
Fundamentals of Physics, Volume 1, Chapter 1-20
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781118233764
Author: David Halliday
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 18, Problem 45P
SSM ILW A gas within a closed chamber undergoes the cycle shown in the p-V diagram of Fig. 18-39. The horizontal scale is set by Vs = 4.0 m3. Calculate the net energy added to the system as heat during one complete cycle.
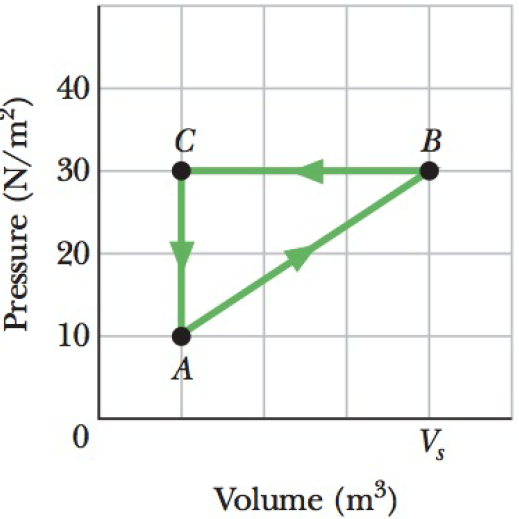
Figure 18-39 Problem 45.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
No chatgpt pls will upvote
No chatgpt pls will upvote
No chatgpt pls will upvote
Chapter 18 Solutions
Fundamentals of Physics, Volume 1, Chapter 1-20
Ch. 18 - The initial length L, change in temperature T, and...Ch. 18 - Figure 18-24 shows three linear temperature...Ch. 18 - Materials A, B, and C are solids that are at their...Ch. 18 - A sample A of liquid water and a sample B of ice,...Ch. 18 - Question 4 continued: Graphs b through f of Fig....Ch. 18 - Figure 18-26 shows three different arrangements of...Ch. 18 - Figure 18-27 shows two closed cycles on p-V...Ch. 18 - For which cycle in Fig. 18-27, traversed...Ch. 18 - Three different materials of identical mass are...Ch. 18 - A solid cube of edge length r, a solid sphere of...
Ch. 18 - A hot object is dropped into a thermally insulated...Ch. 18 - Suppose the temperature of a gas is 373.15 K when...Ch. 18 - Two constant-volume gas thermometers are...Ch. 18 - A gas thermometer is constructed of two...Ch. 18 - a In 1964, the temperature in the Siberian village...Ch. 18 - At what temperature is the Fahrenheit scale...Ch. 18 - On a linear X temperature scale, water freezes at...Ch. 18 - ILW Suppose that on a linear temperature scale X,...Ch. 18 - At 20C, a brass cube has edge length 30 cm. What...Ch. 18 - ILW A circular hole in an aluminum plate is 2.725...Ch. 18 - An aluminum flagpole is 33 m high. By how much...Ch. 18 - Prob. 11PCh. 18 - An aluminum-alloy rod has a length of 10.000 cm at...Ch. 18 - SSM Find the change in volume of an aluminum...Ch. 18 - When the temperature of a copper coin is raised by...Ch. 18 - ILW A steel rod is 3.000 cm in diameter at 25.00C....Ch. 18 - When the temperature of a metal cylinder is raised...Ch. 18 - SSM WWW An aluminum cup of 100 cm3 capacity is...Ch. 18 - At 20C, a rod is exactly 20.05 cm long on a steel...Ch. 18 - GO A vertical glass tube of length L = 1.280 000 m...Ch. 18 - GO In a certain experiment, a small radioactive...Ch. 18 - SSM ILW As a result of a temperature rise of 32 C,...Ch. 18 - One way to keep the contents of a garage from...Ch. 18 - SSM A small electric immersion healer is used to...Ch. 18 - A certain substance has a mass per mole of 50.0...Ch. 18 - Prob. 25PCh. 18 - What muss of butter, which has a usable energy...Ch. 18 - SSM Calculate the minimum amount of energy, in...Ch. 18 - How much water remains unfrozen after 50.2 kJ is...Ch. 18 - In a solar water heater, energy from the Sun is...Ch. 18 - A 0.400 kg simple is placed in a cooling apparatus...Ch. 18 - ILW What mass of steam at 100C must be mixed with...Ch. 18 - The specific heat of a substance varies with...Ch. 18 - Nonmetric version: a How long does a 2.0 105...Ch. 18 - GO Samples A and B are at different initial...Ch. 18 - An insulated Thermos contains l30 cm3 of hot...Ch. 18 - A 150 g copper bowl contains 220 g of water, both...Ch. 18 - A person makes a quantity of iced tea by mixing...Ch. 18 - A 0.530 kg sample of liquid water and a sample of...Ch. 18 - GO Ethyl alcohol has a boiling point of 78.0C, a...Ch. 18 - GO Calculate the specific heat of a metal from the...Ch. 18 - SSM WWW a Two 50 g ice cubes are dropped into 200...Ch. 18 - GO A 20.0 g copper ring at 0.000C has an inner...Ch. 18 - In Fig. 18-37, a gas sample expands from V0 to...Ch. 18 - GO A thermodynamic system is taken from stale A to...Ch. 18 - SSM ILW A gas within a closed chamber undergoes...Ch. 18 - Suppose 200 J of work is done on a system and 70.0...Ch. 18 - Prob. 47PCh. 18 - GO As a gas is held within a closed chamber, it...Ch. 18 - GO Figure 18-42 represents a closed cycle for a...Ch. 18 - GO A lab sample of gas is taken through cycle abca...Ch. 18 - A sphere of radius 0.500 m, temperature 27.0C, and...Ch. 18 - The ceiling of a single-family dwelling in a cold...Ch. 18 - SSM Consider the slab shown in Fig. 18-18. Suppose...Ch. 18 - If you were to walk briefly in space without a...Ch. 18 - ILW A cylindrical copper rod of length 1.2 m and...Ch. 18 - The giant hornet Vespa mandarinia japonica preys...Ch. 18 - Prob. 57PCh. 18 - A solid cylinder of radius r1 = 2.5 cm, length h1...Ch. 18 - Prob. 59PCh. 18 - GO Figure 18-46 shows the cross section of a wall...Ch. 18 - SSM A 5.0 cm slap has formed on an outdoor tank of...Ch. 18 - Leidenfrost effect. A water drop will last about 1...Ch. 18 - GO Figure 18-49 shows in cross section a wall...Ch. 18 - Prob. 64PCh. 18 - Ice has formed on a shallow pond, and a shady...Ch. 18 - GO Evaporative cooling of beverages. A cold...Ch. 18 - In the extrusion of cold chocolate from a tube,...Ch. 18 - Prob. 68PCh. 18 - Figure 18-51 displays a closed cycle for a gas....Ch. 18 - In a certain solar house, energy from the Sun is...Ch. 18 - A 0.300 kg sample is placed in a cooling apparatus...Ch. 18 - The average rate at which energy is conducted...Ch. 18 - What is the volume increase of an aluminum cube...Ch. 18 - In a series of experiment, block B is to be placed...Ch. 18 - Figure 18-54 displays a dosed cycle for a gas....Ch. 18 - Three equal-length straight rods, of aluminum,...Ch. 18 - SSM The temperature of a 0.700 kg cube of ice is...Ch. 18 - GO Icicles. Liquid water coats an active growing...Ch. 18 - SSM A sample of gas expands from an initial...Ch. 18 - Figure 18-56a shows a cylinder containing gas and...Ch. 18 - SSM A sample of gas undergoes a transition from an...Ch. 18 - Prob. 82PCh. 18 - SSM The temperature of a Pyrex disk is changed...Ch. 18 - a Calculate the rate at which body heat is...Ch. 18 - SSM A 2.50 kg Jump of aluminum is heated to 92.0C...Ch. 18 - A glass window pane is exactly 20 cm by 30 cm at...Ch. 18 - A recruit can join the semi-secret 300 F club at...Ch. 18 - A steel rod at 25.0C is bolted at both ends and...Ch. 18 - An athlete needs to lose weight and decides to do...Ch. 18 - Soon after Earth was formed, heat released by the...Ch. 18 - Prob. 91PCh. 18 - A rectangular plate of glass initially has the...Ch. 18 - Suppose that you intercept 5.0 103 of the energy...Ch. 18 - A thermometer of mass 0.0550 kg and of specific...Ch. 18 - A sample of gas expands from V1 = 1.0 m3 and p1 =...Ch. 18 - Figure 18-59 shows a composite bar of length L =...Ch. 18 - On finding your stove out of order, you decide to...Ch. 18 - The p-V diagram in the Fig. 18-60 shows two paths...Ch. 18 - A cube of edge length 6.0 106 m, emissivity 0.75,...Ch. 18 - A flow calorimeter is a device used to measure the...Ch. 18 - An object of mass 6.00 kg falls through a height...Ch. 18 - The Pyrex glass mirror in a telescope has a...Ch. 18 - The area A of a rectangular plate is ab = 1.4 m2....Ch. 18 - Consider the liquid in a barometer whose...Ch. 18 - A pendulum clock with a pendulum made of brass is...Ch. 18 - Prob. 106PCh. 18 - Prob. 107PCh. 18 - A 1700 kg Buick moving at 83 km/h brakes to a...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
16.
a. Calculate the standard free energy change as a pair of electrons is transferred from succinate to mole...
Biochemistry: Concepts and Connections (2nd Edition)
Calculate the lattice energy of CaCl2 using a Born-Haber cycle and data from Appendices F and L and Table 7.5. ...
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Fill in the blanks: a. The wrist is also known as the _________ region. b. The arm is also known as the _______...
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
How are photosynthesis and respiration related to each other?
Microbiology: Principles and Explorations
What are four functions of connective tissue?
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Define histology.
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- You are standing a distance x = 1.75 m away from this mirror. The object you are looking at is y = 0.29 m from the mirror. The angle of incidence is θ = 30°. What is the exact distance from you to the image?arrow_forwardFor each of the actions depicted below, a magnet and/or metal loop moves with velocity v→ (v→ is constant and has the same magnitude in all parts). Determine whether a current is induced in the metal loop. If so, indicate the direction of the current in the loop, either clockwise or counterclockwise when seen from the right of the loop. The axis of the magnet is lined up with the center of the loop. For the action depicted in (Figure 5), indicate the direction of the induced current in the loop (clockwise, counterclockwise or zero, when seen from the right of the loop). I know that the current is clockwise, I just dont understand why. Please fully explain why it's clockwise, Thank youarrow_forwardA planar double pendulum consists of two point masses \[m_1 = 1.00~\mathrm{kg}, \qquad m_2 = 1.00~\mathrm{kg}\]connected by massless, rigid rods of lengths \[L_1 = 1.00~\mathrm{m}, \qquad L_2 = 1.20~\mathrm{m}.\]The upper rod is hinged to a fixed pivot; gravity acts vertically downward with\[g = 9.81~\mathrm{m\,s^{-2}}.\]Define the generalized coordinates \(\theta_1,\theta_2\) as the angles each rod makes with thedownward vertical (positive anticlockwise, measured in radians unless stated otherwise).At \(t=0\) the system is released from rest with \[\theta_1(0)=120^{\circ}, \qquad\theta_2(0)=-10^{\circ}, \qquad\dot{\theta}_1(0)=\dot{\theta}_2(0)=0 .\]Using the exact nonlinear equations of motion (no small-angle or planar-pendulumapproximations) and assuming the rods never stretch or slip, determine the angle\(\theta_2\) at the instant\[t = 10.0~\mathrm{s}.\]Give the result in degrees, in the interval \((-180^{\circ},180^{\circ}]\).arrow_forward
- What are the expected readings of the ammeter and voltmeter for the circuit in the figure below? (R = 5.60 Ω, ΔV = 6.30 V) ammeter I =arrow_forwardsimple diagram to illustrate the setup for each law- coulombs law and biot savart lawarrow_forwardA circular coil with 100 turns and a radius of 0.05 m is placed in a magnetic field that changes at auniform rate from 0.2 T to 0.8 T in 0.1 seconds. The plane of the coil is perpendicular to the field.• Calculate the induced electric field in the coil.• Calculate the current density in the coil given its conductivity σ.arrow_forward
- An L-C circuit has an inductance of 0.410 H and a capacitance of 0.250 nF . During the current oscillations, the maximum current in the inductor is 1.80 A . What is the maximum energy Emax stored in the capacitor at any time during the current oscillations? How many times per second does the capacitor contain the amount of energy found in part A? Please show all steps.arrow_forwardA long, straight wire carries a current of 10 A along what we’ll define to the be x-axis. A square loopin the x-y plane with side length 0.1 m is placed near the wire such that its closest side is parallel tothe wire and 0.05 m away.• Calculate the magnetic flux through the loop using Ampere’s law.arrow_forwardDescribe the motion of a charged particle entering a uniform magnetic field at an angle to the fieldlines. Include a diagram showing the velocity vector, magnetic field lines, and the path of the particle.arrow_forward
- Discuss the differences between the Biot-Savart law and Coulomb’s law in terms of their applicationsand the physical quantities they describe.arrow_forwardExplain why Ampere’s law can be used to find the magnetic field inside a solenoid but not outside.arrow_forward3. An Atwood machine consists of two masses, mA and m B, which are connected by an inelastic cord of negligible mass that passes over a pulley. If the pulley has radius RO and moment of inertia I about its axle, determine the acceleration of the masses mA and m B, and compare to the situation where the moment of inertia of the pulley is ignored. Ignore friction at the axle O. Use angular momentum and torque in this solutionarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Thermodynamics: Crash Course Physics #23; Author: Crash Course;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4i1MUWJoI0U;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY