs to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Molecular geometry is named as molecular shape and it is the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms within a molecule of the environment. Atoms arrange in space with an exact shape to minimize the repulsion. This can be determined using VSEPR theory.
Answer to Problem 74P
Carbons of benzene molecule;trigonal planar.
Carbon of −CH2 / -C(CH3)2NH2 CH2-/-CH3;tetrahedral.
Nitrogen of NH2;trigonal pyramidal.
Explanation of Solution
VSEPR or Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory is a model used to determine the geometry of molecules considering minimum electrostatic repulsion between the valence electrons of central atom in the molecule.
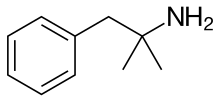
Carbons of benzene molecule;
Number of bonds= 3
Number of lone pairs = 0
Therefore, the shape is trigonal planar.
Carbon of −CH2/ -C(CH3)2NH2CH2-/-CH3;
Number of bonds= 4
Number of lone pairs = 0
Therefore, the shape is tetrahedral.
Nitrogen of NH2;
Number of bonds= 3
Number of lone pairs = 1
Therefore, the shape is trigonal pyramidal.
(c)
Interpretation:
The constitutional isomer containing a primary amine needs to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Constitutional isomers are called as compounds that have the unique molecular formula and different structural connectivity. To determine whether two molecules are constitutional isomer, the number of each atom needs to be counted in both molecules and see how the atoms are arranged.
Answer to Problem 74P
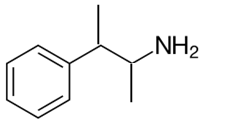
Explanation of Solution
Whether an amine is primary (1o), secondary (2o) or tertiary (3o) depends on the number of hydrogen atoms replaced by an alkyl or aryl group in ammonia. The amine is a primary amine if one hydrogen atom is replaced, it is a secondary amine if 2 hydrogen atoms are replaced and if three hydrogen atoms are replaced it is known as a tertiary amine.

Here all one hydrogen atom is replaced and therefore this amine called a primary amine (1o).
(d)
Interpretation:
The constitutional isomer that contains a secondary amine needs to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Constitutional isomers are called as compounds that have the unique molecular formula and different structural connectivity. To determine whether two molecules are constitutional isomer, the number of each atom needs to be counted in both molecules and see how the atoms are arranged.
Answer to Problem 74P
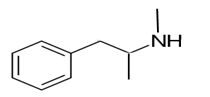
Explanation of Solution
Whether an amine is primary (1o), secondary (2o) or tertiary (3o) depends on the number of hydrogen atoms replaced by an alkyl or aryl group in ammonia. The amine is a primary amine if one hydrogen atom is replaced, it is a secondary amine if 2 hydrogen atoms are replaced and if three hydrogen atoms are replaced it is known as a tertiary amine.

Here all 3 hydrogen atoms are replaced and therefore this amine called as a secondary amine (2o).
(e)
Interpretation:
The structure of phentermine hydrobromide molecule needs to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Phentermine hydrobromide can stimulate the central nervous system and increases the blood pressure and heart rate which decreases the appetite. It is taken along with diet and exercise in order to reduce obesity.
Answer to Problem 74P
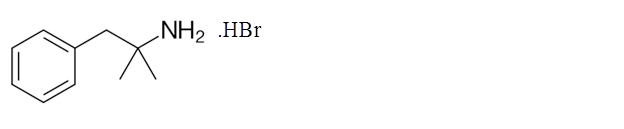
Explanation of Solution
Phentermine hydrobromide can stimulate the central nervous system and increases the blood pressure and heart rate which decreases the appetite. It is taken along with the diet and exercise in order to reduce the obesity.
Its molecular formula is C17H22BrN. It has the following structure.
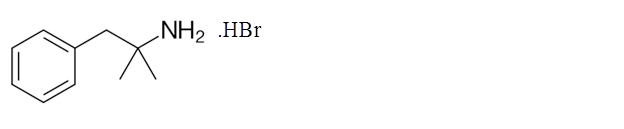
(f)
Interpretation:
The products formed if phentermine is treated with benzoic acid needs to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Amines are derivatives which are derived from ammonia, wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group. They can be called as alkylamines and arylamines.
Answer to Problem 74P
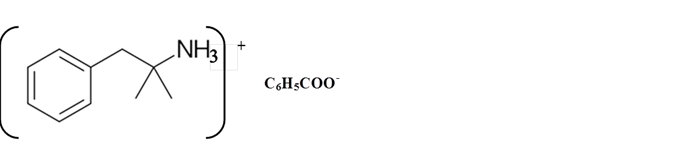
Explanation of Solution
Amines are derivatives which are derived from ammonia, wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group. They can be called as alkylamines and arylamines.
Whether an amine is primary (1o), secondary (2o) or tertiary (3o) depends on the number of hydrogen atoms replaced by an alkyl or aryl group in ammonia. The amine is a primary amine if one hydrogen atom is replaced, it is a secondary amine if 2 hydrogen atoms are replaced and if three hydrogen atoms are replaced it is known as a tertiary amine.
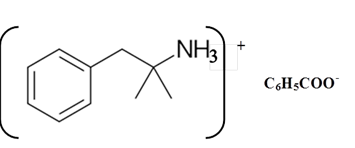
Benzphetamine is a tertiary ammine. It has basic properties and it accepts protons from acids. Acetic acid is donated a proton to this amine and formed below the salt.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
- Determine the structures of the missing organic molecules in the following reaction: H+ O OH H+ + H₂O ☑ ☑ Note: Molecules that share the same letter have the exact same structure. In the drawing area below, draw the skeletal ("line") structure of the missing organic molecule X. Molecule X shows up in multiple steps, but you only have to draw its structure once. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X § ©arrow_forwardTable 1.1 Stock Standard Solutions Preparation. The amounts shown should be dissolved in 100 mL. Millipore water. Calculate the corresponding anion concentrations based on the actual weights of the reagents. Anion Amount of reagent (g) Anion Concentration (mg/L) 0.1649 Reagent Chloride NaCl Fluoride NaF 0.2210 Bromide NaBr 0.1288 Nitrate NaNO3 0.1371 Nitrite NaNO2 0.1500 Phosphate KH2PO4 0.1433 Sulfate K2SO4 0.1814arrow_forwardDraw the structure of the pound in the provided CO as a 300-1200 37(2), 11 ( 110, and 2.5 (20arrow_forward
- Please help me with # 4 and 5. Thanks in advance!arrow_forwardA small artisanal cheesemaker is testing the acidity of their milk before it coagulates. During fermentation, bacteria produce lactic acid (K₁ = 1.4 x 104), a weak acid that helps to curdle the milk and develop flavor. The cheesemaker has measured that the developing mixture contains lactic acid at an initial concentration of 0.025 M. Your task is to calculate the pH of this mixture and determine whether it meets the required acidity for proper cheese development. To achieve the best flavor, texture and reduce/control microbial growth, the pH range needs to be between pH 4.6 and 5.0. Assumptions: Lactic acid is a monoprotic acid H H :0:0: H-C-C H :0: O-H Figure 1: Lewis Structure for Lactic Acid For simplicity, you can use the generic formula HA to represent the acid You can assume lactic acid dissociation is in water as milk is mostly water. Temperature is 25°C 1. Write the K, expression for the dissociation of lactic acid in the space provided. Do not forget to include state symbols.…arrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. :0: :0 H. 0:0 :0: :6: S: :0: Select to Edit Arrows ::0 Select to Edit Arrows H :0: H :CI: Rotation Select to Edit Arrows H. < :0: :0: :0: S:arrow_forward
- 3:48 PM Fri Apr 4 K Problem 4 of 10 Submit Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. Mg. :0: Select to Add Arrows :0: :Br: Mg :0: :0: Select to Add Arrows Mg. Br: :0: 0:0- Br -190 H 0:0 Select to Add Arrows Select to Add Arrows neutralizing workup H CH3arrow_forwardIarrow_forwardDraw the Markovnikov product of the hydrobromination of this alkene. Note for advanced students: draw only one product, and don't worry about showing any stereochemistry. Drawing dash and wedge bonds has been disabled for this problem. + Explanation Check 1 X E 4 1 1 1 1 1 HBr Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 80 LE #3 @ 2 $4 0 I அ2 % 85 F * K M ? BH 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center & 6 27 FG F10 8 9 R T Y U D F G H P J K L Z X C V B N M Q W A S H option command H command optiarrow_forward
- Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds to show the stereochemistry of the products when it's important, for example to distinguish between two different major products. Predict the major products of the following reaction. Explanation Q F1 A Check F2 @ 2 # 3 + X 80 F3 W E S D $ 4 I O H. H₂ 2 R Pt % 05 LL ee F6 F5 T <6 G Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 27 & A 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center Acce Y U H DII 8 9 F10 4 J K L Z X C V B N M T H option command F11 P H commandarrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Use the reaction conditions provided and follow the arrows to draw the intermediate and product in this reaction or mechanistic step(s). Include all lone pairs and charges as appropriate. Ignore stereochemistry. Ignore inorganic byproducts. H :0: CH3 O: OH Q CH3OH2+ Draw Intermediate protonation CH3OH CH3OH nucleophilic addition H Draw Intermediate deprotonation :0: H3C CH3OH2* protonation H 0: H CH3 H.arrow_forwardPredicting the reactants or products of hemiacetal and acetal formation uentify the missing organic reactants in the following reaction: H+ X+Y OH H+ за Note: This chemical equation only focuses on the important organic molecules in the reaction. Additional inorganic or small-molecule reactants or products (like H2O) are not shown. In the drawing area below, draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic reactants X and Y. You may draw the structures in any arrangement that you like, so long as they aren't touching. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ? olo 18 Ar © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibilityarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning

