
Concept explainers
Three 25-lb rotor disks are attached to a shaft that rotates at 720 rpm. Disk A is attached eccentrically so that its mass center is
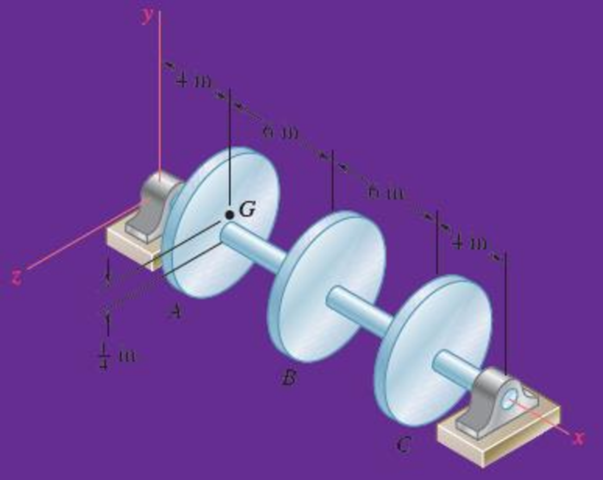
Fig. P18.147
Where should 2 lb weights be bolted to disks B and C to balance the system dynamically.
Answer to Problem 18.147RP
The 2 lb weights be bolted to disks B and C to balance the system dynamically are
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The weight (W) of the disk is 25 lb.
The shaft rotates at 720 rpm.
The mass center of the disk A is
Calculation:
Draw the free body diagram of the system as shown in Figure (1).
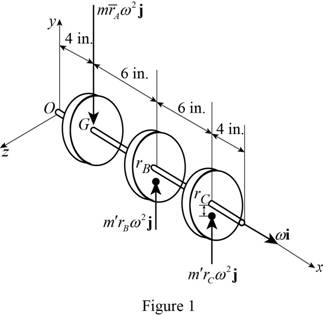
The angular velocity of the shaft is constant. So, the rate of change of angular momentum is zero.
Express the effective force
Here,
Express the effective force
Express the effective force
The sum of the effective forces of the discs should be equal to zero for the system to be in dynamic balance.
Substitute
Substitute
According to principle of impulse momentum, the total momentum is zero.
Express the moment about O:
Here,
Substitute
Substitute
Multiply Equation (1) by
The 2 lb weight is be placed above the shaft for disk C.
Substitute
The 2 lb weight is be placed below the shaft for disk B.
Thus, the 2 lb weights be bolted to disks B and C to balance the system dynamically are
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
<LCPO> VECTOR MECH,STAT+DYNAMICS
- An Inclining experiment done on a ship thats 6500 t, a mass of 30t was moved 6.0 m transvesly causing a 30 cm deflection in a 6m pendulum, calculate the transverse meta centre height.arrow_forwarda ship 150 m long and 20.5 m beam floats at a draught of8 m and displaces 19 500 tonne. The TPC is 26.5 and midshipsection area coefficient 0.94. Calculate the block, prismatic andwaterplane area coefficients.arrow_forwardA vessel loads 680 t fuel between forward and aft deep tanks. centre of gravity of forward tank is 24m forward of ships COG. centre to centre between tanks is 42 m. how much in each tank to keep trim the samearrow_forward
- Beam of a vessel is 11% its length. Cw =0.72. When floating in SW of relative denisity 1.03, TPC is 0.35t greater than in freshwater. Find the length of the shiparrow_forwardAn inclining experiment was carried out on a ship of 4000tonne displacement, when masses of 6 tonne were moved transverselythrough 13.5 m. The deflections of a 7.5 m pendulurnwere 81, 78, 85, 83, 79, 82, 84 and 80 mm respectively.Caiculate the metacentric height.arrow_forwardA ship of 10 000 tonne displacement has a waterplanearea of 1300 m2. The ship loads in water of 1.010 t/m3 andmoves into water of 1.026 t/m3. Find the change in meandraughtarrow_forward
- A ship of 7000 tonne displacement has a waterplane areaof 1500 m2. In passing from sea water into river water of1005 kg/m3 there is an increase in draught of 10 cm. Find the Idensity of the sea water.arrow_forwardA ship has 300 tonne of cargo in the hold, 24 m forward ofmidships. The displacement of the vessel is 6000 tonne and its centre of gravity is 1.2 m forward of midships.Find the new position of the centre of gravity if this cargo ismoved to an after hold, 40 m from midshipsarrow_forwardSketch and describe how ships are supported in dry dock. When and where does the greatest amount of stresses occur?arrow_forward
- Sketch and desribe a balanced rudder and how it is suspendedarrow_forwardA ship 140 m long and 18 m beam floats at a draught of9 m. The immersed cross-sectionai areas at equai intervais are 5,60, 116, 145, 152, 153, 153, 151, 142, 85 and 0 m2 respectively.Calculate:(a) displacement(b) block coefficient(c) midship section area coefficient(d) prismatic coefficient.arrow_forwardA steamer has waterplane area 1680m2 recorded in water with relative denisty 1.013. Displacement = 1200 t, calculate difference in draught in salwater reltive denisity 1.025.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





