
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure for the eight constitutional isomers of molecular formula C4H11N should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
There are three types of
Answer to Problem 18.48P
The structures for the eight constitutional isomers of molecular formula C4H11N are represented as follows:

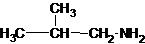
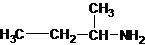
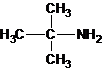
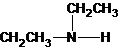
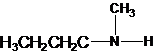
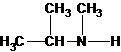
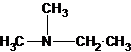
Explanation of Solution
Four structures of primary amines can be drawn with the formula C4H11N.

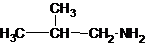
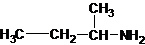
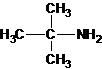
Three structures of secondary amines can also be drawn.
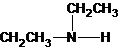
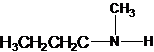
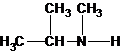
A tertiary structure can also be drawn as follows:
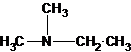
(b)
Interpretation:
The systematic name for each amine should be given.
Concept Introduction:
In nomenclature of primary amine, the longest carbon chain bonded to nitrogen is determined and the −e ending of the parent
Answer to Problem 18.48P
The name of amines are as follows:

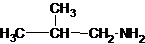
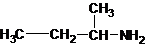
1-butanamine 2-methylpropan-1-amine butan-2-amine
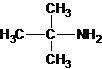
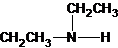
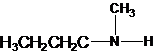
2-methylpropan-2-amine N-ethylethanamine N-methylpropan-1-amine
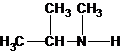
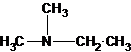
N-methylpropan-2-amine N,N-dimethylethanamine
Explanation of Solution

The longest carbon chain has four carbons. So the alkane name is butane. N is attached to C-1. Therefore, the systematic name of the amine is butanamine.
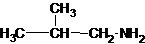
The longest carbon chain has three carbons. There is a methyl group at C-2. So the parent name is 2-methylpropanamine. The N atom is bonded to C-1. Therefore, the name become 2-methylpropan-1-amine.
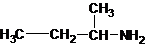
The longest carbon chain bonded to amine group has four carbons. The parent name is butanamine. The N atom is bonded to C-2. Therefore, the systematic name of the amine is butan-2-amine.
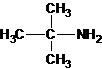
The longest carbon chain bonded to amine group has three carbons. There is a methyl group at C-2. The parent name is 2-methylpropanamine. The N atom is bonded to C-2. Therefore, the systematic name of the amine is 2-methylpropan-2-amine.
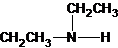
The secondary amine has the longest carbon chain with 2 carbons. So, the parent name is ethanamine. The N atom has bonded to C-1 and has 1 ethyl group as a substituent. Therefore, the systematic name become N-ethylethanamine.
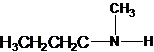
The secondary amine has the longest carbon chain with 3 carbons. So, the parent name is propanamine. The N atom has bonded to C-1 and has 1 methyl group as a substituent. Therefore, the systematic name become N-methylpropan-1-amine.
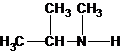
The secondary amine has the longest carbon chain with 3 carbons. So, the parent name is propanamine. The N atom has bonded to C-2 and has 1 methyl group as a substituent. Therefore, the systematic name become N-methylpropan-2-amine.
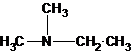
The tertiary amine has the longest carbon chain with 2 carbons. So the parent name is ethanamine. N atom has bonded to C-1 and has two methyl groups and 1 ethyl group as substituents. So, the systematic name of the amine is N,N-dimethylethanamine.
(c)
Interpretation:
The chirality center present in one of the amines should be identified.
Concept Introduction:
An atom that has four different groups bonded to it is referred to as chirality center. A chiral molecule has a non-superimposable mirror image.
Answer to Problem 18.48P
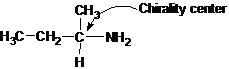
Explanation of Solution
Butan-2-amine has long carbon chain with 4 carbons and amine group is bonded to C-2. This C-2 carbon has four different groups bonded to it as 1 ethyl group, 1 methyl group, 1 amine group and a hydrogen. So, C-2 carbon is a chirality center.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
EBK GENERAL, ORGANIC, & BIOLOGICAL CHEM
- I need help with the followingarrow_forwardFor Raman spectroscopy/imaging, which statement is not true regarding its disadvantages? a) Limited spatial resolution. b) Short integration time. c) A one-dimensional technique. d) Weak signal, only 1 in 108 incident photons is Raman scattered. e) Fluorescence interference.arrow_forwardUsing a cell of known pathlength b = 1.25115 x 10-3 cm, a water absorption spectrum was measured. The band at 1645 cm-1, assigned to the O-H bending, showed an absorbance, A, of 1.40. a) Assuming that water density is 1.00 g/mL, calculate the water molar concentration c (hint: M= mole/L) b) Calculate the molar absorptivity, a, of the 1645 cm-1 band c) The transmitted light, I, can be written as I= Ioexp(-xb), where x is the absorption coefficient (sometimes designated as alpha), Io is the input light, and b is the cell pathlength. Prove that x= (ln10)*x*c. (Please provide a full derivation of the equation for x from the equation for I). d) Calculate x for the 1645 cm-1 bandarrow_forward
- For CARS, which statement is not true regarding its advantages? a) Contrast signal based on vibrational characteristics, no need for fluorescent tagging. b) Stronger signals than spontaneous Raman. c) Suffers from fluorescence interference, because CARS signal is at high frequency. d) Faster, more efficient imaging for real-time analysis. e) Higher resolution than spontaneous Raman microscopy.arrow_forwardDraw the major product of the Claisen condensation reaction between two molecules of this ester. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Incorrect, 5 attempts remaining 1. NaOCH3/CH3OH 2. Acidic workup Select to Draw O Incorrect, 5 attempts remaining The total number of carbons in the parent chain is incorrect. Review the reaction conditions including starting materials and/or intermediate structures and recount the number of carbon atoms in the parent chain of your structure. OKarrow_forwardUsing a cell of known pathlength b = 1.25115 x 10-3 cm, a water absorption spectrum was measured. The band at 1645 cm-1, assigned to the O-H bending, showed an absorbance, A, of 1.40. a) Assuming that water density is 1.00 g/mL, calculate the water molar concentration c (hint: M= mole/L) b) Calculate the molar absorptivity, a, of the 1645 cm-1 band c) The transmitted light, I, can be written as I= Ioexp(-xb), where x is the absorption coefficient (sometimes designated as alpha), Io is the input light, and b is the cell pathlength. Prove that x= (ln10)*x*c d) Calculate x for the 1645 cm-1 bandarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning



