
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The amine needs to be labeled as 10, 20 or 30.
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 73P
A tertiary (3o) amine.
Explanation of Solution
Amines are derivatives which are derived from ammonia, wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group. They can be called as alkylamines and arylamines.
Whether an amine is primary (1o), secondary (2o) or tertiary (3o) depends on the number of hydrogen atoms replaced by an alkyl or aryl group in ammonia. The amine is a primary amine if one hydrogen atom is replaced, it is a secondary amine if 2 hydrogen atoms are replaced and if three hydrogen atoms are replaced, it is known as a tertiary amine.
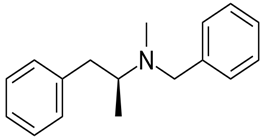
Here, all three hydrogen atoms are replaced and therefore this amine called a tertiary (3o) amine.
(b)
Interpretation:
The chiral center of the benzphetamine molecule needs to be labeled.
Concept Introduction:
The molecules with a chiral center can form a superimposable mirror image and is known as enantiomers. There should not be any plane of symmetry in a molecule to be chiral. A plane that bisects a molecule into two equal halves is known as a plane of symmetry. If there is a plane of symmetry in a molecule and it is identical to any of its mirror image, it is considered as achiral. The chiral center is carbon attached to 4 different groups attached to it.
Answer to Problem 73P
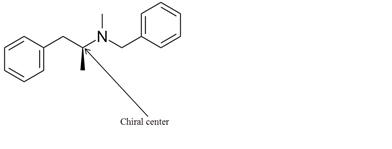
Explanation of Solution
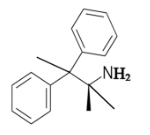
The chiral center in the given molecule is shown as follows:
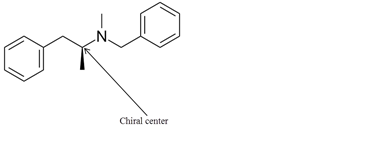
The labeled carbon atom is attached to 4 different groups.
The chiral center has four different groups attached to carbon and no plane of symmetry. The molecule with a chiral center shows optical isomerism. The chiral center is a stereocenter holding the atoms in space, the mirror image so formed are not superimposable.
(c)
Interpretation:
The enantiomers of benzphetamine molecule needs to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The chiral molecules which are mirror images of each other are known as enantiomers. They are non-superimposable mirror images, or they cannot be placed on top of each other.
Answer to Problem 73P
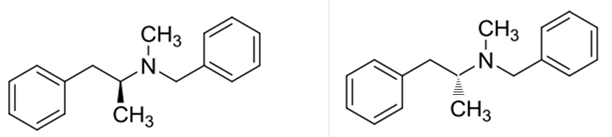
Explanation of Solution
Benzphetamine has two enantiomers due to its one chiral center. It rotates the plane-polarized light. Here, S-benzphetamine rotates the light anticlockwise and R- benzphetamine rotates it clockwise.
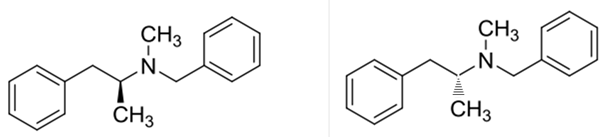
Benzphetaminecan can be called as a racemic mixture of two enantiomers, which are R(+) and S(-).
(d)
Interpretation:
The constitutional isomer that contains a primary amine needs to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Constitutional isomers have the same molecular formula but different structural connectivity. The number of each atom in both the molecules needs to be counted and the arrangement is observed to check whether two molecules are a constitutional isomer of each other or not.
Answer to Problem 73P
Explanation of Solution
Whether an amine is primary (1o), secondary (2o) or tertiary (3o) depends on the number of hydrogen atoms replaced by an alkyl or aryl group in ammonia. The amine is a primary amine if one hydrogen atom is replaced, it is a secondary amine if 2 hydrogen atoms are replaced and if three hydrogen atoms are replaced it is known as a tertiary amine.
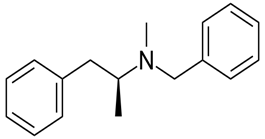
The given compound is as follows:
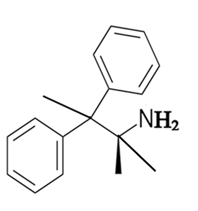
The constitutional isomer with a primary amine is as follows:
Here, only one hydrogen atom is replaced therefore this amine called a primary amine (1o).
(e)
Interpretation:
The constitutional isomer that contains a tertiary amine needs to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Constitutional isomers have the same molecular formula but different structural connectivity. The number of each atom in both the molecules needs to be counted and the arrangement is observed to check whether two molecules are a constitutional isomer of each other or not.
Answer to Problem 73P

Explanation of Solution
Whether an amine is primary (1o), secondary (2o) or tertiary (3o) depends on the number of hydrogen atoms replaced by an alkyl or aryl group in ammonia. The amine is a primary amine if one hydrogen atom is replaced, it is a secondary amine if 2 hydrogen atoms are replaced and if three hydrogen atoms are replaced it is known as a tertiary amine.
The given compound is as follows:
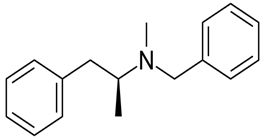
The constitutional isomer with a tertiary amine is represented as follows:
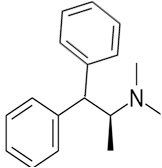
Here all 3 hydrogen atomsare replaced and therefore this amine called as a tertiary amine (3o).
(f)
Interpretation:
The structure of benzphetaminehychloride molecule needs to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Benzphetamine hydrochloride can be defined as the hydrochloride salt version of benzphetamine.
Answer to Problem 73P
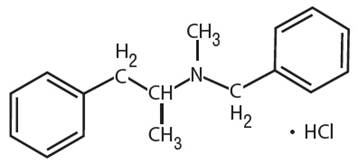
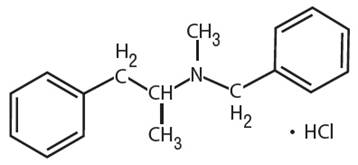
Explanation of Solution
Benzphetamine hydrochloride can be defined as the hydrochloride salt version of benzphetamine. Its molecular formula is C17H22ClN. It has the following structure.
(g)
Interpretation:
The products formed if benzphetamine is treated with acetic acid needs to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Amines are derived from ammonia and formed by replacement of one or more hydrogen atoms by alkyl or aryl groups. They can be called as alkylamines and arylamines. Benzphetamine is a tertiary amine.
Answer to Problem 73P
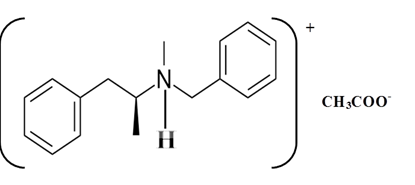
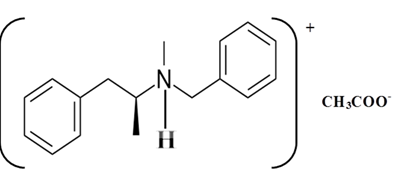
Explanation of Solution
Whether an amine is primary (1o), secondary (2o) or tertiary (3o) depends on the number of hydrogen atoms replaced by an alkyl or aryl group in ammonia. The amine is a primary amine if one hydrogen atom is replaced, it is a secondary amine if 2 hydrogen atoms are replaced and if three hydrogen atoms are replaced it is known as a tertiary amine.
Benzphetamine is a tertiary ammine. It has basic properties and it accepts protons from acids. Acetic acid donates a proton to this amine and formed below the salt.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Loose Leaf for General, Organic and Biological Chemistry with Connect 2 Year Access Card
- Indicate whether the product of the reaction between Naphthalene and CrO3 in acetic acid at 25ºC is 1,4 naphthoquinone or phthalic anhydride.arrow_forwardIndicate the products of the reaction between CH3COCH2COOC2H5 and Na+-OC2H5.arrow_forwardPrimary, Secondary, and Tertiary Alcohols O-H O-H O-H R₁-C-H R₁-C-H R₁-C-R₁ H R₂ R₂ Primary Alcohol Secondary Alcohol ChemistryLearner.com R stands for Carbon group like ethyl methyl propyl Tertiary Alcohol If 1 carbon group with two H attached to alcoholic carbon, then primary If 2 carbon group and 1 H are attached to alcoholic carbon, then secondary IF 3 carbon group and no H attach to alcoholic carbon then tertiary. The bottom line Starting "Weak" oxidant material PCC, DMP, Swern, etc Primary alcohol Aldehyde OH Secondary alcohol Ketone OH "Strong" oxidant KMnO4, H₂CrO4 (or equivalent) OH Carboxylic acid 요 Ketone No reaction No reaction Tertiary alcohol 1. Is ethanol a primary, secondary, or tertiary alcohol? Write out the structures of ethanol and any oxidation products of ethanol. If there is more than one oxidation product, give the structure of each of the products. 2. Is 2-propanol a primary, secondary, or tertiary alcohol? Write out the structures of 2-propanol and any…arrow_forward
- Complete the following equations hand written pleasearrow_forwardComplete the following equations please hand written pleasearrow_forwardUsing the Nernst equation to calculate nonstandard cell voltage A galvanic cell at a temperature of 25.0 °C is powered by the following redox reaction: 3+ 3Cu²+ (aq) +2Al(s) → 3 Cu(s)+2A1³* (aq) 2+ Suppose the cell is prepared with 5.29 M Cu in one half-cell and 2.49 M A1³+ in the other. Calculate the cell voltage under these conditions. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. x10 μ ☑ 00. 18 Ar Иarrow_forward
- Please help me solve this homework problemarrow_forwardPlease help me answer this homework questionarrow_forwardCalculating standard reaction free energy from standard reduction... Using standard reduction potentials from the ALEKS Data tab, calculate the standard reaction free energy AG° for the following redox reaction. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. 3+ H2(g)+2OH¯ (aq) + 2Fe³+ (aq) → 2H₂O (1)+2Fe²+ (aq) 0 kJ x10 Х ? olo 18 Ararrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole



