
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The balanced net ionic equation has to be written and the conjugate acid-base pair for the given
Concept introduction:
The law of conservation of mass states that no atoms can be created or destroyed in a
Most of the ionic compounds are soluble in water, very few of the ionic compounds are sparingly soluble, and some of the ionic compounds are insoluble in water. When it is soluble in water ions gets separated in the solution.
Conjugate acid-Base pairs:
The acid donates the proton to form its conjugate base and the base accepts a proton to form its conjugate acid.
When an acid is dissolved in water, the acid
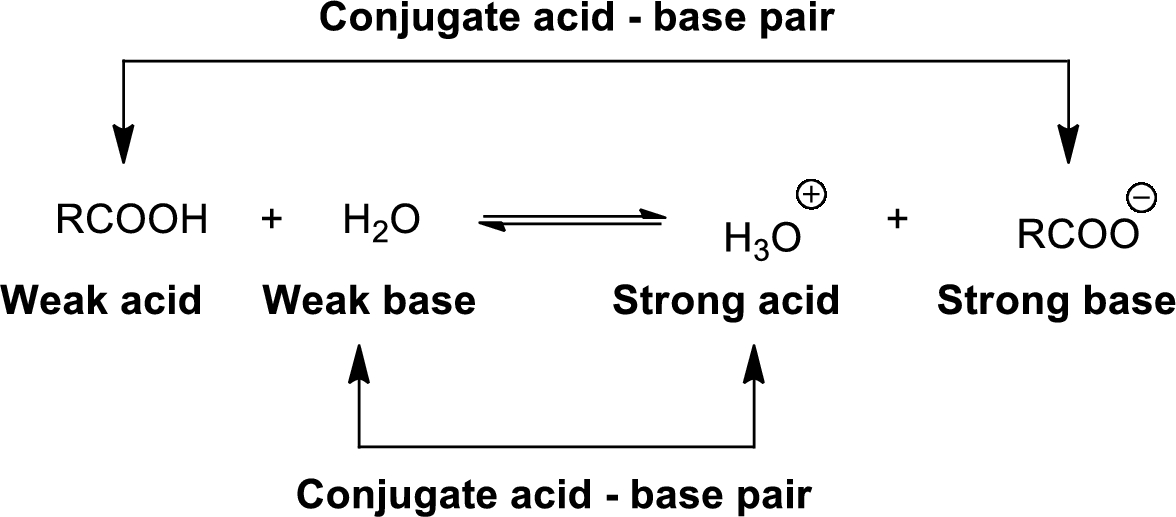
The pair of an Acid –Base differs by a proton called conjugated Acid-Base pair.
(b)
Interpretation:
The balanced net ionic equation has to be written and the conjugate acid-base pair for the given
Concept introduction:
The law of conservation of mass states that no atoms can be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction, therefore, the number of atoms present in the reactants is equal to the number of atoms present in the products.
Most of the ionic compounds are soluble in water, very few of the ionic compounds are sparingly soluble, and some of the ionic compounds are insoluble in water. When it is soluble in water ions gets separated in the solution.
Conjugate acid-Base pairs:
The acid donates the proton to form its conjugate base and the base accepts a proton to form its conjugate acid.
When an acid is dissolved in water, the acid
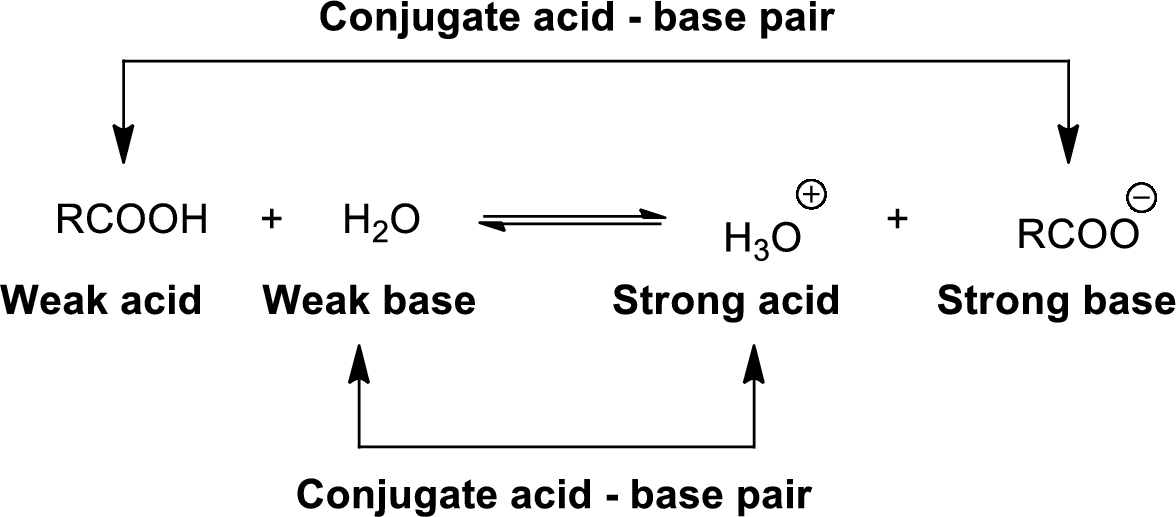
The pair of an Acid –Base differs by a proton called conjugated Acid-Base pair.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 18 Solutions
Chemistry: The Molecular Nature of Matter and Change - Standalone book
- Polymers may be composed of thousands of monomers. draw two repeat units(dimer) of the polymer formed in this reaction. assume there are hydrogen atoms on the two ends of the dimer. ignore inorganic byproducts pleasearrow_forwardDraw the product of the reaction shown below. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicate stereochemistry of substituents on asymmetric centers, Ignore inorganic byproductsarrow_forwardDraw the product of this reaction please. Ignore inorganic byproductsarrow_forward
- One of the pi molecular orbitals of 1,3-butadiene (CH2=CHCH=CH2) is shown below. Please identify the number of nodal planes perpendicular to the bonding axisarrow_forwardDraw the monomers required to synthesize this condensation polymer please.arrow_forwardProvide the correct systematic name for the compound shown here. Please take into account the keyboard options belowarrow_forward
- curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s)arrow_forwardIdentify the 'cartoon' drawing of the acceptor orbital in the first mechanistic step of an electrophilic addition reaction of butadiene with HBr. Pleasearrow_forwardH- H H H H H H Identify and select all structures below that represent a constitutional isomer(s) of the compound shown above. H- H H H A. H H H H-C CI H H D. H H H H H H C C -H H C C H H H H B. H CI H H- C C H H H H E. H CI H C.arrow_forward
- Why doesn't this carry on to form a ring by deprotonating the alpha carbon and the negatively-charged carbon attacking the C=O?arrow_forward6. A solution (0.0004 M) of Fe(S2CNEt2)3 (see the structural drawing below) in chloroform has absorption bands at: 350 nm (absorbance A = 2.34); 514 nm(absorbance A = 0.0532); Calculate the molar absorptivity values for these bands. Comment on their possible nature (charge transfer transitions or d-d S N- transitions?). (4 points)arrow_forwardWhat is the mechanism for this?arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





