
(a)
Interpretation:
Structural formula of the compound whose
Concept-Introduction:
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy:
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy or NMR Spectroscopy is a technique used to find the purity, content and molecular structure of the compound. Resonance transition between energy levels happens if
It is also known as Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. Hydrogen nuclei with in the molecule is considered here.
The NMR signals for the
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Splitting in
In
In
.94ppm will the shift of
13.69ppm will the shift of
So the given values of the
Structural formula of the compound is;
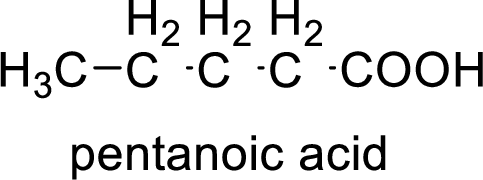
(b)
Interpretation:
Structural formula of the compound whose
Concept-Introduction:
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy:
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy or NMR Spectroscopy is a technique used to find the purity, content and molecular structure of the compound. Resonance transition between energy levels happens if electromagnetic radiation with specific frequency is applied on an atomic nuclei placed in an electromagnetic field. This transition happens only if the frequency of applied radiation matches with the frequency of magnetic field, then it is to be in resonance condition. If an external magnetic field is applied spin gets excited from its ground state to the excited state by absorbing energy. The absorbed radio frequency is emitted back at the same frequency level, when the spin returns to its ground state. This radio frequency will give the NMR spectra. The plot of the spectra is between Intensity of the signal VS magnetic field. Trimethyl Silane ie, TMS is used as the reference. Chemical shift is a term which refers to the position in the spectrum. It is dependent on several factors like electron density around the proton, inductive effect etc.
It is also known as Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. Hydrogen nuclei with in the molecule is considered here.
The NMR signals for the
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Splitting in
In
In
1.08ppm will the shift of
30.69ppm will the shift of
So the given values of the
Structure formula of the compound is:
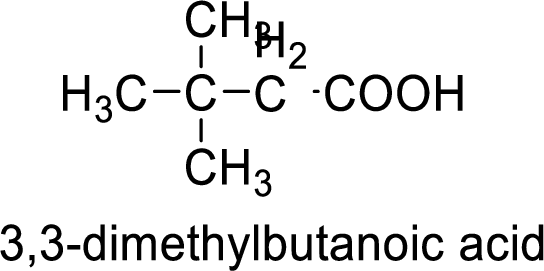
(c)
Interpretation:
Structural formula of the compound whose
Concept-Introduction:
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy:
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy or NMR Spectroscopy is a technique used to find the purity, content and molecular structure of the compound. Resonance transition between energy levels happens if electromagnetic radiation with specific frequency is applied on atomic nuclei placed in an electromagnetic field. This transition happens only if the frequency of applied radiation matches with the frequency of magnetic field, then it is to be in resonance condition. If an external magnetic field is applied spin gets excited from its ground state to the excited state by absorbing energy. The absorbed radio frequency is emitted back at the same frequency level, when the spin returns to its ground state. This radio frequency will give the NMR spectra. The plot of the spectra is between Intensity of the signal VS magnetic field. Trimethyl Silane ie, TMS is used as the reference. Chemical shift is a term which refers to the position in the spectrum. It is dependent on several factors like electron density around the proton, inductive effect etc.
It is also known as Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. Hydrogen nuclei with in the molecule are considered here.
The NMR signals for the
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Splitting in
In
In
.93ppm will the shift of
11.81ppm will be the shift of
So the given values of the
Structural formula of the product is;
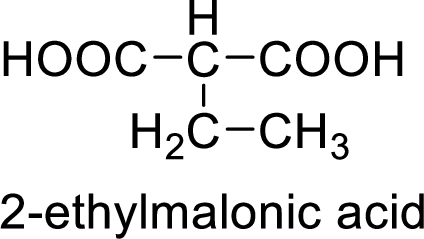
(d)
Interpretation:
Structural formula of the compound whose
Concept-Introduction:
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy:
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy or NMR Spectroscopy is a technique used to find the purity, content and molecular structure of the compound. Resonance transition between energy levels happens if electromagnetic radiation with specific frequency is applied on an atomic nuclei placed in an electromagnetic field. This transition happens only if the frequency of applied radiation matches with the frequency of magnetic field, then it is to be in resonance condition. If an external magnetic field is applied spin gets excited from its ground state to the excited state by absorbing energy. The absorbed radio frequency is emitted back at the same frequency level, when the spin returns to its ground state. This radio frequency will give the NMR spectra. The plot of the spectra is between Intensity of the signal VS magnetic field. Trimethyl Silane ie, TMS is used as the reference. Chemical shift is a term which refers to the position in the spectrum. It is dependent on several factors like electron density around the proton, inductive effect etc.
It is also known as Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. Hydrogen nuclei with in the molecule are considered here.
The NMR signals for the
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Splitting in
In
In
1.29ppm will the shift of
22.56ppm will the shift of
So the given values of
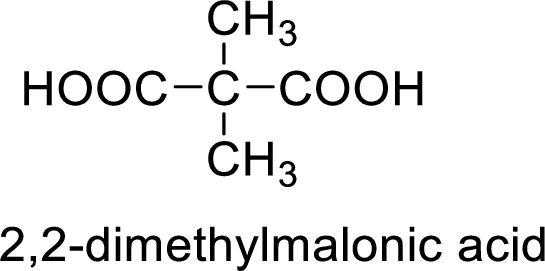
(e)
Interpretation:
Structural formula of the compound whose
Concept-Introduction:
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy:
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy or NMR Spectroscopy is a technique used to find the purity, content and molecular structure of the compound. Resonance transition between energy levels happens if electromagnetic radiation with specific frequency is applied on an atomic nuclei placed in an electromagnetic field. This transition happens only if the frequency of applied radiation matches with the frequency of magnetic field, then it is to be in resonance condition. If an external magnetic field is applied spin gets excited from its ground state to the excited state by absorbing energy. The absorbed radio frequency is emitted back at the same frequency level, when the spin returns to its ground state. This radio frequency will give the NMR spectra. The plot of the spectra is between Intensity of the signal VS magnetic field. Trimethyl Silane ie, TMS is used as the reference. Chemical shift is a term which refers to the position in the spectrum. It is dependent on several factors like electron density around the proton, inductive effect etc.
It is also known as Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. Hydrogen nuclei with in the molecule are considered here.
The NMR signals for the
(e)
Explanation of Solution
Splitting in
In
In
1.91ppm will the shift of
18.11ppm will the shift of
So the given values of
Structural formula of the product;
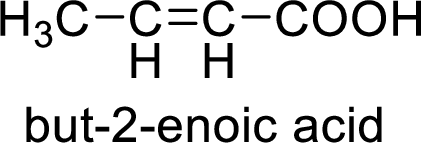
(f)
Interpretation:
Structural formula of the compound whose
Concept-Introduction:
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy:
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy or NMR Spectroscopy is a technique used to find the purity, content and molecular structure of the compound. Resonance transition between energy levels happens if electromagnetic radiation with specific frequency is applied on an atomic nuclei placed in an electromagnetic field. This transition happens only if the frequency of applied radiation matches with the frequency of magnetic field, then it is to be in resonance condition. If an external magnetic field is applied spin gets excited from its ground state to the excited state by absorbing energy. The absorbed radio frequency is emitted back at the same frequency level, when the spin returns to its ground state. This radio frequency will give the NMR spectra. The plot of the spectra is between Intensity of the signal VS magnetic field. Trimethyl Silane ie, TMS is used as the reference. Chemical shift is a term which refers to the position in the spectrum. It is dependent on several factors like electron density around the proton, inductive effect etc.
It is also known as Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. Hydrogen nuclei with in the molecule are considered here.
The NMR signals for the
(f)
Explanation of Solution
Splitting in
In
In
2.34ppm will the shift of
34.02ppm will the shift of
So the given values of
Structure of the product
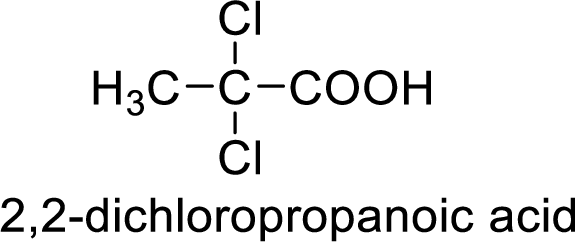
(g)
Interpretation:
Structural formula of the compound whose
Concept-Introduction:
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy:
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy or NMR Spectroscopy is a technique used to find the purity, content and molecular structure of the compound. Resonance transition between energy levels happens if electromagnetic radiation with specific frequency is applied on an atomic nuclei placed in an electromagnetic field. This transition happens only if the frequency of applied radiation matches with the frequency of magnetic field, then it is to be in resonance condition. If an external magnetic field is applied spin gets excited from its ground state to the excited state by absorbing energy. The absorbed radio frequency is emitted back at the same frequency level, when the spin returns to its ground state. This radio frequency will give the NMR spectra. The plot of the spectra is between Intensity of the signal VS magnetic field. Trimethyl Silane ie, TMS is used as the reference. Chemical shift is a term which refers to the position in the spectrum. It is dependent on several factors like electron density around the proton, inductive effect etc.
It is also known as Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. Hydrogen nuclei with in the molecule are considered here.
The NMR signals for the
(g)
Explanation of Solution
Splitting in
In
In
1.42ppm will the shift of
13.69ppm will the shift of
So the given values of
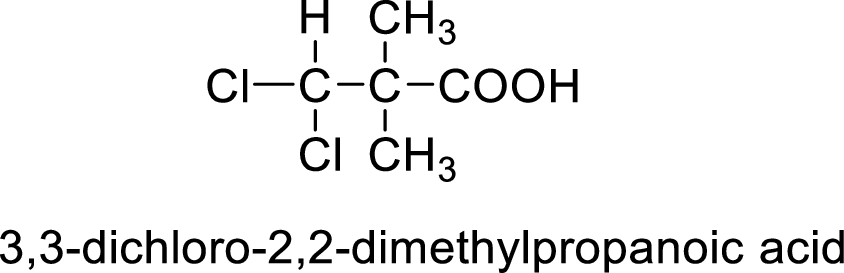
(h)
Interpretation:
Structural formula of the compound whose
Concept-Introduction:
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy:
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy or NMR Spectroscopy is a technique used to find the purity, content and molecular structure of the compound. Resonance transition between energy levels happens if electromagnetic radiation with specific frequency is applied on an atomic nuclei placed in an electromagnetic field. This transition happens only if the frequency of applied radiation matches with the frequency of magnetic field, then it is to be in resonance condition. If an external magnetic field is applied spin gets excited from its ground state to the excited state by absorbing energy. The absorbed radio frequency is emitted back at the same frequency level, when the spin returns to its ground state. This radio frequency will give the NMR spectra. The plot of the spectra is between Intensity of the signal VS magnetic field. Trimethyl Silane ie, TMS is used as the reference. Chemical shift is a term which refers to the position in the spectrum. It is dependent on several factors like electron density around the proton, inductive effect etc.
It is also known as Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. Hydrogen nuclei with in the molecule are considered here.
The NMR signals for the
(h)
Explanation of Solution
Splitting in
In
In
97ppm will the shift of
13.24ppm will the shift of
So the given values of
Structural formula of the compound is;
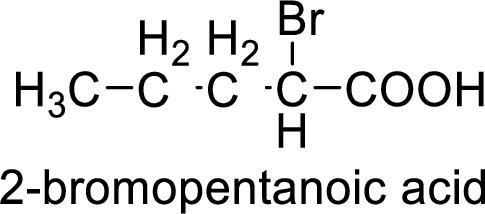
(i)
Interpretation:
Structural formula of the compound whose
Concept-Introduction:
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy:
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy or NMR Spectroscopy is a technique used to find the purity, content and molecular structure of the compound. Resonance transition between energy levels happens if electromagnetic radiation with specific frequency is applied on atomic nuclei placed in an electromagnetic field. This transition happens only if the frequency of applied radiation matches with the frequency of magnetic field, then it is to be in resonance condition. If an external magnetic field is applied spin gets excited from its ground state to the excited state by absorbing energy. The absorbed radio frequency is emitted back at the same frequency level, when the spin returns to its ground state. This radio frequency will give the NMR spectra. The plot of the spectra is between Intensity of the signal VS magnetic field. Trimethyl Silane ie, TMS is used as the reference. Chemical shift is a term which refers to the position in the spectrum. It is dependent on several factors like electron density around the proton, inductive effect etc.
It is also known as Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. A hydrogen nucleus with in the molecule is considered here.
The NMR signals for the
(i)
Explanation of Solution
Splitting in
In
In
3.38ppm will the shift of
34.75ppm will the shift of
So the given values of
So the structure of the product is;
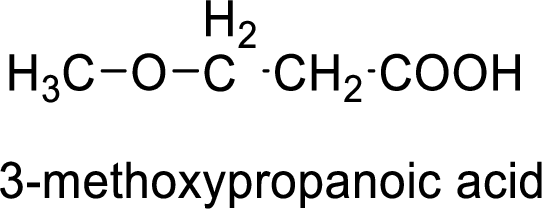
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Organic Chemistry, Loose-leaf Version
- Draw the major product of this solvolysis reaction. Ignore any inorganic byproducts. + CH3CH2OH Drawing Q Atoms, Bonds and Rings OCH2CH3 || OEt Charges OH 00-> | Undo Reset | Br Remove Done Drag To Pan +arrow_forwardDraw the major product of this SN1 reaction. Ignore any inorganic byproducts. CH3CO2Na CH3CO2H Drawing + Br Q Atoms, Bonds and Rings OAC Charges OH ОАс Na ဂ Br Undo Reset Remove Done Drag To Pan +arrow_forwardOrganic Functional Groups entifying positions labeled with Greek letters in acids and derivatives 1/5 ssible, replace an H atom on the a carbon of the molecule in the drawing area with a ce an H atom on the ẞ carbon with a hydroxyl group substituent. ne of the substituents can't be added for any reason, just don't add it. If neither substi er the drawing area. O H OH Oneither substituent can be added. Check D 1 Accessibility ado na witharrow_forward
- Differentiate between electrophilic and nucleophilic groups. Give examples.arrow_forwardAn aldehyde/ketone plus an alcohol gives a hemiacetal, and an excess of alcohol gives an acetal. The reaction is an equilibrium; in aldehydes, it's shifted to the right and in ketones, to the left. Explain.arrow_forwardDraw a Haworth projection or a common cyclic form of this monosaccharide: H- -OH H- OH H- -OH CH₂OHarrow_forward
- Answer the question in the first photoarrow_forwardGgggffg2258555426855 please don't use AI Calculate the positions at which the probability of a particle in a one-dimensional box is maximum if the particle is in the fifth energy level and in the eighth energy level.arrow_forwardExplain the concepts of hemiacetal and acetal.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
