
Concept explainers
Shannon, Inc., has two divisions. One produces and sells paper party supplies (napkins, paper plates, invitations); the other produces and sells cookware. A segmented income statement for the most recent quarter is given below:
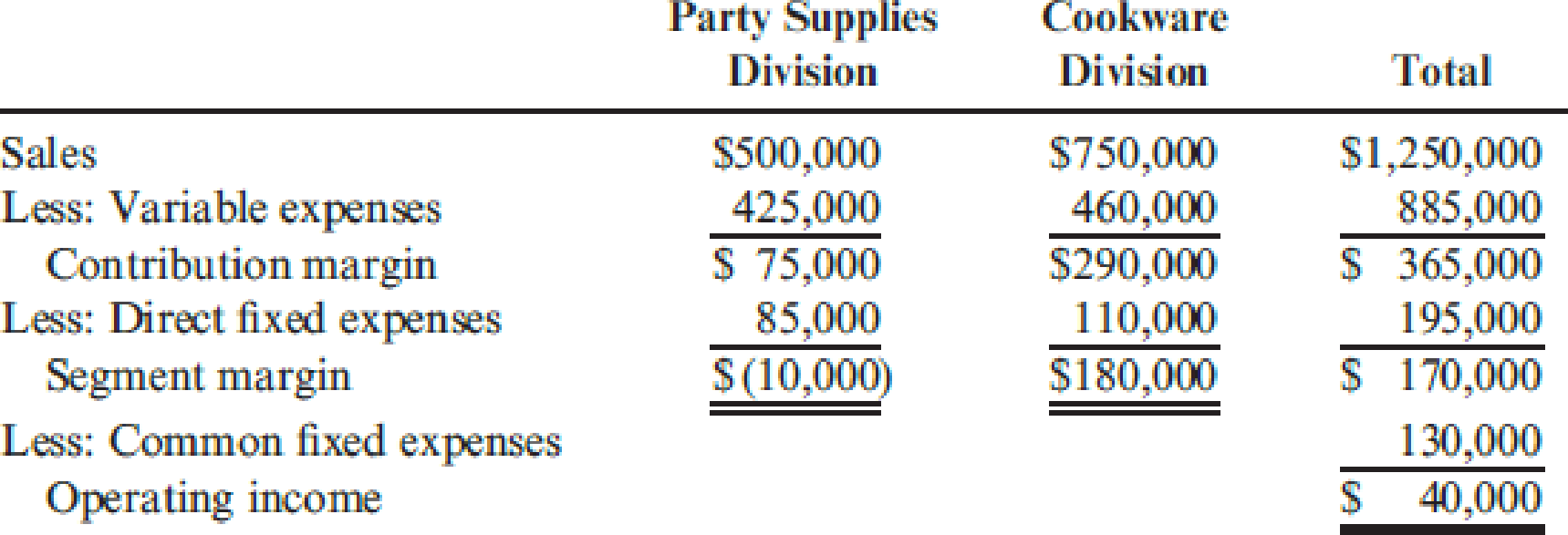
On seeing the quarterly statement, Madge Shannon, president of Shannon, Inc., was distressed and discussed her disappointment with Bob Ferguson, the company’s vice president of finance.
MADGE: “The Party Supplies Division is killing us. It’s not even covering its own fixed costs. I’m beginning to believe that we should shut down that division. This is the seventh consecutive quarter it has failed to provide a positive segment margin. I was certain that Paula Kelly could turn it around. But this is her third quarter, and she hasn’t done much better than the previous divisional manager.”
BOB: “Well, before you get too excited about the situation, perhaps you should evaluate Paula’s most recent proposals. She wants to spend $10,000 per quarter for the right to use familiar cartoon figures on a new series of invitations, plates, and napkins and at the same time increase the advertising budget by $25,000 per quarter to let the public know about them. According to her marketing people, sales should increase by 10 percent if the right advertising is done—and done quickly. In addition, Paula wants to lease some new production machinery that will increase the rate of production, lower labor costs, and result in less waste of materials. Paula claims that variable costs will be reduced by 30 percent. The cost of the lease is $95,000 per quarter.”
Upon hearing this news, Madge calmed considerably and, in fact, was somewhat pleased. After all, she was the one who had selected Paula and had a great deal of confidence in Paula’s judgment and abilities.
Required:
- 1. Assuming that Paula’s proposals are sound, should Madge Shannon be pleased with the prospects for the Party Supplies Division? Prepare a segmented income statement for the next quarter that reflects the implementation of Paula’s proposals. Assume that the Cookware Division’s sales increase by 5 percent for the next quarter and that the same cost relationships hold.
- 2. Suppose that everything materializes as Paula projected except for the 10 percent increase in sales—no change in sales revenues takes place. Are the proposals still sound? What if the variable costs are reduced by 40 percent instead of 30 percent with no change in sales?
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 18 Solutions
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Series)
- Please don't use AI And give correct answer .arrow_forwardLouisa Pharmaceutical Company is a maker of drugs for high blood pressure and uses a process costing system. The following information pertains to the final department of Goodheart's blockbuster drug called Mintia. Beginning work-in-process (40% completed) 1,025 units Transferred-in 4,900 units Normal spoilage 445 units Abnormal spoilage 245 units Good units transferred out 4,500 units Ending work-in-process (1/3 completed) 735 units Conversion costs in beginning inventory $ 3,250 Current conversion costs $ 7,800 Louisa calculates separate costs of spoilage by computing both normal and abnormal spoiled units. Normal spoilage costs are reallocated to good units and abnormal spoilage costs are charged as a loss. The units of Mintia that are spoiled are the result of defects not discovered before inspection of finished units. Materials are added at the beginning of the process. Using the weighted-average method, answer the following question: What are the…arrow_forwardQuick answerarrow_forward
- Financial accounting questionarrow_forwardOn November 30, Sullivan Enterprises had Accounts Receivable of $145,600. During the month of December, the company received total payments of $175,000 from credit customers. The Accounts Receivable on December 31 was $98,200. What was the number of credit sales during December?arrow_forwardPaterson Manufacturing uses both standards and budgets. For the year, estimated production of Product Z is 620,000 units. The total estimated cost for materials and labor are $1,512,000 and $1,984,000, respectively. Compute the estimates for: (a) a standard cost per unit (b) a budgeted cost for total production (Round standard costs to 2 decimal places, e.g., $1.25.)arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning


