
Concept explainers
(a)
The electric field at the center of the triangular configuration of charges.
Answer to Problem 23PE
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Point charges located at the corners of an equilateral triangle 25.0 cm on a side.
Formula used:
Total electric field
Calculation:
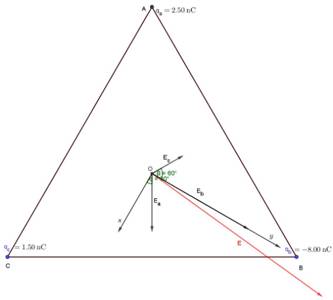
Let O be the centroid of our equilateral triangle CBA. Distance from O to any vertex is
Electric field is generally three-dimensional, but since all charges are coplanar with O, z component vanishes, so find x and y components (projections) of
Notice that
Analogously
It's tilted
Conclusion:
Thus,
(b)
The combination of charges that will give a zero-strength electric field at the center of the triangular configuration.
Answer to Problem 23PE
There is no combination of charges other than
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Point charges located at the corners of an equilateral triangle
Calculation:
Suppose
Conclusion:
There is no combination of charges other than
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
COLLEGE PHYSICS
- Can someone help me answer this physics 2 questions. Thank you.arrow_forwardFour capacitors are connected as shown in the figure below. (Let C = 12.0 μF.) a C 3.00 με Hh. 6.00 με 20.0 με HE (a) Find the equivalent capacitance between points a and b. 5.92 HF (b) Calculate the charge on each capacitor, taking AV ab = 16.0 V. 20.0 uF capacitor 94.7 6.00 uF capacitor 67.6 32.14 3.00 µF capacitor capacitor C ☑ με με The 3 µF and 12.0 uF capacitors are in series and that combination is in parallel with the 6 μF capacitor. What quantity is the same for capacitors in parallel? μC 32.14 ☑ You are correct that the charge on this capacitor will be the same as the charge on the 3 μF capacitor. μCarrow_forwardIn the pivot assignment, we observed waves moving on a string stretched by hanging weights. We noticed that certain frequencies produced standing waves. One such situation is shown below: 0 ст Direct Measurement ©2015 Peter Bohacek I. 20 0 cm 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Which Harmonic is this? Do NOT include units! What is the wavelength of this wave in cm with only no decimal places? If the speed of this wave is 2500 cm/s, what is the frequency of this harmonic (in Hz, with NO decimal places)?arrow_forward
- Four capacitors are connected as shown in the figure below. (Let C = 12.0 µF.) A circuit consists of four capacitors. It begins at point a before the wire splits in two directions. On the upper split, there is a capacitor C followed by a 3.00 µF capacitor. On the lower split, there is a 6.00 µF capacitor. The two splits reconnect and are followed by a 20.0 µF capacitor, which is then followed by point b. (a) Find the equivalent capacitance between points a and b. µF(b) Calculate the charge on each capacitor, taking ΔVab = 16.0 V. 20.0 µF capacitor µC 6.00 µF capacitor µC 3.00 µF capacitor µC capacitor C µCarrow_forwardTwo conductors having net charges of +14.0 µC and -14.0 µC have a potential difference of 14.0 V between them. (a) Determine the capacitance of the system. F (b) What is the potential difference between the two conductors if the charges on each are increased to +196.0 µC and -196.0 µC? Varrow_forwardPlease see the attached image and answer the set of questions with proof.arrow_forward
- How, Please type the whole transcript correctly using comma and periods as needed. I have uploaded the picture of a video on YouTube. Thanks,arrow_forwardA spectra is a graph that has amplitude on the Y-axis and frequency on the X-axis. A harmonic spectra simply draws a vertical line at each frequency that a harmonic would be produced. The height of the line indicates the amplitude at which that harmonic would be produced. If the Fo of a sound is 125 Hz, please sketch a spectra (amplitude on the Y axis, frequency on the X axis) of the harmonic series up to the 4th harmonic. Include actual values on Y and X axis.arrow_forwardSketch a sign wave depicting 3 seconds of wave activity for a 5 Hz tone.arrow_forward
- Sketch a sine wave depicting 3 seconds of wave activity for a 5 Hz tone.arrow_forwardThe drawing shows two long, straight wires that are suspended from the ceiling. The mass per unit length of each wire is 0.050 kg/m. Each of the four strings suspending the wires has a length of 1.2 m. When the wires carry identical currents in opposite directions, the angle between the strings holding the two wires is 20°. (a) Draw the free-body diagram showing the forces that act on the right wire with respect to the x axis. Account for each of the strings separately. (b) What is the current in each wire? 1.2 m 20° I -20° 1.2 marrow_forwardplease solve thisarrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





