
(a)
Interpretation:
From the given compounds from E to H, a compound containing a primary amine and a primary amide needs to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Amine − is an organic N compounds formed by replacing one or more H atoms of
Amide- is an organic compound contains the group of
Answer to Problem 31P
Structure H.
Explanation of Solution
Amines are formed by replacing one or more hydrogen atoms of ammonia with alkyl groups.
Furthermore,
In the below structure, bond that is indicated in red color is the single
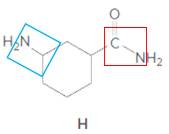
Hence, structure H is a compound that contains a
(b)
Interpretation:
From the given compounds from E to H, a compound containing a primary amine and a secondary amide needs to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Amine − is an organic N compounds formed by replacing one or more H atoms of
Amide- is an organic compound contains the group of
Answer to Problem 31P
Structure F.
Explanation of Solution
Amines are formed by replacing one or more hydrogen atoms of ammonia with alkyl groups.
Furthermore,
In the below structure, bonds that are indicated in red color are the two
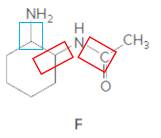
Hence, structure F is a compound that contains a
(c)
Interpretation:
From the given compounds from E to H, a compound containing a secondary amine and a tertiary amide needs to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Amine − is an organic N compounds formed by replacing one or more H atoms of
Amide- is an organic compound contains the group of
Answer to Problem 31P
Structure E.
Explanation of Solution
Amines are formed by replacing one or more hydrogen atoms of ammonia with alkyl groups.
Furthermore,
In the below structure, bonds that are indicated in red color are the three
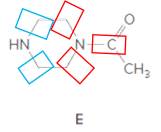
Hence, structure E is a compound that contains a
(d)
Interpretation:
From the given compounds from E to H, a compound containing a tertiary amine and a tertiary amide needs to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Amine − is an organic N compounds formed by replacing one or more H atoms of
Amide- is an organic compound contains the group of
Answer to Problem 31P
Structure G.
Explanation of Solution
Amines are formed by replacing one or more hydrogen atoms of ammonia with alkyl groups.
Furthermore,
In the below structure, bonds that are indicated in red color are the three
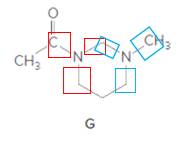
Hence, structure G is a compound that contains a
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
- . Provide IUPAC names for each of the following structures OR draw structures corresponding to each of the following names: [Three only]kk a. H₂N- 0 COCH2CH3 benzocaine b. What is the correct structure for phenylbenzoate? C a. 0 C-O O b. H3C-C-O 0 0 C-O-CH3 d. CH₂O C-CHZ c. Acetyl chloride d. 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl chloridearrow_forward. Draw structures corresponding to each of the following names or Provide IUPAC names for each of the ollowing structures [for 4 ONLY]. A. 2-propylpentanoic acid. B. m-chlorobenzoic acid. C. 0 0 HOC(CH2) COH glutaricadd D. E. F. 0 OH HO OH HO INCO salicylicadd H3C CH3 C=C tgicadd H COOH CH₂C=N 4arrow_forwardThe reaction of a carboxylic acid with an alcohol in the presence of acid is termed Fischer esterification. 0 0 C .C. OH + CH3OH OCH3 + H₂O HCI A B C A. The nucleophile in this reaction is B. Compound C functions as a. a base scavenger b. a solvent C. a catalyst in this reaction. d. a neutralizer C. Fischer esterification is an example of: ........ a. nucleophilic acyl addition b. nucleophilic acyl substitution c. nucleophilic acyl elimination d. nucleophilic acyl rearrangementarrow_forward
- The Handbook of Chemistry and Physics gives solubilities of the following compounds in grams per 100 mL of water. Because these compounds are only slightly soluble, assume that the volume does not change on dissolution and calculate the solubility product for each. (a) BaSeO4, 0.0118 g/100 mLarrow_forwardCan I please get help with answering this?arrow_forwardThese are in the wrong boxes. Why does the one on the left have a lower molar mass than the one on the right?arrow_forward
- SYNTHESIS REACTIONS. For the following reactions, synthesize the given products from the given reactants. Multiple reactions/steps will be needed. For the one of the steps (ie reactions) in each synthesis, write out the mechanism for that reaction and draw an energy diagram showing the correct number of hills and valleys for that step's mechanism. CI b. a. Use acetylene (ethyne) and any alkyl halide as your starting materials Br C. d. "OH OH III. OHarrow_forwardCalculate the pH and the pOH of each of the following solutions at 25 °C for which the substances ionize completely: (a) 0.200 M HClarrow_forwardCalculate the pH and the pOH of each of the following solutions at 25 °C for which the substances ionize completely: (a) 0.000259 M HClO4arrow_forward
- What is the pH of a 1.0 L buffer made with 0.300 mol of HF (Ka = 6.8 × 10⁻⁴) and 0.200 mol of NaF to which 0.160 mol of NaOH were added?arrow_forwardDetermine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. NaN₃arrow_forwardCan I please get help with this?arrow_forward

 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning

