
Concept explainers
Find the Fourier series representation of the signal shown in Fig. 17.64.
Figure 17.64
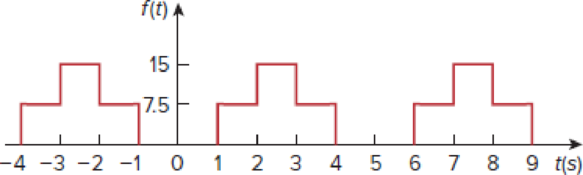
Find the Fourier series representation of the signal shown in Figure 17.64.
Answer to Problem 26P
The Fourier series representation
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Refer to Figure 17.64 in the textbook.
Formula used:
Write the expression to calculate the fundamental angular frequency.
Here,
Write the general expression to calculate trigonometric Fourier series of
Here,
Write the expression to calculate the dc component of the function
Write the expression to calculate Fourier coefficients.
Calculation:
The given waveform is drawn as Figure 1.
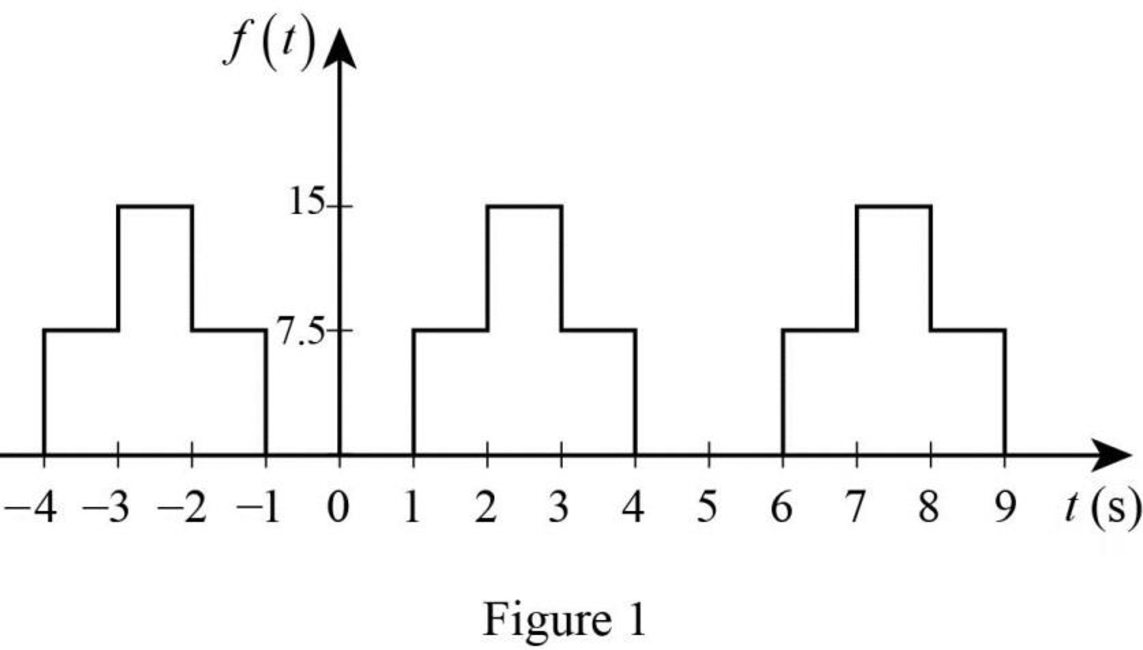
Refer to the Figure 1. The Fourier series function of the waveform is defined as,
The time period of the function in Figure 1 is,
Substitute
Substitute
Simplify the above equation to find
Substitute
Simplify the above equation to find
Simplify the above equation to find
Substitute
Simplify the above equation to find
Simplify the above equation to find
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, the Fourier series representation
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
- Solve on paper not using chatgptarrow_forwardAssume that a building manager instructed you to install a water heater. The specs on the water heater nameplate reveals the following 240V, 2PH, 60HZ, 5.7KW. The manager insisted for the installation to be done with 10 AWG copper THWN-2 conductor, the length of run is 1200 FT away from the service panel. Calculate the voltage after the installation.arrow_forwardPlease confirm that my solution is correct, especially the block diagram. Please DRAW (not type) what the block diagram would look like if it's incorrect. thank youarrow_forward
- use this code on the bottom to answer the question in the photo clc; clearvars; % Read the file [y, Fs] = audioread('106miles.wav'); N = length(y); Nfft = 2^nextpow2(N); dt = 1/Fs; t = (0:dt:(N-1)*dt)'; % Ensure t is a column vector y = y - mean(y); % Remove DC component (if not already zero-mean) % Carrier signal (25 kHz) fc = 25000; % Carrier frequency in Hz carrier = cos(2 * pi * fc * t); % DSB-SC Modulation modulated_signal = y .* carrier; % Plot Time Domain Signal figure; subplot(2,1,1); plot(t, y); title('Original Signal (Time Domain)'); xlabel('Time (s)'); ylabel('Amplitude'); subplot(2,1,2); plot(t, modulated_signal); title('DSB-SC Modulated Signal (Time Domain)'); xlabel('Time (s)'); ylabel('Amplitude'); % Frequency Domain (FFT) Y = fft(y, Nfft) / Nfft; Modulated_Y = fft(modulated_signal, Nfft) / Nfft; f = Fs * (0:(Nfft/2)) / Nfft; % Frequency vector % Plot Frequency Domain Signal figure; subplot(2,1,1); plot(f, abs(Y(1:Nfft/2+1))); title('Original Signal…arrow_forward5-9 A 230 V shunt motor has a nominal arma- ture current of 60 A. If the armature resist- ance is 0.152, calculate the following: a. The counter-emf [V] b. The power supplied to the armature [W] c. The mechanical power developed by the motor, [kW] and [hp] 5-10 a. In Problem 5-9 calculate the initial start- ing current if the motor is directly con- nected across the 230 V line. b. Calculate the value of the starting resistor needed to limit the initial current to 115 A.arrow_forwardhow to solve this?arrow_forward
- For the circuit in Fig. P8.52, choose the load impedance ZLso that the power dissipated in it is a maximum. How much powerwill that be?arrow_forwardhow to solve the attached question? please explain or give reference where required in the solution.arrow_forwardHANDWRITTEN SOLUTION REQUIRED NOT USING CHATGPTarrow_forward
- Please only do part E and F. Please show your work and be as detailed as possible. Please explain the relationship between K the gain and stability of the system. Also, show how to plot the poles and why they are on either the real or imaginary axis. What is it about the example that indicated that? thank youarrow_forwardPlease draw the block diagram for this problem and explain how. thank youarrow_forwardPlease show your work and be as detailed as possible. I would like to really understand the connection between the type of loop, the dampness, and the gain, K. Thank youarrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





