
Concept explainers
a.
Interpretation:
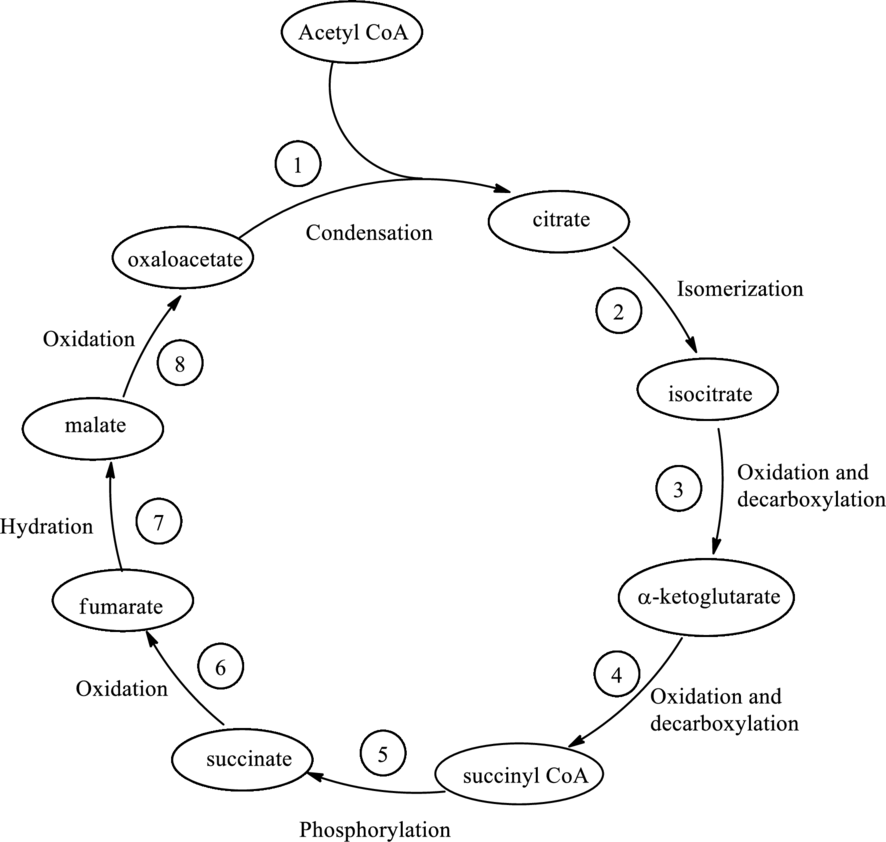
Steps in citric acid cycle that generates NADH have to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Citric acid cycle is the third stage for energy production. In this stage, acetyl CoA is oxidized to form
b.
Interpretation:
Steps in citric acid cycle that remove
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part a.
c.
Interpretation:
Steps in citric acid cycle that utilizes FAD have to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part a.
d.
Interpretation:
Steps in citric acid cycle that forms new carbon-carbon single bond have to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part a.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 18 Solutions
Principles of General, Organic, Biological Chemistry
- In mass spectrometry, alpha cleavages are common in molecules with heteroatoms. Draw the two daughter ions that would be observed in the mass spectrum resulting from an alpha cleavage of this molecule. + NH2 Q Draw Fragment with m/z of 72arrow_forwardDon't used Ai solution and don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardIf 3.8 moles of Ca2 are consumed in this reaction, how many grams of H2O are needed?If 3.8 moles of Ca2 are consumed in this reaction, how many grams of H2O are needed?arrow_forward
- Don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardWrite the systematic (IUPAC) name for each of the following organic molecules: F structure Br LL Br Br الحمد name ☐ ☐arrow_forwardDraw an appropriate reactant on the left-hand side of this organic reaction. Also, if any additional major products will be formed, add them to the right-hand side of the reaction. + + Х ง C 1. MCPBA Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 2. NaOH, H₂O Explanation Check OI... OH ol OH 18 Ar © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibilityarrow_forward
- Calculate the atomic packing factor of quartz, knowing that the number of Si atoms per cm3 is 2.66·1022 and that the atomic radii of silicon and oxygen are, respectively, 0.038 and 0.117 nm.arrow_forward3. a. Use the periodic table to add up the molecular weight of thionyl chloride (SOCl2) and show your work. b. The actual value obtained for the molecular ion on a high resolution mass spectrometer is 117.9041. Explain the discrepancy. c. Show the calculations that correctly result in the exact mass of 117.9041 for SOC₁₂. Use Table 11.2 or Appendix E in your calculations.arrow_forward6. Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. B₂2+ B22+, B2, C22, B22- and N22+ Molecular Orbital Diagram B2 C22- B22- N22+ Which molecule is paramagnetic?arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage Learning




