
Concept explainers
The uniform rods AB and BC are of mass 3 kg and 8 kg, respectively, and collar C has a mass of 4 kg. Knowing that at the instant shown the velocity of collar C is 0.9 m/s downward, determine the velocity of point B after rod AB has rotated through 90°.
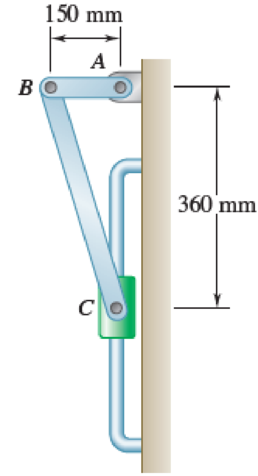
Fig. P17.45
Find the velocity of point B after rod AB has rotated through
Answer to Problem 17.45P
The velocity of point B after rod AB has rotated through
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The mass
The mass
The mass
The velocity
Calculation:
Refer the system shown.
Find the length
Find the mass moment of inertia
Substitute 3 kg for
Find the mass moment of inertia
Substitute 8 kg for
Consider the position 1 of the system as shown.
Sketch the position 1 as shown in Figure (1).
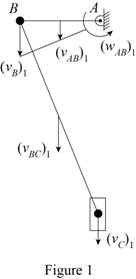
Refer Figure (1).
Since
Find the velocity
Here,
Substitute 0.9 m/s for
Consider rod AB rotates about point A.
Find the angular velocity of rod AB
Substitute 0.9 m/s for
Find the velocity of rod AB using the kinematics.
Substitute 150 mm for
Find the kinetic energy
Substitute 3 kg for
Refer Figure (1),
Consider the datum is a level line through point A.
Find the potential energy
Substitute
Substitute 3 kg for
Consider the position 2 of the system when the rod AB has rotated
Sketch the position 2 as shown in Figure (2).
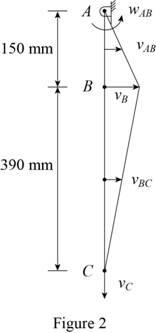
Consider rod AB rotates about point A.
Find the angular velocity of rod AB
Substitute 150 mm for
Find the velocity of rod AB using the kinematics.
Substitute 150 mm for
Consider the point C is the instantaneous center of rod BC. Therefore the velocity at point C at position 2
Find the angular velocity of rod BC
Substitute 390 mm for
Find the velocity of rod AB using the kinematics.
Substitute 390 mm for
Find the kinetic energy
Substitute 3 kg for
Refer Figure (1).
Consider the datum is a level line through point A.
Find the potential energy
Substitute
Substitute 3 kg for
Consider the conservation of energy equation:
Find the velocity of point B
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, velocity of point B after rod AB has rotated through
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
VECTOR MECH. FOR EGR: STATS & DYNAM (LL
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
SURVEY OF OPERATING SYSTEMS
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
- Test for exactness. If exact, solve. If not, use an integrating factor as given or obtained by inspection or by the theorems in the text. a. 2xydx+x²dy = 0 b. (x2+y2)dx-2xydy = 0 c. 6xydx+5(y + x2)dy = 0arrow_forwardNewton's law of cooling. A thermometer, reading 5°C, is brought into a room whose temperature is 22°C. One minute later the thermometer reading is 12°C. How long does it take until the reading is practically 22°C, say, 21.9°C?arrow_forwardSolve a. y' + 2xy = ex-x² b. y' + y sin x = ecosx, y(0) = −1 y(0) = −2.5arrow_forward
- = MMB 241 Tutorial 3.pdf 2/6 90% + + 5. The boat is traveling along the circular path with a speed of v = (0.0625t²) m/s, where t is in seconds. Determine the magnitude of its acceleration when t = 10 s. 40 m v = 0.0625² 6. If the motorcycle has a deceleration of at = (0.001s) m/s² and its speed at position A is 25 m/s, determine the magnitude of its acceleration when it passes point B. .A 90° 300 m n B 2arrow_forward= MMB 241 Tutorial 3.pdf 4/6 67% + 9. The car is traveling along the road with a speed of v = (2 s) m/s, where s is in meters. Determine the magnitude of its acceleration when s = 10 m. v = (2s) m/s 50 m 10. The platform is rotating about the vertical axis such that at any instant its angular position is u = (4t 3/2) rad, where t is in seconds. A ball rolls outward along the radial groove so that its position is r = (0.1+³) m, where t is in seconds. Determine the magnitudes of the velocity and acceleration of the ball when t = 1.5s.arrow_forwardThe population of a certain country is known to increase at a rate proportional to the number of people presently living in the country. If after two years the population has doubled, and after three years the population is 20,000, estimate the number of people initially living in the country.arrow_forward
- = MMB 241 Tutorial 3.pdf 6/6 100% + | 日 13. The slotted link is pinned at O, and as a result of the constant angular velocity *= 3 rad/s it drives the peg P for a short distance along the spiral guide r = (0.40) m, where 0 is in radians. Determine the radial and transverse components of the velocity and acceleration of P at the instant = 1/3 rad. 0.5 m P r = 0.40 =3 rad/sarrow_forward= MMB 241 Tutorial 3.pdf 1/6 90% + DYNAMICS OF PARTICLES (MMB 241) Tutorial 3 Topic: Kinematics of Particles:- Path and Polar coordinate systems and general curvilinear QUESTIONS motion. 1. Determine the acceleration at s = 2 m if v = (2 s) m/s², where s is in meters. At s = 0, v = 1 m/s. 3 m 2. Determine the acceleration when t=1s if v = (4t2+2) m/s, where t is in seconds. v=(4²+2) m/s 6 marrow_forward5.112 A mounting bracket for electronic components is formed from sheet metal with a uniform thickness. Locate the center of gravity of the bracket. 0.75 in. 3 in. ༧ Fig. P5.112 1.25 in. 0.75 in. y r = 0.625 in. 2.5 in. 1 in. 6 in. xarrow_forward
- 4-105. Replace the force system acting on the beam by an equivalent resultant force and couple moment at point B. A 30 in. 4 in. 12 in. 16 in. B 30% 3 in. 10 in. 250 lb 260 lb 13 5 12 300 lbarrow_forwardSketch and Describe a hatch coaming and show how the hatch coamings are framed in to ships strucure?arrow_forwardSketch and describe hatch coamings. Describe structrual requirements to deck plating to compensate discontinuity for corners of a hatch. Show what is done to the deck plating when the decks are cut away and include the supporting members.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





