
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The name of the given compound has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
In chemistry structure is the arrangement of
According to
The order of priority is,
Amide: One
Depending on the number of carbon side chain of the amide, different types of amides can form.
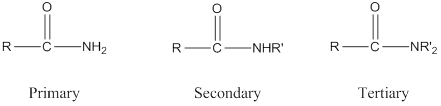
Primary amides can be named in the IUPAC system in several ways,
For simple amides the suffix – amide is added to the name of the alkyl substituent.
The suffix- amide can be used in place of the final –e in the name of the parent compound.
For a secondary amides an N prefixes the compound giving the shorter carbon chain and its chain prefix name.
For a tertiary amides an N, N prefixes the compound giving the two shorter carbon chains and their side chain prefix names.
(b)
Interpretation:
The name of the given compound has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
In chemistry structure is the arrangement of chemical bonds between atoms in a molecule, specifically which atoms are chemically bonded to what other atoms with what kind of chemical bond.
According to IUPAC nomenclature, the naming of compound is determined by the priority of the functional group if more than one functional group is present. The carbon attached to the functional group having most priority should get the least number while naming the compound.
The order of priority is,
Carboxylic acid: One
Amide: One
Depending on the number of carbon side chain of the amide, different types of amides can form.
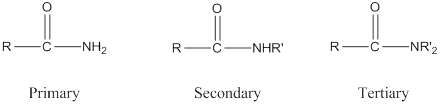
Primary amides can be named in the IUPAC system in several ways,
For simple amides the suffix – amide is added to the name of the alkyl substituent.
The suffix- amide can be used in place of the final –e in the name of the parent compound.
For a secondary amides an N prefixes the compound giving the shorter carbon chain and its chain prefix name.
For a tertiary amides an N, N prefixes the compound giving the two shorter carbon chains and their side chain prefix names.
(c)
Interpretation:
The name of the given compounds has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
In chemistry structure is the arrangement of chemical bonds between atoms in a molecule, specifically which atoms are chemically bonded to what other atoms with what kind of chemical bond.
According to IUPAC nomenclature, the naming of compound is determined by the priority of the functional group if more than one functional group is present. The carbon attached to the functional group having most priority should get the least number while naming the compound.
The order of priority is,
Carboxylic acid: One
Amide: One
Depending on the number of carbon side chain of the amide, different types of amides can form.
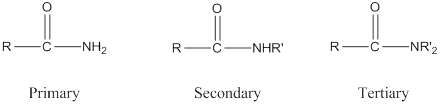
Primary amides can be named in the IUPAC system in several ways,
For simple amides the suffix – amide is added to the name of the alkyl substituent.
The suffix- amide can be used in place of the final –e in the name of the parent compound.
For a secondary amides an N prefixes the compound giving the shorter carbon chain and its chain prefix name.
For a tertiary amides an N, N prefixes the compound giving the two shorter carbon chains and their side chain prefix names.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 17 Solutions
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry, Books a la Carte Plus Mastering Chemistry with Pearson eText -- Access Card Package (8th Edition)
- Show a mechanism that leads to the opening of the ring below under acid-catalyzed conditions. Give the correct Fischer projection for this sugar.arrow_forwardWhat is the stereochemical relationship between B & C?arrow_forwardDon't use ai or any chat gpt will dislike okk just use accurate information okkk okkk just solve full accurate. don't use guidelines okk just did it accurate 100% sure experts solve it correct complete solutions okkk follow all instructions requirements okkkarrow_forward
- Problem 15 of 15 Submit Using the following reaction data points, construct Lineweaver-Burk plots for an enzyme with and without an inhibitor by dragging the points to their relevant coordinates on the graph and drawing a line of best fit. Using the information from this plot, determine the type of inhibitor present. 1 mM-1 1 s mM -1 [S]' V' with 10 μg per 20 54 10 36 20 5 27 2.5 23 1.25 20 Answer: |||arrow_forward12:33 CO Problem 4 of 15 4G 54% Done On the following Lineweaver-Burk -1 plot, identify the by dragging the Km point to the appropriate value. 1/V 40 35- 30- 25 20 15 10- T Км -15 10 -5 0 5 ||| 10 15 №20 25 25 30 1/[S] Г powered by desmosarrow_forward1:30 5G 47% Problem 10 of 15 Submit Using the following reaction data points, construct a Lineweaver-Burk plot for an enzyme with and without a competitive inhibitor by dragging the points to their relevant coordinates on the graph and drawing a line of best fit. 1 -1 1 mM [S]' s mM¹ with 10 mg pe 20 V' 54 10 36 > ст 5 27 2.5 23 1.25 20 Answer: |||arrow_forward
 Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning





