
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure for the eight constitutional isomers of molecular formula C4H11N should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
There are three types of
Answer to Problem 42P
The structures for the eight constitutional isomers of molecular formula C4H11N are represented as follows:

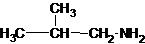
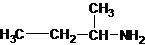
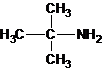
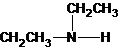
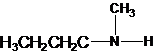
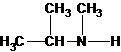
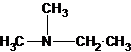
Explanation of Solution
Four structures of primary amines can be drawn with the formula C4H11N.

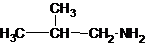
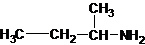
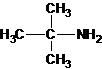
Three structures of secondary amines can also be drawn.
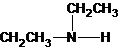
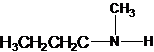
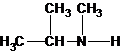
A tertiary structure can also be drawn as follows:
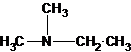
(b)
Interpretation:
The systematic name for each amine should be given.
Concept Introduction:
In nomenclature of primary amine, the longest carbon chain bonded to nitrogen is determined and the −e ending of the parent
Answer to Problem 42P
The name of amines are as follows:

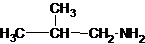
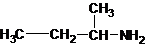
1-butanamine 2-methylpropan-1-amine butan-2-amine
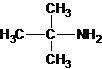
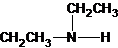
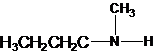
2-methylpropan-2-amine N-ethylethanamine N-methylpropan-1-amine
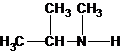
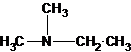
N-methylpropan-2-amine N,N-dimethylethanamine
Explanation of Solution

The longest carbon chain has four carbons. So the alkane name is butane. N is attached to C-1. Therefore, the systematic name of the amine is butanamine.
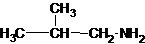
The longest carbon chain has three carbons. There is a methyl group at C-2. So the parent name is 2-methylpropanamine. The N atom is bonded to C-1. Therefore, the name become 2-methylpropan-1-amine.
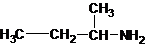
The longest carbon chain bonded to amine group has four carbons. The parent name is butanamine. The N atom is bonded to C-2. Therefore, the systematic name of the amine is butan-2-amine.
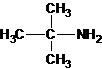
The longest carbon chain bonded to amine group has three carbons. There is a methyl group at C-2. The parent name is 2-methylpropanamine. The N atom is bonded to C-2. Therefore, the systematic name of the amine is 2-methylpropan-2-amine.
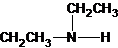
The secondary amine has the longest carbon chain with 2 carbons. So, the parent name is ethanamine. The N atom has bonded to C-1 and has 1 ethyl group as a substituent. Therefore, the systematic name become N-ethylethanamine.
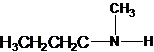
The secondary amine has the longest carbon chain with 3 carbons. So, the parent name is propanamine. The N atom has bonded to C-1 and has 1 methyl group as a substituent. Therefore, the systematic name become N-methylpropan-1-amine.
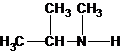
The secondary amine has the longest carbon chain with 3 carbons. So, the parent name is propanamine. The N atom has bonded to C-2 and has 1 methyl group as a substituent. Therefore, the systematic name become N-methylpropan-2-amine.
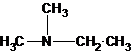
The tertiary amine has the longest carbon chain with 2 carbons. So the parent name is ethanamine. N atom has bonded to C-1 and has two methyl groups and 1 ethyl group as substituents. So, the systematic name of the amine is N,N-dimethylethanamine.
(c)
Interpretation:
The chirality center present in one of the amines should be identified.
Concept Introduction:
An atom that has four different groups bonded to it is referred to as chirality center. A chiral molecule has a non-superimposable mirror image.
Answer to Problem 42P
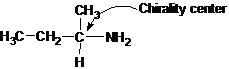
Explanation of Solution
Butan-2-amine has long carbon chain with 4 carbons and amine group is bonded to C-2. This C-2 carbon has four different groups bonded to it as 1 ethyl group, 1 methyl group, 1 amine group and a hydrogen. So, C-2 carbon is a chirality center.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Loose Leaf for General, Organic and Biological Chemistry with Connect 2 Year Access Card
- The predominant components of our atmosphere are N₂, O₂, and Ar in the following mole fractions: χN2 = 0.780, χO2 = 0.21, χAr = 0.01. Assuming that these molecules act as ideal gases, calculate ΔGmix, ΔSmix, and ΔHmix when the total pressure is 1 bar and the temperature is 300 K.arrow_forwarddG = Vdp - SdT + μA dnA + μB dnB + ... so that under constant pressure and temperature conditions, the chemical potential of a component is the rate of change of the Gibbs energy of the system with respect to changing composition, μJ = (∂G / ∂nJ)p,T,n' Using first principles prove that under conditions of constant volume and temperature, the chemical potential is a measure of the partial molar Helmholtz energy (μJ = (∂A / ∂nJ)V,T,n')arrow_forwardThe vapor pressure of dichloromethane at 20.0 °C is 58.0 kPa and its enthalpy of vaporization is 32.7 kJ/mol. Estimate the temperature at which its vapor pressure is 66.0 kPa.arrow_forward
- Draw the structure of A, the minor E1 product of the reaction. Cl Skip Part Check F1 esc CH_CH OH, D 3 2 Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 80 R3 F4 F2 F3 @ 2 # $ 4 3 Q W 95 % KO 5 F6 A F7 × G ☐ Save For Later Sub 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy C ►II A A F8 F9 F10 FL 6 7 88 & * 8 9 LLI E R T Y U A S D lock LL F G H 0 P J K L Z X C V B N M 9 Harrow_forwardFrom the choices given, which two substances have the same crystal structure? (Select both) Group of answer choices ZnS (zincblende) Diamond TiO2 (rutile) ZnS (wurtzite)arrow_forwardPotassium (K) blends with germanium (Ge) to form a Zintl phase with a chemical formula of K4Ge4. Which of the following elements would you expect potassium to blend with to form an alloy? Electronegativities: As (2.0), Cl (3.0), Ge (1.8), K (0.8), S (2.5), Ti (1.5) Group of answer choices Arsenic (As) Sulfur (S) Chlorine (Cl) Titanium (Ti)arrow_forward
- Consider two elements, X and Z. Both have cubic-based unit cells with the same edge lengths. X has a bcc unit cell while Z has a fcc unit cell. Which of the following statements is TRUE? Group of answer choices Z has a larger density than X X has more particles in its unit cell than Z does X has a larger density than Z Z has a larger unit cell volume than Xarrow_forwardHow many particles does a face-centered cubic (fcc) unit cell contain? Group of answer choices 2 14 8 4arrow_forwardV Highlight all of the carbon atoms that have at least one beta (B) hydrogen, using red for one ẞ hydrogen, blue for two ẞ hydrogens, and green for three ẞ hydrogens. If none of the carbon atoms have ẞ hydrogens, check the box underneath the molecule. ED X None of the carbon atoms have ẞ hydrogens. Explanation esc 2 Check * F1 F2 1 2 80 # 3 Q W tab A caps lock shift fn control F3 N S option O 694 $ F4 F5 F6 005 % E R D F LL 6 olo 18 Ar B © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility A DII F7 F8 87 & * 8 T Y U G H 4 F9 F10 ( 9 0 E F11 F12 உ J K L + || X C V B N M H H command option commandarrow_forward
- Consider the reaction below and answer the following questions. Part 1 of 4 Br NaOCH2CH3 Identify the mechanisms involved. Check all that apply. SN 1 SN 2 E1 E2 None of the above Part 2 of 4 Skip Part Check esc F1 F2 lock 1 2 Q W A S #3 80 F3 F4 F5 F6 Save For © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms ˇˇ % & 4 5 6 89 7 IK A 分 བ F7 F8 F9 F * E R T Y U 8 9 D F G H K V B N M 0 Oarrow_forwardWhat kind of holes are not generated when solid-state particles adopt a close packing pattern? Group of answer choices tetrahedral cubic octahedral None of the other choices are correctarrow_forwardFor the reaction below: 1. Draw all reasonable elimination products to the right of the arrow. 2. In the box below the reaction, redraw any product you expect to be a major product. 田 Major Product: Check ☐ + I Na OH esc F1 F2 2 1 @ 2 Q W tab A caps lock S #3 80 F3 69 4 σ F4 % 95 S Click and drag to sta drawing a structure mm Save For Later 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use GO DII F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 F10 6 CO 89 & 7 LU E R T Y U 8* 9 0 D F G H J K L Z X C V B N M 36arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning

