
(a)
Interpretation: Mechanism for the given type of decarboxylation reaction has to be proposed and it should be compared with the mechanism of decarboxylation of
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acids contain a carbonyl attached to a hydroxyl group as shown below,
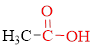
If
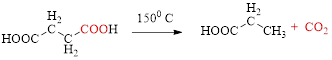
Decarboxylation of
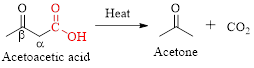
The mechanism of thermal decarboxylation involves two processes,
- (i) Redistribution of electrons in a cyclic transition state.
- (ii) Cyclic transition state possesses keto-enol tautomerism.
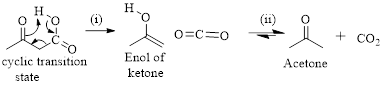
(b)
Interpretation: Mechanism for the given type of decarboxylation reaction has to be proposed and it should be compared with the mechanism of decarboxylation of
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acids contain a carbonyl attached to a hydroxyl group as shown below,

If carboxylic acid is heated to a very high temperature then of carbon dioxide will be eliminated from it this reaction is known as decarboxylation. Simple carboxylic acids do not decarboxylate readily.
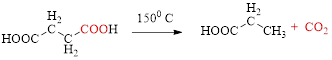
Decarboxylation of
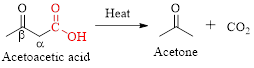
Simply the mechanism of thermal decarboxylation involves two processes,
- (i) Redistribution of electrons in a cyclic transition state.
- (ii) Cyclic transition state possesses keto-enol tautomerism.
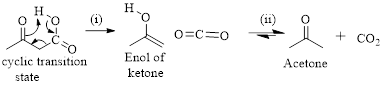
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 17 Solutions
Organic Chemistry, Loose-leaf Version
- Please answer the question for the reactions, thank youarrow_forwardWhat is the product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalyst to produce the correct product. The correct answer is IV.arrow_forwardPlease complete the reactions, thank youarrow_forward
- Consider the synthesis. What is compound Y? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing to show how the compound Y creates the product. The correct answer is D.arrow_forwardWhat would be the major product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include steps and a drawing to show this reaction proceeds and how the final product is formed. The correct answer is B. I put answer D and I don't really understand what is going on in the question.arrow_forwardWhat is the product of the following reaction? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalysts to product the correct product. The correct answer is B.arrow_forward
- What is the missing intermediate 1 and the final product 2. Please include a detailed explanation explaining the steps of malonic ester synthesis. Please include drawings of the intermediate and how it occurs and how the final product is former.arrow_forwardWhat would be the reagents and conditions above and below the arrow that will complete the proposed acetoacetic ester synthesis? If it cannot be done efficiently, then I will choose that answer. There could be 2 or 4 reagents involved. Please provide a detailed explanation and drawings showing how it would proceed with the correct reagents.arrow_forwardFor benzene, the ∆H° of vaporization is 30.72 kJ/mol and the ∆S° of vaporization is 86.97 J/mol・K. At 1.00 atm and 228.0 K, what is the ∆G° of vaporization for benzene, in kJ/mol?arrow_forward
- The reaction Q(g) + R(g) → Z(l) is shown to be exothermic. Which of the following is true concerning the reaction. it is spontaneous only at High T, it is spontaneous at low T it is nonspontaneous at all T it is spontanrous at all T. it is non spontaneous only at low T.arrow_forwardThe reaction Q(g) + R(g) → Z(l) is shown to be exothermic. Which of the following is true concerning the reactionarrow_forwardWhich of the following has the largest standard molar entropy, S° (298.15 K) He H2 NaCl KBr Hgarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT


